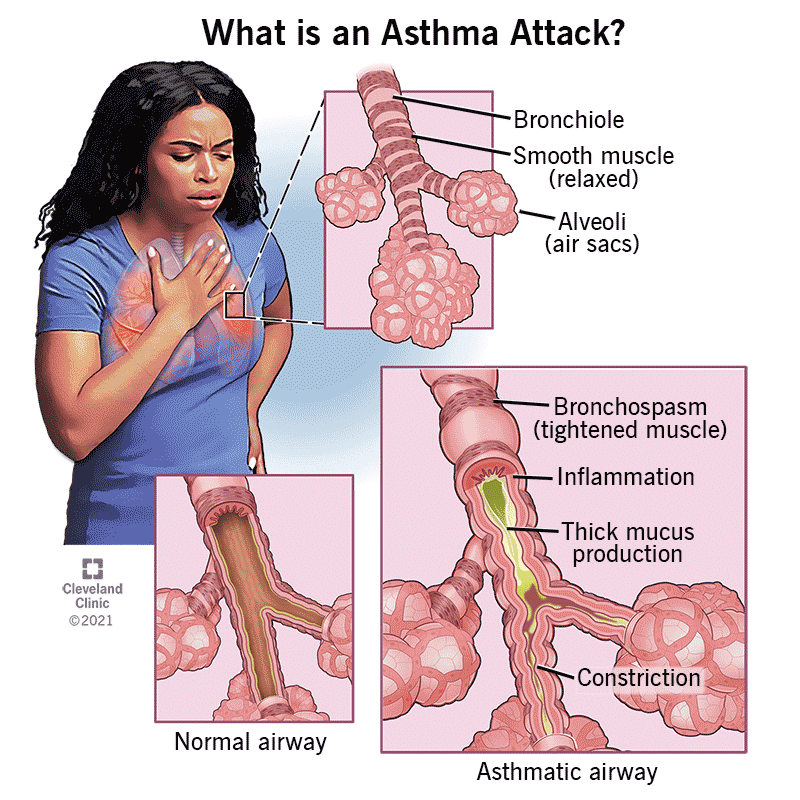
If you or someone you know has ever struggled with asthma, you are well aware of the impact it can have on daily life. Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of people around the world. From its causes to its symptoms and treatment options, this article aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of asthma. By exploring the triggers, identifying the common symptoms, and discussing various treatment approaches, this article will empower you with the knowledge to manage your asthma effectively and lead a fulfilling life. So, let’s delve into the world of asthma and discover how to take control of this condition.
Understanding Asthma: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Asthma is a chronic respiratory condition that affects millions of individuals worldwide. If you have been diagnosed with asthma or suspect that you may have it, it’s essential to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options available to manage this condition effectively.
Causes
Asthma can be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors. While the exact cause of asthma is not fully understood, researchers have identified certain factors that are commonly associated with the development of this condition.
Genetic factors
Genetics play a significant role in asthma development. If you have a family history of asthma, allergies, or other respiratory conditions, you may have an increased risk of developing asthma. Genetic variations can affect how your immune system responds to environmental triggers, making you more susceptible to developing asthma.
Environmental factors
Environmental factors also contribute to the development of asthma. Exposure to allergens such as pet dander, pollen, dust mites, and mold can trigger asthma symptoms in susceptible individuals. Other environmental factors, such as air pollution, tobacco smoke, and occupational hazards, can also worsen existing asthma symptoms.
Symptoms
Asthma symptoms can vary from person to person, but some common signs indicate the presence of this condition. It’s important to be aware of these symptoms and seek medical attention if you experience them.
Coughing
Persistent coughing that worsens at night or early in the morning is a common symptom of asthma. This cough may be dry or accompanied by mucus production, and it can last for several weeks or even months.
Wheezing
Wheezing is a high-pitched whistling sound that occurs when airflow through the narrowed airways is restricted. It is a classic symptom of asthma and is often heard during exhalation but can also be present during inhalation.
Shortness of breath
Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing is another hallmark symptom of asthma. It may feel like you cannot take a deep breath or that you are not getting enough air. This sensation can be frightening and may result in anxiety or panic.
Chest tightness
Individuals with asthma often experience a feeling of tightness or pressure in their chest. This discomfort can range from mild to severe and may be accompanied by other symptoms such as coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath.

Diagnosis
To diagnose asthma, your healthcare provider will perform a comprehensive evaluation involving your medical history, physical examination, and lung function tests.
Medical history
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, including the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, as well as any known triggers or family history of respiratory conditions. Providing accurate and detailed information about your symptoms is crucial for an accurate diagnosis.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, your doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for wheezing or any abnormal sounds. They may also examine your nose, throat, and eyes for signs of allergies that could be contributing to your asthma symptoms.
Lung function tests
Lung function tests, such as spirometry and peak flow measurements, are essential in determining how well your lungs are functioning. These tests evaluate the amount of air you can exhale forcefully and how quickly you can do it. They can help confirm an asthma diagnosis and determine its severity.
Triggers
Identifying and avoiding triggers is crucial for asthma management. Common triggers can vary from person to person, but some triggers are universally recognized.
Allergens
Allergens such as pollen, dust mites, mold, and pet dander are common triggers for asthma symptoms. If you have identified specific allergens that exacerbate your asthma, taking steps to minimize exposure can help prevent symptoms and asthma attacks.
Respiratory infections
Respiratory infections, particularly viral infections like the common cold or flu, can trigger asthma symptoms. It is important to practice good hand hygiene and avoid close contact with individuals who are sick to reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Irritants
Irritants such as tobacco smoke, strong perfumes, and strong odors can irritate the airways and trigger asthma symptoms. Avoiding exposure to these irritants can help prevent asthma attacks.
Exercise
Exercise-induced asthma occurs when physical activity triggers asthma symptoms. It is essential to warm up before exercising, use appropriate medications as prescribed, and choose activities that are less likely to trigger symptoms, such as swimming or walking instead of running.

