In this article, we will explore the ins and outs of an intriguing illness called Brucellosis. From its symptoms to diagnosis and treatment, you will gain a comprehensive understanding of this disease. So, sit back, relax, and let’s delve into the world of Brucellosis together.

Symptoms of Brucellosis
Brucellosis is an infectious disease caused by the bacteria of the Brucella genus. It can affect both humans and animals, and it is important to be aware of the symptoms in order to seek timely medical attention. The symptoms of brucellosis can vary from person to person, but there are several common signs to watch out for.
One of the most common symptoms of brucellosis is fever. You may experience a persistent low-grade fever that comes and goes over a period of time. Fatigue is another symptom that is often associated with brucellosis. You may feel extremely tired and lack energy, even after getting adequate rest. Loss of appetite is also common, and you may find yourself having no interest in eating.
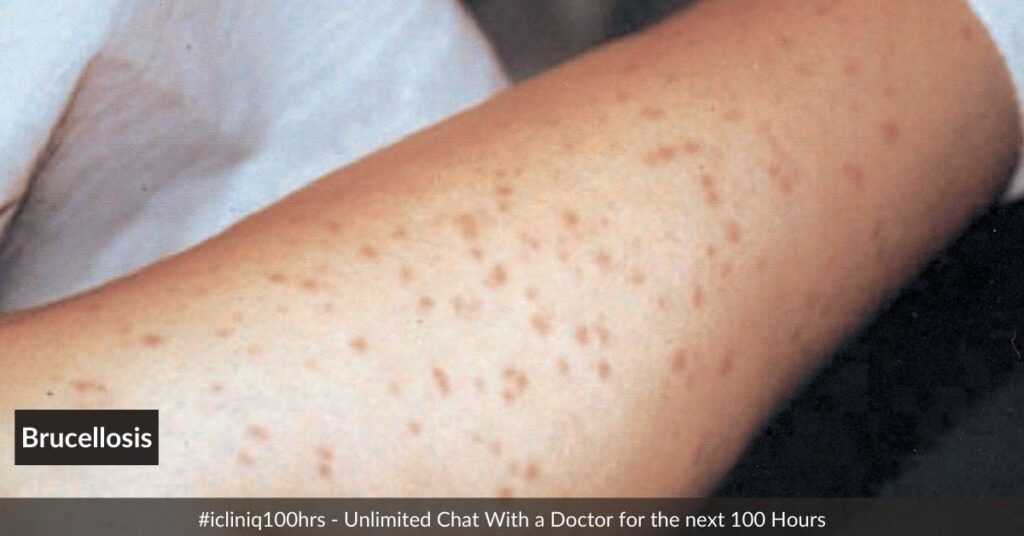
Headache is another symptom that can be experienced by individuals with brucellosis. It may range from mild to severe and can be accompanied by other symptoms such as sensitivity to light and sound. Joint pain and muscle pain are also common symptoms of brucellosis. You may experience pain and stiffness in your joints, making it difficult to move. Muscle pain can also be present, making everyday tasks challenging.
Sweating is a symptom that many individuals with brucellosis experience. You may notice excessive sweating, especially during the night. Additionally, swollen lymph nodes can be a sign of brucellosis. You may notice enlarged lymph nodes in your neck, armpits, or groin area.
If you experience any of these symptoms and suspect you may have brucellosis, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan.
Diagnosis of Brucellosis
To diagnose brucellosis, a healthcare professional will typically start by taking a detailed medical history and conducting a physical examination. They will ask about your symptoms, potential exposure to animals or animal products, and any recent travel to endemic regions.
Blood tests are commonly used to diagnose brucellosis. These tests can detect antibodies produced by your immune system in response to the Brucella bacteria. Additionally, a bone marrow culture may be performed to isolate the bacteria from a sample of your bone marrow. A joint fluid culture may also be conducted if you have symptoms of joint involvement. Imaging tests such as X-rays or ultrasound may be used to detect any complications or abnormalities associated with brucellosis.
It is important to cooperate with your healthcare professional during the diagnostic process to ensure an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment.
Treatment of Brucellosis
Brucellosis can be effectively treated with antibiotic therapy. The choice of antibiotics and the duration of treatment may vary depending on the severity of your symptoms and the specific strain of Brucella bacteria causing the infection. Commonly used antibiotics for brucellosis treatment include doxycycline, rifampin, and trimethoprim-sulfamethoxazole.
