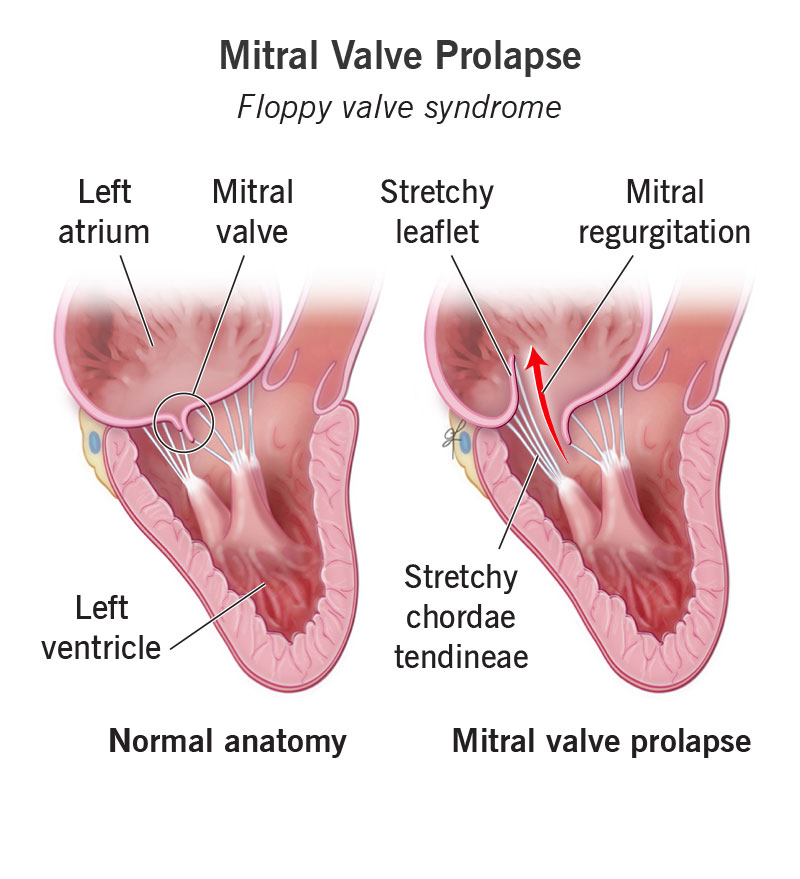
Mitral Valve Prolapse, a condition where the valve between your heart’s left atrium and left ventricle doesn’t close properly, affects millions of people worldwide. If you have recently been diagnosed with this condition, you may be wondering about the available treatment options. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the various treatment options available for Mitral Valve Prolapse, including lifestyle changes, medications, and surgical interventions. By exploring these treatment options, you will be empowered to make informed decisions regarding your own health and well-being.
Medications
Beta blockers
Beta blockers are a commonly prescribed medication for individuals with mitral valve prolapse. These medications work by blocking the effects of adrenaline, which can help to reduce the symptoms associated with this condition. By slowing down the heart rate and decreasing blood pressure, beta blockers can help to alleviate chest pain, shortness of breath, and palpitations.
Calcium channel blockers
Calcium channel blockers are another type of medication that can be used to manage the symptoms of mitral valve prolapse. These medications work by relaxing the muscles in the blood vessels and reducing the strain on the heart. By doing so, they can help to improve blood flow and relieve symptoms such as chest pain and palpitations.
Antiarrhythmic drugs
If you experience irregular heart rhythms or arrhythmias as a result of mitral valve prolapse, your doctor may prescribe antiarrhythmic drugs. These medications help to stabilize the electrical activity in the heart, reducing the occurrence and severity of abnormal heart rhythms. By regulating your heart’s rhythm, antiarrhythmic drugs can help to alleviate symptoms and improve overall heart function.
Blood thinners
In some cases, individuals with mitral valve prolapse may be at a higher risk for blood clots. To reduce this risk, your doctor may prescribe blood thinners such as aspirin or anticoagulants. These medications help to prevent the formation of clots and can protect against complications such as stroke or heart attack.
Angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitors
ACE inhibitors are commonly used to manage high blood pressure, which is a common complication of mitral valve prolapse. By blocking the production of a hormone called angiotensin, ACE inhibitors help to relax and widen the blood vessels, reducing blood pressure. This can help to alleviate symptoms and improve overall heart health.
