Anxiety is a common and often misunderstood mental health condition that affects millions of people worldwide. From racing thoughts and rapid heartbeat to feelings of dread and apprehension, anxiety disorders can be debilitating and have a significant impact on daily life. This article aims to shed light on the causes and symptoms of anxiety disorders, providing a clearer understanding of this prevalent issue and offering insights that can help individuals navigate their anxiety more effectively.
Understanding Anxiety Disorders: Causes and Symptoms
Anxiety is a common emotion that everyone experiences from time to time. It is a normal reaction to stress or a perceived threat, and it often helps us remain alert and focused. However, when anxiety becomes persistent, excessive, and interferes with daily life, it may be an indication of an anxiety disorder. Anxiety disorders are a group of mental health conditions characterized by intense and uncontrollable worries and fears that cause significant distress and impairment.
What is Anxiety?
Anxiety is a complex emotional state that involves feelings of apprehension, fear, and unease. It is a natural response to potential threats or stressful situations. When you experience anxiety, your body undergoes various changes, such as increased heart rate, rapid breathing, and heightened alertness. These physiological responses prepare you to either confront the threat or flee from it, commonly known as the “fight-or-flight” response. However, anxiety disorders can cause these natural responses to occur in excess, leading to significant disruption in daily functioning.

Prevalence of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders are one of the most common mental health conditions worldwide. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), approximately 264 million people of all ages are affected by anxiety disorders globally. In the United States alone, anxiety disorders affect around 40 million adults, making it the most common mental illness in the country. Despite its prevalence, anxiety disorders are often underdiagnosed and undertreated, with only a fraction of individuals seeking professional help.
Causes of Anxiety Disorders
The exact causes of anxiety disorders are not fully understood, but research suggests that they are influenced by a combination of genetic, environmental, and neurological factors. Some individuals may have a genetic predisposition to anxiety disorders, meaning that they are more likely to develop the condition if they have a family history of anxiety. Environmental factors, such as traumatic events or chronic stress, can also contribute to the development of anxiety disorders. Additionally, certain imbalances in brain chemicals, such as serotonin and gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), may play a role in the manifestation of anxiety disorders.
Types of Anxiety Disorders
The Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders (DSM-5) classifies anxiety disorders into several distinct categories, each with its own set of symptoms and diagnostic criteria. The main types of anxiety disorders include:
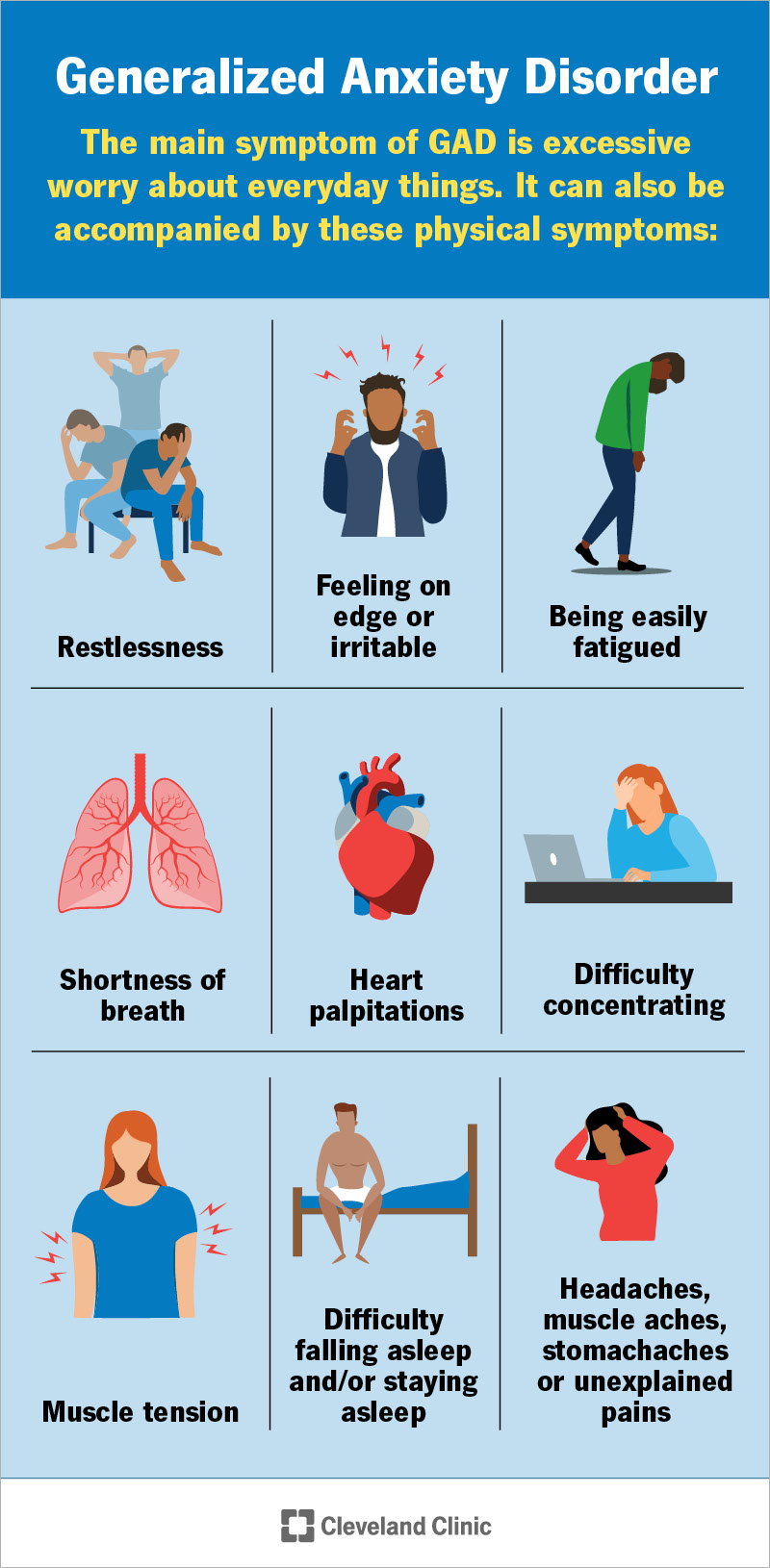
Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD)
Generalized Anxiety Disorder is characterized by excessive and persistent worry about various aspects of life, such as work, health, or relationships. Individuals with GAD often find it challenging to control their worries, leading to physical symptoms like restlessness, muscle tension, and sleep disturbances.
Panic Disorder