The duration of treatment is typically several weeks or even months, as brucellosis can be a stubborn infection that requires long-term antibiotic therapy to fully eradicate the bacteria. It is crucial to complete the prescribed course of antibiotics even if your symptoms improve, as stopping the treatment prematurely can lead to relapse.
To prevent relapse, your healthcare professional may closely monitor your condition and conduct follow-up blood tests to ensure that the infection has been successfully treated. In cases where complications arise, such as meningitis or endocarditis, additional measures may be taken to manage these conditions.
Transmission of Brucellosis
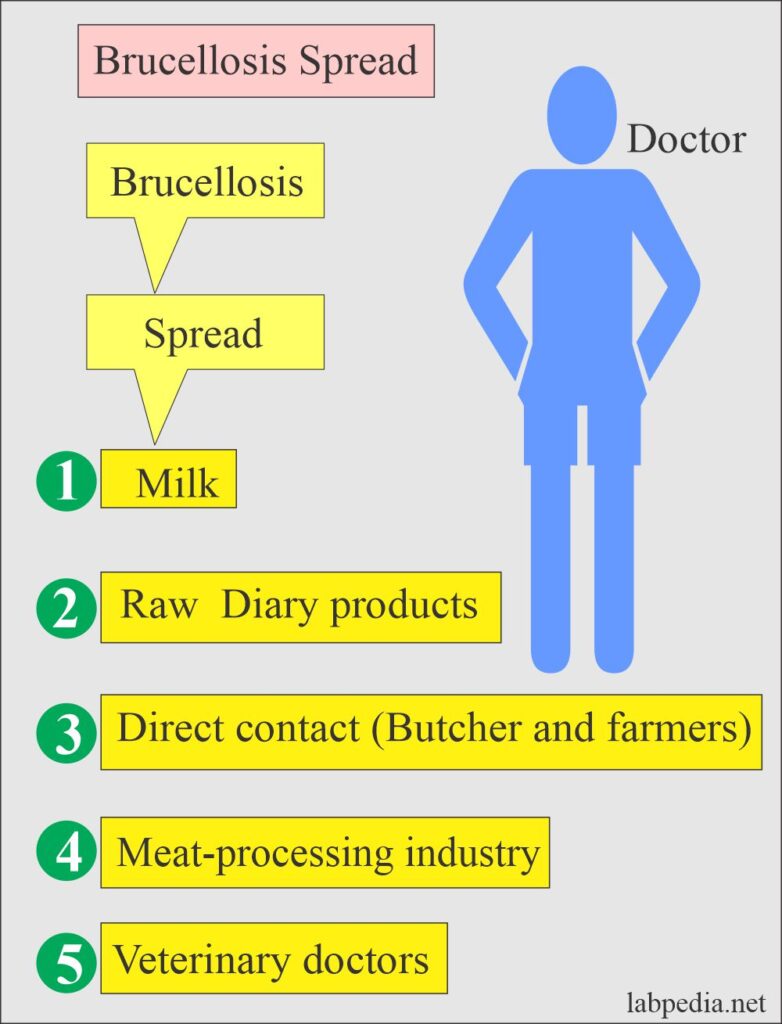
Brucellosis can be transmitted to humans in several ways. The most common mode of transmission is through direct contact with infected animals. This can occur through handling of tissues, secretions, or excretions from infected animals, such as cows, goats, or pigs. Inhalation of contaminated air can also lead to infection, especially in settings where infected animals are being processed or butchered.
Consuming contaminated animal products, particularly unpasteurized dairy products, is another common mode of transmission. It is important to ensure that any dairy products you consume have been properly pasteurized to eliminate the risk of brucellosis.
Although human-to-human transmission is rare, it is theoretically possible through sexual contact or from mother to unborn child. However, these modes of transmission are extremely rare and not a significant concern in the general population.

Risk Factors for Brucellosis
Certain factors can increase your risk of contracting brucellosis. Occupational exposure, such as working with livestock or in slaughterhouses, can put you at a higher risk of coming into contact with infected animals or their products. It is important to take appropriate safety precautions, such as wearing protective clothing and following hygiene protocols, in these settings.
Consumption of unpasteurized dairy products is another significant risk factor for brucellosis. Milk or cheese that has not undergone pasteurization may contain the Brucella bacteria, increasing the risk of infection. Be sure to check the labels and opt for pasteurized dairy products to minimize the risk.
Travel to endemic regions, where brucellosis is more prevalent, can also increase your risk. It is important to familiarize yourself with the local epidemiology of brucellosis and take appropriate precautions if you plan on traveling to these areas.
