If you or someone you know is struggling with Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD), you may be curious about the role of medication in its treatment. ADHD can pose significant challenges, affecting daily life and overall well-being. Fortunately, medication can play a crucial role in managing symptoms and enhancing focus, attention, and impulse control. By understanding the potential benefits, risks, and different types of medications available, you can make informed decisions about the most effective treatment plan for yourself or a loved one with ADHD.
The Basics of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder
What is Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder?
Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD) is a neurodevelopmental disorder that affects both children and adults. It is characterized by persistent patterns of inattention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity that can interfere with daily functioning and social interactions. Individuals with ADHD often struggle with staying focused, organizing tasks, and controlling impulsive behaviors. It is important to note that ADHD is a legitimate medical condition and not simply a result of laziness or a lack of discipline.
Prevalence of ADHD
ADHD is one of the most commonly diagnosed neurodevelopmental disorders in children, with research indicating prevalence rates of around 5-7% globally. While it is more frequently diagnosed in boys, ADHD can occur in both males and females. It is worth noting that ADHD symptoms may persist into adulthood for some individuals, impacting various aspects of their lives, including relationships, academics, and work performance.
Symptoms of ADHD
The symptoms of ADHD can be categorized into two main groups: inattention and hyperactivity/impulsivity. Inattentive symptoms include difficulty staying focused, easily being distracted, forgetfulness, trouble organizing tasks, and a tendency to lose things frequently. On the other hand, hyperactive and impulsive symptoms manifest as restlessness, excessive talking, difficulty staying still, impatience, interrupting others, and engaging in risky behaviors without considering potential consequences.
Understanding the Role of Medication in Treating ADHD
Main Goals of Medication in ADHD Treatment
The primary goals of medication in treating ADHD are to reduce the core symptoms and improve overall functioning and quality of life. Medication can help individuals with ADHD improve their focus, attention span, and impulse control, allowing them to better manage daily tasks, perform well academically or professionally, and enhance their social interactions. It is important to remember that medication is not a cure for ADHD, but rather a tool to help manage symptoms and support individuals in reaching their full potential.
Types of Medication for ADHD
There are various types of medications prescribed to treat ADHD, with the most commonly used being stimulant and non-stimulant medications. Stimulant medications, such as methylphenidate and amphetamines, work by increasing the levels of specific neurotransmitters in the brain, improving attention and impulse control. Non-stimulant medications, like atomoxetine and guanfacine, work differently by targeting different neurotransmitters to alleviate ADHD symptoms. The specific medication prescribed will depend on factors such as the individual’s age, medical history, and response to previous treatments.
Effectiveness of Medication in ADHD Treatment
Research has consistently shown that medication can be highly effective in reducing ADHD symptoms and improving overall functioning. In many cases, medication is considered the first-line treatment for ADHD, especially when symptoms significantly impair daily life. Studies have demonstrated that properly prescribed medication can lead to improved academic performance, behavioral functioning, and social interactions. It is important to note that medication effectiveness may vary among individuals, and finding the right medication and dosage may require some trial and error.
Stimulant Medications for ADHD
How Stimulant Medications Work
Stimulant medications are the most commonly prescribed treatment for ADHD. They work by increasing the levels of certain chemicals in the brain, such as dopamine and norepinephrine, which play crucial roles in regulating attention and impulse control. By enhancing these neurotransmitters’ activity, stimulant medications help individuals with ADHD to improve their focus, reduce hyperactivity, and enhance self-control.
Commonly Prescribed Stimulant Medications
There are several stimulant medications commonly prescribed to treat ADHD. Methylphenidate-based medications like Ritalin, Concerta, and Focalin, as well as amphetamine-based medications like Adderall and Vyvanse, are frequently prescribed. Each medication has different formulations that provide different durations of action, allowing for personalized treatment plans based on an individual’s needs and lifestyle.
Benefits and Potential Side Effects of Stimulant Medications
Stimulant medications have been shown to be highly effective in reducing ADHD symptoms and improving functional outcomes. They can significantly enhance attention, impulse control, and overall performance. Common side effects may include decreased appetite, sleep disturbances, and irritability, but these are usually mild and transient. It is crucial to monitor individuals closely for potential side effects and work collaboratively with healthcare providers to find the optimal medication and dosage that maximizes benefits while minimizing any discomfort.