Panic Disorder is characterized by recurring panic attacks – sudden and intense episodes of fear that reach their peak within minutes. These panic attacks are accompanied by physical symptoms such as heart palpitations, sweating, trembling, and a sense of impending doom.
Social Anxiety Disorder
Social Anxiety Disorder, also known as social phobia, involves an intense fear of social situations and the fear of being negatively judged or humiliated. Individuals with social anxiety disorder often experience extreme self-consciousness, leading to avoidance of social interactions, public speaking, or any situation where they may feel scrutinized.
Specific Phobias
Specific Phobias are marked by an overwhelming fear of a particular object, situation, or activity. Common phobias include heights, spiders, flying, or certain animals. Individuals with specific phobias will go to great lengths to avoid the phobic stimulus, resulting in significant distress and disruption in their lives.
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD)
Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder is characterized by recurring intrusive thoughts (obsessions) and repetitive behaviors (compulsions) performed in response to these thoughts. People with OCD often engage in rituals or compulsions to alleviate anxiety or prevent a feared outcome, even though they understand that their actions are excessive or irrational.
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD)
Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder is triggered by experiencing or witnessing a traumatic event, such as a natural disaster, war, or physical assault. Individuals with PTSD may experience intrusive memories, nightmares, flashbacks, and intense emotional distress even long after the traumatic event has occurred.
Symptoms of Anxiety Disorders
Anxiety disorders can manifest in various ways and affect individuals differently. The symptoms of anxiety disorders can be classified into four main categories:
Physical Symptoms
Physical symptoms of anxiety disorders often include increased heart rate, rapid breathing, sweating, trembling, muscle tension, dizziness, and gastrointestinal distress. These physical sensations are the result of the body’s natural stress response, which prepares you to face a perceived threat.
Cognitive Symptoms
Cognitive symptoms of anxiety disorders involve excessive worrying, intrusive thoughts, difficulty concentrating, and racing thoughts. Individuals with anxiety disorders may constantly anticipate the worst-case scenario and have a heightened sense of alertness, making it challenging to focus on everyday tasks.
Emotional Symptoms
Emotional symptoms of anxiety disorders often include feelings of apprehension, irritability, restlessness, and a constant sense of dread. Anxiety can also lead to a decreased ability to handle stress and an exaggerated startle response.
Behavioral Symptoms
Behavioral symptoms of anxiety disorders may manifest as avoidance of certain situations or activities, isolating oneself socially, or engaging in repetitive behaviors to reduce anxiety. People with anxiety disorders may also experience disrupted sleep patterns, changes in appetite, and difficulty performing daily tasks.

Conclusion
Understanding anxiety disorders is crucial for recognizing the signs and seeking appropriate help. Remember, anxiety disorders are treatable, and seeking professional support from mental health providers can lead to effective management and improved quality of life. If you or someone you know is experiencing excessive and persistent anxiety, don’t hesitate to reach out to a healthcare professional to discuss diagnosis and treatment options. Remember, support is available, and you are not alone.