Angiotensin receptor blockers (ARBs)
ARBs, like ACE inhibitors, are used to manage high blood pressure in individuals with mitral valve prolapse. These medications work by blocking the effects of angiotensin, a hormone that narrows blood vessels and increases blood pressure. By widening the blood vessels, ARBs can help to improve blood flow and reduce the strain on the heart.
Diuretics
In some cases, individuals with mitral valve prolapse may experience fluid retention, leading to swelling in the legs and ankles. Diuretics, also known as water pills, can be prescribed to help eliminate excess fluid from the body. By increasing urine production, diuretics can help to reduce swelling and alleviate symptoms of fluid retention.
Lifestyle Changes
Maintaining a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is important for individuals with mitral valve prolapse, as being overweight can put additional strain on the heart. By following a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise, you can achieve and maintain a healthy weight, which can help to improve symptoms and overall heart health.
Regular exercise
Engaging in regular exercise is highly beneficial for individuals with mitral valve prolapse. Exercise helps to strengthen the heart muscle, improve cardiac function, and reduce the risk of complications. It is important to consult with your doctor before starting any exercise program to ensure that it is suitable for your specific condition.
Low-sodium diet
A low-sodium diet can help to manage symptoms associated with mitral valve prolapse, particularly if you experience fluid retention. By reducing your intake of sodium, you can help to reduce fluid buildup and alleviate swelling. It is important to read food labels carefully and avoid processed foods that may be high in sodium.
Quitting smoking
Smoking is known to increase the risk of heart disease and can exacerbate symptoms of mitral valve prolapse. Quitting smoking is one of the most important lifestyle changes you can make to improve your heart health. If you need assistance with quitting, speak to your doctor who can provide resources and support.
Reducing stress
Stress can have a negative impact on heart health and may exacerbate symptoms of mitral valve prolapse. Finding healthy ways to manage and reduce stress, such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in hobbies, or seeking support from friends and family, can help to improve symptoms and overall well-being.
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can have a detrimental effect on heart health and may worsen symptoms associated with mitral valve prolapse. It is important to consume alcohol in moderation, if at all, and to discuss your alcohol consumption with your doctor to ensure it is safe for your specific condition.

Surgical Options
Mitral valve repair
In cases where the mitral valve is damaged or leaking, surgical repair may be necessary. Mitral valve repair involves repairing the valve to improve its functioning and prevent blood from backing up into the left atrium. This procedure is often preferred over valve replacement, as it allows the preservation of the patient’s own valve and avoids the need for long-term medication.
Mitral valve replacement
In some cases, the damage to the mitral valve may be extensive, making repair not feasible. In these situations, a mitral valve replacement may be necessary. During this procedure, the damaged valve is replaced with a mechanical or biological valve. While mechanical valves are durable and long-lasting, they require long-term anticoagulant therapy. Biological valves, on the other hand, may not last as long but do not require lifelong medication.
Minimally invasive surgery
Minimally invasive surgery is a technique that allows surgical intervention for mitral valve prolapse while reducing the invasiveness and recovery time associated with traditional open-heart surgery. In these procedures, small incisions are made on the side of the chest, and specialized instruments and a camera are used to repair or replace the mitral valve.
Transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVR)
Transcatheter mitral valve repair is a minimally invasive procedure that can be an alternative to open-heart surgery. In this procedure, a catheter is threaded through a blood vessel to the heart, where a small device is implanted to repair the valve. TMVR is performed under X-ray guidance and can help to improve symptoms and reduce complications associated with mitral valve prolapse.
Percutaneous Mitral Balloon Valvotomy (PMBV)
Procedure
Percutaneous mitral balloon valvotomy is a non-surgical procedure used to treat mitral valve stenosis, a condition where the mitral valve narrows and restricts blood flow. During the procedure, a catheter with a deflated balloon on its tip is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. The balloon is then inflated to widen the narrowed valve, improving blood flow.
Benefits
PMBV can provide significant relief from symptoms such as fatigue, shortness of breath, and chest pain. It can improve exercise tolerance and overall quality of life for individuals with mitral valve stenosis. The procedure offers a less invasive alternative to surgery, with a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery time.
