In this article, you will gain a deeper understanding of what hyperglycemia is and the causes and symptoms associated with it. Hyperglycemia, or high blood sugar, is a condition that can affect anyone, whether diagnosed with diabetes or not. By exploring the factors that contribute to this condition and recognizing the signs and symptoms, you will be equipped with valuable knowledge to take control of your health. So, let’s embark on this informative journey together and unravel the mysteries behind hyperglycemia.
Understanding Hyperglycemia: Causes and Symptoms
Hyperglycemia is a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels in the body. It occurs when the body is unable to properly regulate the amount of sugar (glucose) in the bloodstream. This can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, medication side effects, stress, and illness. It is important to understand the causes and symptoms of hyperglycemia in order to properly manage and treat the condition.
Definition of Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia is defined as a condition in which there is an abnormally high concentration of glucose (sugar) in the bloodstream. In a healthy individual, the body maintains normal blood sugar levels by utilizing insulin, a hormone produced by the pancreas. However, in individuals with hyperglycemia, the body either does not produce enough insulin or is unable to effectively utilize it, leading to elevated blood sugar levels.
Hyperglycemia vs Hypoglycemia
It is important to distinguish between hyperglycemia and hypoglycemia, as they are two different conditions with opposite effects on blood sugar levels. Hyperglycemia refers to high blood sugar levels, while hypoglycemia refers to low blood sugar levels. Both conditions can have serious consequences if left untreated, but their causes and treatment approaches differ.

Causes of Hyperglycemia
Hyperglycemia can be caused by various factors, the most common being diabetes. There are three main types of diabetes: type 1 diabetes, type 2 diabetes, and gestational diabetes. In type 1 diabetes, the body does not produce insulin, while in type 2 diabetes, the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin. Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and usually resolves after childbirth. Other causes of hyperglycemia include medication side effects, stress, illness, insulin pump failure, and uncontrolled blood sugar levels.
Type 1 Diabetes
Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disease in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys the insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. As a result, the body is unable to produce insulin, leading to high blood sugar levels. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in childhood or adolescence, and individuals with this condition require daily insulin injections or the use of an insulin pump to manage their blood sugar levels.

Type 2 Diabetes
Type 2 diabetes is the most common form of diabetes, accounting for approximately 90% of all diabetes cases. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to the effects of insulin or fails to produce enough insulin to properly regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes is often associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, physical inactivity, and poor diet choices. Treatment for type 2 diabetes may involve lifestyle modifications, oral medications, or insulin therapy, depending on the severity of the condition.
Gestational Diabetes
Gestational diabetes occurs during pregnancy and affects approximately 10% of pregnant women. It is caused by hormonal changes that affect insulin production and utilization in the body. Gestational diabetes usually resolves after childbirth and does not necessarily indicate that the woman will develop diabetes in the future. However, it is important to properly manage blood sugar levels during pregnancy to prevent complications for both the mother and the baby.

Medication Side Effects
Certain medications, such as corticosteroids and antipsychotics, can cause elevated blood sugar levels as a side effect. This is particularly common in individuals without diabetes, but it can also occur in those with pre-existing diabetes. If you are taking any medications and notice symptoms of hyperglycemia, it is important to consult your healthcare provider to determine if the medication is the cause and discuss potential alternatives.
Stress and Illness
Both physical and emotional stress can contribute to hyperglycemia. During periods of stress, the body releases stress hormones that can raise blood sugar levels. Illnesses, particularly infections, can also lead to temporary spikes in blood sugar levels. It is important to be mindful of your stress levels and take measures to manage stress effectively, as well as to properly manage your blood sugar levels during illness.

