Jaundice is a common medical condition that affects many individuals around the world, causing their skin and eyes to turn yellow. This article aims to provide you with a clear understanding of jaundice, including its causes, symptoms, and possible treatment options. By delving into the various factors that contribute to this condition, we hope to give you a comprehensive overview that will help you recognize the signs, seek appropriate medical attention, and take necessary steps towards a healthier life. So, let’s dig into the fascinating world of jaundice together!

What is Jaundice?
Definition
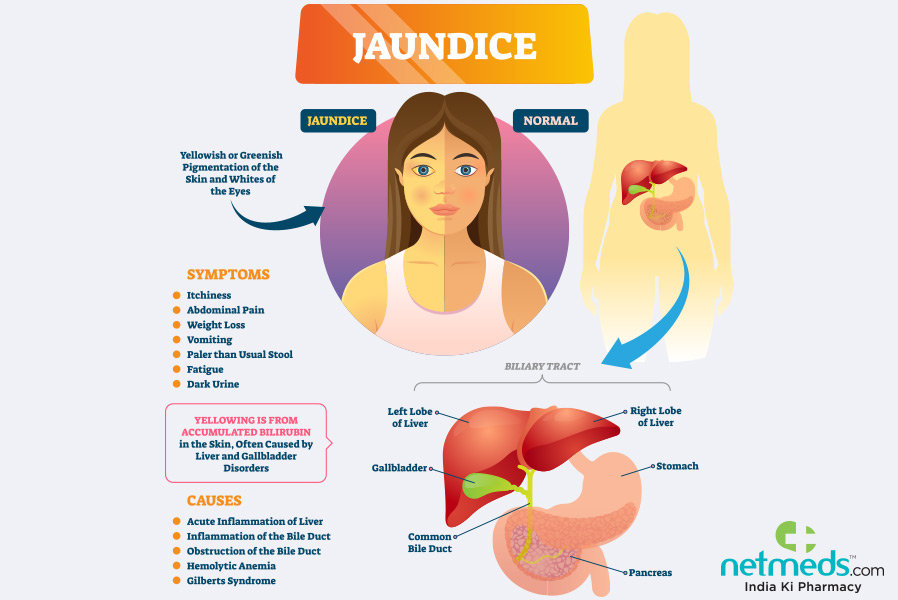
Jaundice is a medical condition characterized by the yellowing of the skin and eyes. It occurs when there is an excess of bilirubin, a yellow pigment produced during the breakdown of red blood cells, in the body. Jaundice can be a symptom of an underlying health problem or a condition in itself. It is important to understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for jaundice to ensure proper care and management.
Types of Jaundice
There are three main types of jaundice:
-
Prehepatic Jaundice: This type of jaundice occurs before the bilirubin reaches the liver. It is typically caused by excessive breakdown of red blood cells or certain genetic disorders.
-
Hepatic Jaundice: Hepatic jaundice is caused by liver conditions that prevent the proper metabolism and excretion of bilirubin. This can include liver disease, hepatitis, cirrhosis, or alcohol-related liver damage.
-
Posthepatic Jaundice: Posthepatic jaundice, also known as obstructive jaundice, happens when the bile ducts become blocked, preventing the flow of bile from the liver to the intestines. This can be caused by gallstones, tumors, or other factors.
Causes of Jaundice
Liver Conditions
Various liver conditions can lead to jaundice. These include hepatitis (inflammation of the liver), liver cirrhosis (scarring of the liver), alcoholic liver disease, and liver cancer. These conditions interfere with the liver’s ability to process bilirubin and may cause it to accumulate in the body.
Blood Disorders
Certain blood disorders, such as hemolytic anemia or sickle cell disease, can result in increased red blood cell breakdown. As a result, more bilirubin is produced, overwhelming the liver’s capacity to remove it efficiently. This can lead to the development of jaundice.
Bile Duct Problems
Obstruction or inflammation of the bile ducts can prevent the normal flow of bile from the liver to the intestines. This can be caused by gallstones, tumors, infections, or strictures. When bile cannot be properly excreted, bilirubin accumulates in the body, causing jaundice.
Other Causes
Jaundice can also be caused by factors unrelated to the liver, blood, or bile ducts. These include viral infections, such as mononucleosis or cytomegalovirus (CMV), certain medications or toxins, autoimmune diseases, genetic conditions, and pregnancy-related factors.