Prevention of Brucellosis
Prevention is key when it comes to brucellosis, and there are several measures you can take to protect yourself from infection. Vaccination of animals is an important preventive measure, as it helps reduce the prevalence of brucellosis in livestock. This can ultimately decrease the risk of human exposure to the bacteria.
Strict hygiene measures are also crucial in preventing brucellosis. This includes practicing proper hand hygiene, especially after coming into contact with animals or their products. It is important to wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water, or use hand sanitizers if soap and water are not readily available.
Avoiding the consumption of unpasteurized dairy products is another important preventive measure. Choose products that have been pasteurized, as this process helps kill any harmful bacteria, including Brucella.
By taking these preventive measures, you can significantly reduce your risk of contracting brucellosis.
Complications of Brucellosis
While brucellosis is typically a self-limiting disease, meaning it usually resolves on its own with proper treatment, there can be complications in some cases. These complications may arise from the spread of the bacteria to other parts of the body or from the immune response to the infection.
Chronic fatigue syndrome is a potential complication of brucellosis. Some individuals may experience persistent fatigue and weakness even after successful treatment. Meningitis, an infection and inflammation of the membranes surrounding the brain and spinal cord, is another possible complication. It can cause symptoms such as severe headache, neck stiffness, and sensitivity to light.
Endocarditis, an infection of the heart valves, is a rare but serious complication of brucellosis. It can lead to damage to the heart valves and require surgical intervention. Hepatitis, inflammation of the liver, can also occur as a complication of brucellosis, leading to symptoms such as jaundice, abdominal pain, and elevated liver enzymes.
Osteomyelitis, an infection of the bones, is another potential complication. It can cause localized pain, swelling, and limited range of motion in the affected bone.
It is important to be aware of these potential complications and seek medical attention if you experience any concerning symptoms during or after treatment for brucellosis.
Epidemiology of Brucellosis
Brucellosis is a global disease, and it has a significant impact on public health in many parts of the world. The distribution of brucellosis varies by region, with certain areas experiencing higher incidence rates compared to others.
In some regions, such as parts of Africa, Asia, and the Middle East, brucellosis is endemic, meaning it is constantly present in the population. In these areas, brucellosis can have a substantial impact on the health and livelihoods of individuals, particularly those who rely on livestock for sustenance or income.
The incidence rates of brucellosis can vary widely depending on the region and population studied. It is estimated that there are hundreds of thousands of new cases of brucellosis reported each year worldwide. However, the true burden of disease is likely underestimated, as many cases go undiagnosed or unreported.
Efforts are being made to improve surveillance, diagnosis, and treatment of brucellosis in order to better understand its epidemiology and reduce its impact on public health.
Brucellosis in animals
Brucellosis not only affects humans but also has a significant impact on animals, particularly livestock. Infected animals may experience a variety of symptoms, including abortion or stillbirth in pregnant females, decreased milk production, and infertility in males. The economic consequences of brucellosis in animals can be significant, as it can lead to financial losses for farmers and agricultural industries.
It is important to recognize the zoonotic potential of brucellosis, meaning it can be transmitted from animals to humans. This highlights the importance of controlling brucellosis in animals through measures such as vaccination, testing, and culling of infected animals.
Control measures for brucellosis in animals may vary depending on the specific circumstances and regulations of each country or region. Collaboration between veterinary and public health authorities is crucial to effectively manage and prevent the spread of brucellosis in animals.
Current Research on Brucellosis
Research on brucellosis is ongoing, aiming to improve our understanding of the disease and develop more effective diagnostic methods, treatment options, and preventive strategies. Some areas of current research include:
-
Development of new diagnostic methods: Researchers are exploring innovative approaches to detect and diagnose brucellosis more rapidly and accurately. This includes the use of advanced laboratory techniques and the development of point-of-care tests that can be used in resource-limited settings.
-
Alternative treatment options: While antibiotic therapy remains the mainstay of brucellosis treatment, researchers are investigating new drug candidates and treatment regimens to improve outcomes and reduce the duration of therapy. This is especially important in regions where antibiotic resistance is a growing concern.
-
Understanding the immune response: Researchers are studying the immune response to brucellosis in order to develop vaccines and immunotherapeutic approaches. By understanding how the body’s immune system interacts with the Brucella bacteria, they hope to develop novel strategies to prevent or treat the infection.
By continuing to invest in research and collaboration, we can make strides in our fight against brucellosis and improve the lives of both humans and animals affected by this infectious disease.