Non-Stimulant Medications for ADHD
When Non-Stimulant Medications Are Used
Non-stimulant medications are typically considered when stimulant medications are ineffective, not well-tolerated, or when there are specific contraindications. They may also be prescribed as a first-line treatment for individuals with certain medical conditions or individuals who prefer non-stimulant options. Additionally, non-stimulant medications are often used as adjunctive therapy with stimulant medications to enhance treatment response or manage specific symptoms.
Examples of Non-Stimulant Medications for ADHD
There are different classes of non-stimulant medications used in the treatment of ADHD. Atomoxetine is a selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor that can improve attention and impulse control. Guanfacine and clonidine, which are primarily used to treat hypertension, have also been found to be effective in reducing ADHD symptoms. These medications work on different neurotransmitters and have different durations of action, allowing for individualized treatment plans.
Benefits and Potential Side Effects of Non-Stimulant Medications
Non-stimulant medications can provide significant benefits for individuals with ADHD, especially for those who do not respond well to stimulant medications or cannot tolerate their side effects. They can help improve attention, hyperactivity, and impulsivity, often leading to improved academic and social functioning. Side effects may include drowsiness, dry mouth, and dizziness, but they are generally mild. As with any medication, close monitoring and collaboration with healthcare providers are essential to ensure safety and optimal treatment response.

Individualizing Medication Treatment for ADHD
Factors Considered in Prescribing Medication for ADHD
The decision to start medication treatment for ADHD is based on several factors. These include the severity of symptoms, the individual’s age, medical history, and preferences, as well as the impact of symptoms on daily functioning and quality of life. It is crucial to conduct a comprehensive evaluation to assess the individual’s specific needs and to consider any potential risks or contraindications before initiating medication treatment.
Dosage and Administration of ADHD Medications
The optimal dosage of ADHD medications varies for each individual and is determined based on several factors, including age, weight, and medication response. Healthcare providers typically start with a low dose and adjust gradually to achieve the desired therapeutic effect while minimizing side effects. Medication administration instructions should be carefully followed, as some medications may need to be taken with food or at specific times of the day to maximize effectiveness.
Monitoring and Adjusting Medication Treatment
Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are essential when initiating medication treatment for ADHD. The healthcare team will monitor the individual’s response to medication, assess any side effects, and make necessary adjustments to dosage or medication type if needed. It is crucial to maintain open communication and report any concerns or changes in symptoms to ensure the most effective and safe treatment plan.
Combination Therapy for ADHD
When Combination Therapy is Recommended
Combination therapy, which involves the use of multiple medications, may be recommended for individuals with ADHD who have not adequately responded to monotherapy or who have specific symptoms that are not fully addressed by a single medication. Combination therapy can be particularly beneficial for individuals with complex or severe presentations of ADHD, allowing for a more comprehensive and personalized treatment approach.
Benefits and Considerations of Combination Therapy
Combining different medications for ADHD can provide several benefits. It allows for targeting multiple symptoms simultaneously, enhancing overall symptom reduction. Combination therapy may also offer a more tailored approach by addressing specific symptoms that were not adequately managed with a single medication. However, it is essential to carefully monitor for potential side effects and drug interactions when using combination therapy, as well as to regularly assess the need for ongoing medication management.
Common Combinations of Medications for ADHD
The specific combination of medications used for ADHD will depend on the individual’s symptoms, treatment response, and healthcare provider’s expertise. Common combinations may involve a stimulant medication along with a non-stimulant medication, or different stimulant medications with varying durations of action. The goal is to maximize symptom reduction while minimizing any potential side effects or risks.