Symptoms of Jaundice
Yellowing of the Skin and Eyes
The most notable symptom of jaundice is the yellowing of the skin and whites of the eyes. This occurs due to the accumulation of bilirubin in the body and is often the first sign that something is wrong.
Dark Urine
Jaundice can cause the urine to appear dark or tea-colored. This change in urine color is a result of the excess bilirubin being excreted through the kidneys.
Pale Stools
Another common symptom of jaundice is pale or clay-colored stools. This happens when the liver is unable to properly process bilirubin, resulting in a lack of the normal brown color in the stools.
Fatigue
Many individuals with jaundice experience extreme fatigue and weakness. This can be due to the underlying liver dysfunction or the body’s response to the accumulation of bilirubin.
Abdominal Pain
In some cases, jaundice may be accompanied by abdominal pain or discomfort. This can occur if the underlying cause of jaundice is related to liver inflammation, gallstones, or other abdominal conditions.
Nausea and Vomiting
Jaundice can also cause nausea and vomiting, particularly if the liver dysfunction is severe. These symptoms can be a result of the accumulation of toxins in the body.
Diagnosing Jaundice
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, a healthcare provider will examine the skin and eyes for signs of yellowing. They may also feel the abdomen to check for any abnormalities or tenderness.
Blood Tests
Blood tests are crucial in diagnosing the underlying cause of jaundice. These tests measure the levels of bilirubin, liver enzymes, and other markers that can indicate liver or gallbladder dysfunction.
Liver Function Tests
Liver function tests help assess how well the liver is functioning. These tests measure the levels of various enzymes and proteins that are produced by the liver. Abnormal results can provide insights into the cause and severity of jaundice.
Imaging Tests
Imaging tests, such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs, may be ordered to evaluate the liver, bile ducts, and gallbladder. These tests can help identify any obstructions, tumors, or other structural abnormalities that may be causing jaundice.

Complications of Jaundice
Liver Damage
If left untreated, jaundice can lead to further liver damage, potentially progressing to liver failure. Proper management of the underlying cause of jaundice is essential to prevent long-term complications.
Malnutrition
Jaundice can interfere with the absorption and digestion of nutrients, leading to malnutrition. Adequate nutritional support and dietary adjustments are essential to maintain optimal health during jaundice recovery.
Fluid and Electrolyte Imbalances
In severe cases of jaundice, there may be imbalances in fluid and electrolyte levels in the body. This can be due to inadequate fluid intake, excessive fluid loss, or impaired kidney function. Monitoring and correction of these imbalances are important for overall well-being.
Treatment of Jaundice
Treating the Underlying Cause
The treatment of jaundice depends on the underlying cause. For example, if jaundice is caused by hepatitis, antiviral medications may be prescribed. If it is due to bile duct obstruction, surgery or other interventions may be necessary.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms, reduce liver inflammation, or support liver function. These can include antiviral drugs, anti-inflammatory medications, or medications to improve bile flow.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is a common treatment for newborns with jaundice. It involves exposing the baby’s skin to special lights that help break down the excess bilirubin.
Surgery
In certain cases, surgical intervention may be required to address underlying causes of jaundice. This can include procedures to remove gallstones or repair bile duct obstructions.

Preventing Jaundice
Vaccinations
Some forms of jaundice, such as hepatitis, can be prevented through immunization. Vaccinations for hepatitis A and B are available and can significantly reduce the risk of developing these viral infections.
Health and Hygiene
Practicing good hygiene, such as frequent handwashing, can help prevent the spread of infections that can lead to jaundice. Avoiding contact with contaminated blood or bodily fluids is also important for preventing viral hepatitis.
When to See a Doctor
Seek Medical Attention if:
- You experience persistent yellowing of the skin and eyes
- You have dark urine and pale stools
- You develop severe abdominal pain or persistent nausea and vomiting
- You have unexplained fatigue and weakness
Emergency Situations
If jaundice is accompanied by symptoms such as confusion, severe abdominal pain, difficulty breathing, or bleeding, seek immediate medical attention. These may indicate a serious complication that requires urgent care.
Lifestyle Management for Jaundice
Dietary Considerations
During jaundice recovery, it is important to follow a balanced diet that supports liver health. This includes consuming adequate proteins, vitamins, and minerals while limiting the intake of fatty and processed foods.
Avoiding Alcohol
Alcohol can further damage the liver and exacerbate the symptoms of jaundice. It is essential to avoid alcohol completely during jaundice recovery to promote optimal liver function.
Exercise and Physical Activity
Regular exercise can help improve liver function and overall health. Engaging in moderate physical activity, such as walking or swimming, can be beneficial during jaundice recovery. However, it is important to consult a healthcare provider before starting any exercise regimen.
Stress Management
Stress can negatively impact liver function and overall well-being. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help promote relaxation and support recovery.
Support and Coping
Taking Care of Mental Health
Dealing with jaundice can be emotionally challenging. It is important to prioritize mental health during this time. Seeking support from loved ones, engaging in hobbies, and seeking professional help if needed, can all contribute to better mental well-being.
Joining Support Groups
Joining support groups for individuals with liver conditions or jaundice can provide valuable emotional support and a sense of community. Connecting with others who have similar experiences can offer guidance and reassurance throughout the journey of recovery.