Medications
There are various medications available to manage asthma symptoms and prevent asthma attacks. The two main types of medications used for asthma treatment are quick-relief medications and long-term control medications.
Quick-relief medications
Quick-relief medications, also known as rescue medications, are used to provide immediate relief from asthma symptoms during an asthma attack. These medications work by quickly relaxing the muscles around the airways, making it easier to breathe. Examples of quick-relief medications include short-acting beta-agonists like albuterol.
Long-term control medications
Long-term control medications are taken regularly to manage and prevent asthma symptoms over time. These medications help reduce airway inflammation, keep the airways open, and minimize the risk of asthma attacks. Long-term control medications include inhaled corticosteroids, long-acting beta-agonists, leukotriene modifiers, and immunomodulators.
Inhalers
Inhalers are commonly used to deliver medications directly to the airways, providing quick and effective relief for asthma symptoms. There are two main types of inhalers: metered-dose inhalers (MDIs) and dry-powder inhalers (DPIs).
Metered-dose inhalers
Metered-dose inhalers deliver a measured dose of medication in aerosol form. These inhalers require coordination between pressing down on the canister and inhaling the medication. Proper technique is essential to ensure the medication reaches the airways effectively.
Dry-powder inhalers
Dry-powder inhalers deliver medication in a powdered form that is activated by the user’s inhalation. They do not require coordination between inhalation and pressing down on a canister like MDIs. DPIs are often preferred by individuals who have difficulty using MDIs correctly.

Other Treatment Options
In addition to medications and inhalers, there are other treatment options available for individuals with asthma, depending on the severity of their symptoms.
Nebulizers
Nebulizers are devices that convert liquid medication into a fine mist that can be inhaled through a mask or mouthpiece. They are commonly used for individuals who have difficulty using inhalers, such as young children or older adults.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy, also known as allergy shots, can be beneficial for individuals with asthma triggered by allergens. This treatment involves receiving regular injections of small amounts of allergens over time, gradually desensitizing the immune system and reducing the severity of allergic reactions.
Bronchial thermoplasty
For individuals with severe asthma that is not well-controlled with medications, bronchial thermoplasty may be an option. This procedure involves delivering controlled heat to the airways to reduce the smooth muscle that contributes to airway constriction. It can help improve asthma symptoms and reduce the frequency of asthma attacks.
Lifestyle changes
In addition to medical treatment, lifestyle changes can play a significant role in managing asthma and reducing the frequency and severity of asthma attacks.
Avoiding triggers
One of the most important lifestyle changes for managing asthma is avoiding triggers. Once you identify the specific triggers that worsen your symptoms, taking steps to minimize exposure can help prevent asthma attacks.
Maintaining a healthy weight
Maintaining a healthy weight can help improve asthma control. Obesity has been linked to increased asthma severity and a higher risk of asthma-related hospitalizations. A balanced diet and regular exercise can help achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Exercising regularly
Regular exercise can improve lung function, strengthen respiratory muscles, and reduce asthma symptoms. It is important to choose activities that are less likely to trigger symptoms, warm up before exercising, and use appropriate medications as prescribed.

Managing an Asthma Attack
If you experience an asthma attack, it’s important to take immediate action to relieve your symptoms and prevent complications.
Using quick-relief medicines
During an asthma attack, using quick-relief medications as prescribed can help open up the airways and provide immediate relief. Follow the instructions given by your healthcare provider and use your inhaler correctly.
Seeking medical help
If your symptoms worsen despite using quick-relief medications, it is crucial to seek immediate medical assistance. Severe asthma attacks can be life-threatening, and prompt medical attention is necessary to manage the situation effectively.
Creating an asthma action plan
Working with your healthcare provider, create an asthma action plan that outlines steps to manage asthma attacks based on your symptoms and triggers. This plan can help you take quick action during an emergency and ensure you receive the appropriate medical care.
Preventing Asthma Attacks
Prevention is key in managing asthma and reducing the frequency of asthma attacks. Here are some strategies to help prevent asthma attacks:
Identifying and avoiding triggers
Identify the specific triggers that worsen your asthma symptoms and take steps to avoid them. This may involve minimizing exposure to allergens, maintaining good indoor air quality, and practicing good hand hygiene to reduce the risk of respiratory infections.
Taking prescribed medications regularly
Take your prescribed medications as directed, even when you are not experiencing symptoms. Long-term control medications are meant to reduce airway inflammation and prevent asthma attacks, so they need to be taken regularly to be effective.
Monitoring symptoms and lung function
Keep track of your asthma symptoms and monitor your lung function regularly. This can help you identify patterns or triggers that worsen your symptoms and allow you to adjust your treatment plan accordingly. Regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are also important to assess your asthma control and make any necessary adjustments to your medications or treatment plan.
In conclusion, understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for asthma is vital for effectively managing this chronic condition. By working closely with your healthcare provider, identifying and avoiding triggers, taking prescribed medications regularly, and making necessary lifestyle changes, you can significantly reduce the frequency and severity of asthma attacks, improving your overall quality of life. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and with the right support and care, you can successfully manage your asthma and live a fulfilling, active life.