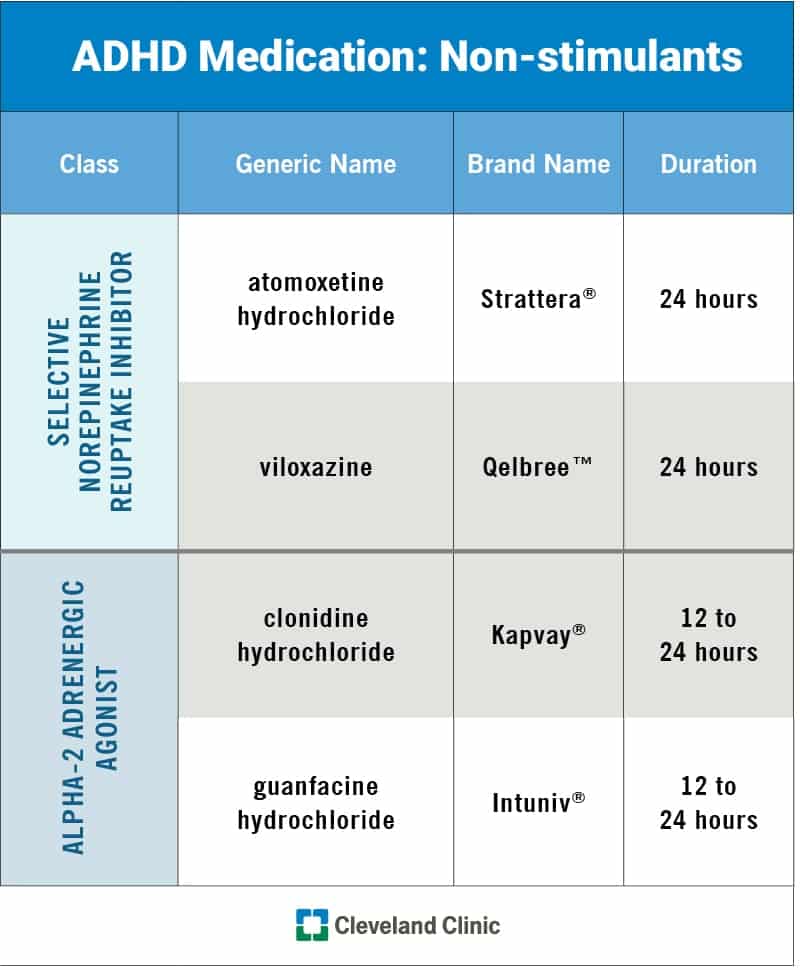
Side Effects and Risks of Medication for ADHD
Common Side Effects of ADHD Medications
While medication can provide significant benefits, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects. Common side effects of ADHD medications may include decreased appetite, insomnia, stomachache, increased heart rate, or mood changes. These side effects are generally mild and temporary, and healthcare providers carefully monitor and adjust medications to minimize discomfort. Open communication with healthcare providers is crucial to address any concerns and ensure a safe and effective treatment plan.
Long-Term Risks and Benefits of Medication Use
Research has shown that long-term medication use for ADHD can provide consistent symptom improvement and enhance overall functioning in many individuals. However, there have been concerns about the potential risks associated with long-term medication use, including growth suppression or cardiovascular effects. It is important to note that studies have not consistently supported these concerns, and the benefits of medication treatment often outweigh potential risks. Healthcare providers closely monitor individuals on long-term medication treatment to ensure safety and address any emerging concerns.
Addressing Concerns and Managing Side Effects
If you have concerns or experience side effects related to ADHD medication, it is crucial to discuss them openly with your healthcare provider. They can provide guidance, adjust dosage, or consider alternative medications to address any discomfort or adverse effects. It is essential not to discontinue or adjust medication treatment without professional guidance, as this can lead to a relapse or worsening of symptoms. With proper monitoring and support, medication treatment can be effectively managed to optimize benefits and minimize any potential side effects.
Alternative and Complementary Treatments for ADHD
Supplements and Herbal Remedies
In addition to medication, some individuals may consider alternative or complementary treatments for ADHD. However, it is crucial to approach these options with caution, as the evidence supporting their effectiveness is often limited. Supplements such as omega-3 fatty acids, iron, or zinc have been explored, but their specific benefits in ADHD treatment are still being researched. Herbal remedies like ginkgo biloba or valerian root have also been suggested, but their safety and efficacy remain uncertain. It is essential to consult with healthcare providers before incorporating these treatments to ensure their compatibility with other medications or potential risks.