Risks and complications
As with any medical procedure, PMBV carries a risk of complications. These can include bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or the heart, irregular heart rhythms, and valve damage. However, the risks are generally low, and complications can be minimized by choosing an experienced and skilled medical team.
Recovery and follow-up
After PMBV, you will likely spend a day or two in the hospital for monitoring and recovery. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-procedure care, including medication management, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments. It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up visits to ensure the success of the procedure and to monitor your progress.

Cardiac Catheterization
Procedure
Cardiac catheterization is a diagnostic procedure used to assess the function of the heart and blood vessels. During the procedure, a thin tube called a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. Contrast dye is injected, allowing the doctor to visualize the blood vessels and determine the presence of any abnormalities or blockages.
Benefits
Cardiac catheterization provides valuable information about the function of the heart and can help guide treatment decisions for mitral valve prolapse. The procedure allows the doctor to assess the severity of valve abnormalities, evaluate coronary artery disease, and determine the need for further interventions or surgery.
Risks and complications
Cardiac catheterization is generally a safe procedure, but like any medical procedure, it carries a risk of complications. These can include bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or the heart, irregular heart rhythms, and allergic reactions to the contrast dye. However, these risks are relatively low, and the benefits of the procedure usually outweigh the potential complications.
Recovery and follow-up
After cardiac catheterization, you will be monitored for a period of time to ensure your condition is stable. Recovery time can vary, but most individuals are able to return home the same day or the following day. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-procedure care, such as activity restrictions and medication management. It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up visits to discuss the results of the procedure and determine any necessary next steps.
Transesophageal Echocardiogram (TEE)
Procedure
A transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE) is a diagnostic test that provides detailed images of the heart by inserting a small probe into the esophagus. This allows for closer visualization of the heart structures, including the mitral valve. The procedure is performed under local anesthesia, and the images obtained can help to assess the severity of mitral valve prolapse and guide treatment decisions.
Benefits
TEE provides more detailed and accurate images of the heart and mitral valve compared to a standard echocardiogram. It allows the doctor to assess the structure and function of the valve, identify any abnormalities, and determine the need for intervention or surgery. TEE can help guide the treatment plan and ensure optimal outcomes for individuals with mitral valve prolapse.
Risks and complications
Like any medical procedure, TEE carries a risk of complications. These can include injury to the esophagus or surrounding structures, bleeding, infection, irregular heart rhythms, and an adverse reaction to the sedation or anesthesia used during the procedure. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the test usually outweigh the potential complications.
Recovery and follow-up
After TEE, you will typically spend some time in a recovery area until the sedation wears off. You may experience a sore throat or bloating sensation after the procedure, but these symptoms usually resolve quickly. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-procedure care and any necessary follow-up appointments. It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up visits to review the results of the test and discuss any further treatment plans.

Electrophysiologic Study (EPS)
Procedure
An electrophysiologic study (EPS) is a diagnostic test that evaluates the electrical activity of the heart. During the procedure, thin, flexible wires called electrodes are inserted through a blood vessel and guided to the heart. These electrodes measure electrical signals in various areas of the heart, helping to identify abnormal rhythms or electrical pathways.
Benefits
EPS is particularly useful for individuals with mitral valve prolapse who experience abnormal heart rhythms or arrhythmias. The procedure provides valuable information about the electrical conduction system of the heart, allowing for a more accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment planning. EPS can help guide decisions regarding the use of antiarrhythmic medications, catheter ablation, or other interventions.
Risks and complications
As with any medical procedure, EPS carries a risk of complications. These can include bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or the heart, irregular heart rhythms, and blood clots. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the test usually outweigh the potential complications. Your medical team will take precautions to minimize these risks and monitor your condition closely throughout the procedure.
Recovery and follow-up
After EPS, you will spend some time in a recovery area to allow for monitoring and observation. You may experience mild bruising or soreness at the insertion site, but these symptoms typically resolve within a few days. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-procedure care, including medication management and any necessary follow-up appointments. It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up visits to review the results of the study and discuss any further treatment plans.