Insulin Pump Failure
For individuals with type 1 diabetes who rely on insulin pumps for insulin delivery, pump failure can result in elevated blood sugar levels. This can occur due to technical malfunctions, such as blockages or leaks in the pump, or user error, such as forgetting to change the infusion set or properly monitor blood sugar levels. It is crucial to regularly check and maintain the functionality of your insulin pump to avoid potential complications associated with hyperglycemia.
Uncontrolled Blood Sugar Levels
Failure to properly manage and control blood sugar levels can lead to persistent hyperglycemia. This can occur in individuals with diabetes who do not adhere to their prescribed treatment plan, including medication, diet, and exercise recommendations. Uncontrolled blood sugar levels can have serious long-term consequences, including damage to the blood vessels, nerves, and organs. It is essential for individuals with diabetes to work closely with their healthcare team to develop a comprehensive and personalized management plan.
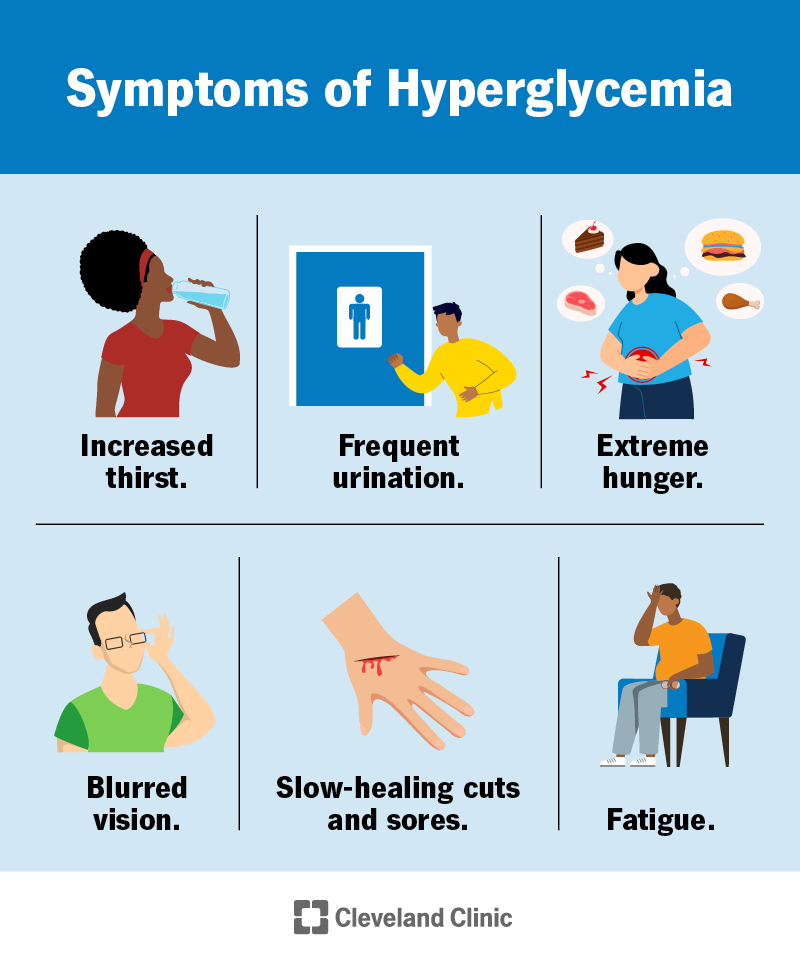
Symptoms of Hyperglycemia
The symptoms of hyperglycemia can vary depending on the severity of the condition. Common symptoms include increased thirst and urination, fatigue, blurred vision, frequent infections, slow healing, unexplained weight loss, and ketoacidosis.
Increased Thirst and Urination
Excessive thirst, also known as polydipsia, is a common symptom of hyperglycemia. When blood sugar levels are high, the body tries to eliminate the excess sugar through increased urine production, leading to increased urination, also known as polyuria. If you notice that you are urinating more frequently and experiencing intense thirst, it is important to monitor your blood sugar levels and consult your healthcare provider if necessary.
Fatigue
Persistent fatigue is another common symptom of hyperglycemia. When blood sugar levels are high, the body is unable to effectively utilize glucose for energy, leading to feelings of tiredness and lethargy. If you find yourself constantly feeling exhausted despite adequate rest, it could be a sign of elevated blood sugar levels and should be addressed with your healthcare provider.
Blurred Vision
High blood sugar levels can cause changes in the shape of the lens of the eye, leading to blurred vision. This symptom usually resolves once blood sugar levels are brought under control. If you notice sudden changes in your vision, it is important to have your eyes checked by an optometrist or ophthalmologist to rule out any underlying eye conditions.
Frequent Infections
Hyperglycemia weakens the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to infections. High blood sugar levels provide an optimal environment for bacteria and fungi to thrive, leading to frequent infections, particularly urinary tract infections, skin infections, and yeast infections. If you find that you are experiencing recurrent infections, it may be a sign of uncontrolled blood sugar levels and should be discussed with your healthcare provider.
Slow Healing
Elevated blood sugar levels can impair the body’s ability to heal wounds and injuries. This is due to the fact that high levels of sugar in the bloodstream can damage blood vessels and affect the delivery of essential nutrients and oxygen to the affected area. If you notice that cuts, bruises, or other wounds are slow to heal, it may indicate poorly controlled blood sugar levels and should be addressed with your healthcare provider.
Weight Loss
Unexplained weight loss can be a symptom of hyperglycemia, particularly in individuals with type 1 diabetes. When blood sugar levels are high, the body is unable to properly utilize glucose for energy and begins to break down fat and muscle tissue for fuel, leading to weight loss. If you are experiencing rapid and unexplained weight loss, it is important to consult your healthcare provider to determine the underlying cause.
Ketoacidosis
Ketoacidosis is a potentially life-threatening complication of hyperglycemia, particularly in individuals with type 1 diabetes. It occurs when the body does not have enough insulin to utilize glucose for energy and begins to break down fat for fuel instead. This process produces toxic ketones as a byproduct, which can build up in the bloodstream and cause a dangerous imbalance in the body’s pH levels. Symptoms of ketoacidosis include nausea, vomiting, abdominal pain, rapid breathing, and fruity-smelling breath. If you experience these symptoms, it is important to seek immediate medical attention.
Diagnostic Tests for Hyperglycemia
If you are experiencing symptoms of hyperglycemia or are at risk for the condition due to factors such as family history or obesity, your healthcare provider may recommend diagnostic tests to assess your blood sugar levels. The most common test is the fasting plasma glucose test, which measures your blood sugar level after an overnight fast. Other tests, such as the oral glucose tolerance test and the hemoglobin A1C test, may also be conducted to provide a comprehensive assessment of your glucose metabolism.
In conclusion, hyperglycemia is a condition characterized by elevated blood sugar levels and can be caused by various factors, including diabetes, medication side effects, stress, and illness. It is important to be aware of the symptoms of hyperglycemia, such as increased thirst, fatigue, blurred vision, frequent infections, slow healing, weight loss, and ketoacidosis. If you experience these symptoms or are at risk for hyperglycemia, it is crucial to consult your healthcare provider for proper diagnosis and treatment. Managing and controlling blood sugar levels is essential for long-term health and well-being.