Dietary Approaches in ADHD Treatment
Some individuals and families have explored dietary approaches as adjunctive treatments for ADHD. While some studies suggest that a balanced diet with essential nutrients can support overall brain function, specific dietary interventions targeting ADHD symptoms have shown mixed results. Restrictive diets or eliminating certain food groups may have unintended consequences, and it is crucial not to replace evidence-based treatment with dietary approaches alone. Collaborating with a registered dietitian or nutritionist can provide guidance on healthy eating habits that support overall well-being.
Behavioral and Psychological Therapies as Complementary Treatments
Behavioral and psychological therapies are important components of comprehensive ADHD treatment. These therapies, such as cognitive-behavioral therapy or behavioral interventions, can help individuals develop coping strategies, improve executive functioning skills, and enhance social interactions. They can be used alone or in combination with medication to provide a multidimensional approach to ADHD management. Healthcare providers, therapists, and educators work collaboratively to tailor these therapies to each individual’s unique needs and challenges, promoting self-awareness and effective self-regulation.

Medication Challenges and Considerations in ADHD Treatment
Medication Non-Response and Reasons
While medication treatment can be highly beneficial for many individuals with ADHD, there are cases where individuals may not respond adequately to medication. Non-response may occur due to several factors, including individual variations in medication metabolism, suboptimal dosage, or inaccurately diagnosed ADHD. In cases of non-response, healthcare providers will reassess the treatment plan, potentially consider alternative medications or dosage adjustments, and evaluate if there are co-occurring conditions contributing to the lack of response.
Medication Tolerance and Loss of Effectiveness
Over time, individuals taking ADHD medication may experience a reduced response or loss of effectiveness. This phenomenon, known as medication tolerance, may occur due to various factors, such as changes in the body’s metabolism or neurotransmitter systems. In such cases, healthcare providers can adjust dosages, switch medications, or explore other treatment modalities like behavioral therapies or lifestyle changes to optimize treatment response.
Long-Term Medication Management for ADHD
ADHD is a chronic condition that often requires ongoing medication management throughout an individual’s life. Regular follow-up appointments with healthcare providers are crucial to assess treatment response, monitor for side effects, and adjust medication as needed. The long-term management of ADHD involves collaboration between the individual, their parents (in the case of children), healthcare providers, therapists, and educators to ensure a holistic and comprehensive approach that supports sustained symptom reduction and overall well-being.
The Importance of Collaborative Care and Monitoring
Role of Healthcare Team in ADHD Medication Treatment
ADHD medication treatment involves a collaborative approach that includes various healthcare professionals and individuals’ support network. The healthcare team typically comprises primary care providers, psychiatrists, psychologists, and therapists who work together to assess, diagnose, and implement an individualized treatment plan. Collaboration and coordination among these professionals ensure comprehensive care that addresses not only medication treatment but also behavioral therapies, educational support, and psychosocial interventions.
Regular Monitoring and Follow-Up Appointments
Regular monitoring is essential when initiating and maintaining medication treatment for ADHD. It allows healthcare providers to assess treatment response, monitor side effects, and make necessary adjustments to optimize outcomes. Follow-up appointments provide an opportunity for individuals and their families to express concerns, ask questions, and collaborate with healthcare providers on any necessary modifications to the treatment plan. Open communication and active involvement in the monitoring process contribute to a successful treatment experience.
Collaboration with Parents, Teachers, and Therapists
Collaboration with parents, teachers, and therapists is crucial to support individuals with ADHD in various environments. Open lines of communication ensure that all parties are aware of treatment goals, strategies, and potential challenges. Parents can provide valuable insights into the individual’s response to medication at home, while teachers can offer observations in educational settings. Therapists play an essential role in providing behavioral and psychological therapies that complement medication treatment, as well as addressing any emotional or social challenges individuals may face. By working together, a consistent and supportive environment is created, maximizing the individual’s potential for success.