Mitral Valve Clip
Procedure
The mitral valve clip procedure, also known as transcatheter mitral valve repair (TMVr), is a minimally invasive treatment option for individuals with mitral valve regurgitation. During the procedure, a catheter is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the heart. A small device, known as a clip, is then used to grasp and bring together the leaflets of the mitral valve, reducing the amount of blood flowing backward.
Benefits
The mitral valve clip procedure offers several benefits for individuals with mitral valve regurgitation. It can improve symptoms such as shortness of breath and fatigue, and reduce the risk of complications associated with the condition. The procedure is less invasive compared to traditional open-heart surgery and generally results in a shorter hospital stay and faster recovery time.
Risks and complications
As with any medical procedure, the mitral valve clip procedure carries a risk of complications. These can include bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or the heart, irregular heart rhythms, and valve damage. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the procedure usually outweigh the potential complications. Your medical team will take precautions to minimize these risks and monitor your condition closely throughout the procedure.
Recovery and follow-up
After the mitral valve clip procedure, you will typically spend a day or two in the hospital for monitoring and recovery. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-procedure care, including medication management, activity restrictions, and follow-up appointments. It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up visits to review the success of the procedure and monitor your progress.

Radiofrequency Ablation
Procedure
Radiofrequency ablation is a treatment option for individuals with mitral valve regurgitation who experience irregular heart rhythms or arrhythmias. During the procedure, a catheter with a special tip is inserted into a blood vessel and guided to the area of the heart responsible for the abnormal rhythm. Radiofrequency energy is then delivered through the tip of the catheter to destroy or modify the abnormal tissue, restoring normal heart rhythm.
Benefits
Radiofrequency ablation can provide significant relief from the symptoms associated with irregular heart rhythms and improve overall heart function. The procedure offers a less invasive alternative to antiarrhythmic medications, which may have side effects. By restoring a normal heart rhythm, radiofrequency ablation can improve symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and enhance overall quality of life.
Risks and complications
As with any medical procedure, radiofrequency ablation carries a risk of complications. These can include bleeding, infection, damage to blood vessels or the heart, irregular heart rhythms, and blood clots. However, these risks are generally low, and the benefits of the procedure usually outweigh the potential complications. Your medical team will take precautions to minimize these risks and monitor your condition closely throughout the procedure.
Recovery and follow-up
After radiofrequency ablation, you will spend some time in a recovery area for monitoring and observation. You may experience a sore throat or mild discomfort at the catheter insertion site, but these symptoms generally resolve within a few days. Your doctor will provide specific instructions for post-procedure care, including medication management and any necessary follow-up appointments. It is important to attend all scheduled follow-up visits to review the results of the procedure and discuss any further treatment plans.
Exercise and Physical Activities Recommendations
Types of exercise
Regular exercise is highly beneficial for individuals with mitral valve prolapse. It is important to choose exercises that are low-impact and do not put excessive strain on the heart. Walking, swimming, cycling, and yoga are all excellent options. It is important to find activities that you enjoy and that can be sustained over the long term.
Intensity and duration
When starting an exercise program, it is important to begin slowly and gradually increase both the duration and intensity of your workouts. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity aerobic exercise per week, such as brisk walking or cycling. If you are unable to do continuous exercise, you can break it up into shorter sessions throughout the day.
Precautions and considerations
Before starting any exercise program, it is important to consult with your doctor to ensure it is safe for your specific condition. Your doctor can provide guidance on any precautions or modifications that may be necessary. It is also important to listen to your body and not push yourself too hard. If you experience chest pain, dizziness, or other concerning symptoms during exercise, stop and seek medical attention.
Monitoring symptoms
During exercise, it is important to pay attention to your body and monitor any symptoms that may arise. If you experience chest pain, shortness of breath, palpitations, or feel faint or dizzy, it is important to stop exercising and rest. These symptoms may indicate that you are exceeding your body’s limits and should be evaluated by a medical professional.
In conclusion, the treatment options for mitral valve prolapse vary depending on the severity of the condition and the presence of symptoms. Medications, lifestyle changes, and various procedures can be employed to manage symptoms, improve heart function, and reduce the risk of complications. It is important to work closely with your medical team to determine the most appropriate treatment plan for your specific situation. By combining medical interventions with lifestyle modifications, individuals with mitral valve prolapse can lead a full and healthy life.