In this informative article, you will explore the various types of burns and gain a deeper understanding of their characteristics and treatments. From first-degree burns that affect the outer layer of skin, to second-degree burns that penetrate deeper and may cause blistering, and finally, third-degree burns that can result in permanent tissue damage, each type presents unique challenges and requires different approaches for effective healing. By familiarizing yourself with these different types of burns, you will be better equipped to recognize and respond to burn injuries with confidence and care.
Understanding the Different Types of Burns

Introduction
Burns can happen to anyone, at any time, and can be caused by various factors. Understanding the different types of burns is crucial for proper treatment and prevention. In this article, we will provide an overview of burns, classify them into different degrees, and discuss the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for each degree.
Overview of Burns
A burn is a type of injury caused by heat, chemicals, electricity, or radiation. It damages the skin and can affect deeper tissues as well. Burns are classified into four degrees: first-degree, second-degree, third-degree, and fourth-degree. The severity and required treatment differ based on the degree of the burn.

Classification of Burns
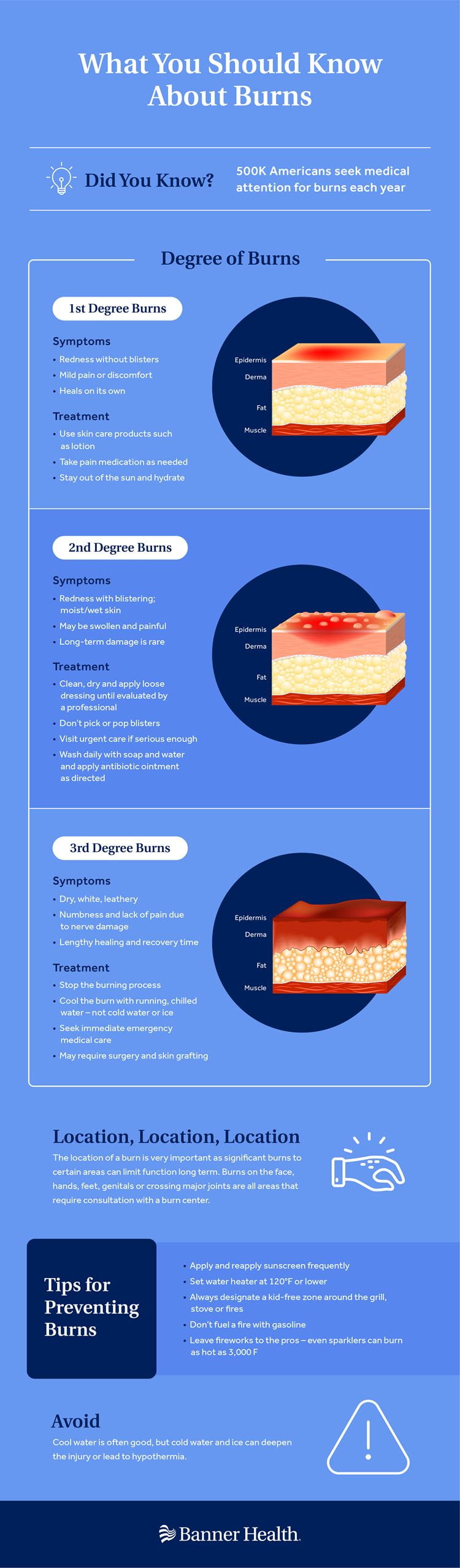
Burns are categorized into four degrees:
First-Degree Burns
First-degree burns, also known as superficial burns, only affect the outer layer of the skin. They are characterized by redness, mild pain, and slight swelling. Sunburn is a common example of a first-degree burn.
Causes of First-Degree Burns
First-degree burns are commonly caused by exposure to heat from hot liquids, steam, hot objects, or prolonged sun exposure without protection.
Symptoms of First-Degree Burns
The symptoms of first-degree burns typically include redness, mild pain, and slight swelling. The affected area may feel tender to the touch.

Treatment for First-Degree Burns
First-degree burns typically heal on their own within a week. However, you can provide immediate relief by cooling the burn with cold water or a cold compress. Applying aloe vera gel or an over-the-counter burn ointment can also help soothe the pain and promote healing. It is important to keep the burn clean and avoid popping any blisters that may form.
Second-Degree Burns
Second-degree burns, also known as partial-thickness burns, extend beyond the outer layer of the skin and may involve the deeper layers. They are characterized by redness, intense pain, blistering, and swelling.

Causes of Second-Degree Burns
Second-degree burns can be caused by contact with hot liquids, flames, chemicals, or prolonged exposure to sunburn. Additionally, electrical burns can also result in second-degree burns.
Symptoms of Second-Degree Burns
Symptoms of second-degree burns include intense pain, redness, blistering, swelling, and the formation of clear or whitish fluid-filled blisters. The affected area may appear moist, shiny, and weeping.
Treatment for Second-Degree Burns
For second-degree burns, it is important to seek medical attention. In the meantime, you can start emergency treatment by applying cold water or a cold compress to the burn to cool it down. Avoid using ice or very cold water, as it can further damage the skin. Do not pop any blisters. Over-the-counter burn ointments and antibiotic creams may be recommended by a healthcare professional to prevent infection. A non-stick dressing can also be applied to protect the burn.
Third-Degree Burns
Third-degree burns, also known as full-thickness burns, penetrate all layers of the skin and can extend to the underlying tissues. They are characterized by white or blackened skin, a leathery appearance, and a lack of sensation in the burned area due to nerve damage.
Causes of Third-Degree Burns
Third-degree burns are often caused by prolonged exposure to flames, hot objects, chemicals, or electricity. These burns can also occur as a result of second-degree burns that were not properly treated.
Symptoms of Third-Degree Burns
The symptoms of third-degree burns include white or blackened skin, a leathery appearance, a lack of sensation in the burned area, and the presence of exposed fat, muscle, or bone. These burns can be incredibly painful.
Treatment for Third-Degree Burns
Third-degree burns are considered a medical emergency, and immediate medical attention should be sought. While waiting for medical professionals, it is best to cover the burn with a cool, moist, sterile bandage. Do not apply ice or ointments to the burn. It is crucial to keep the victim warm and elevate the burnt area if possible. Pain management and intravenous fluids may be administered at the hospital. Skin grafting or other surgical procedures may be required for proper healing.
Fourth-Degree Burns
Fourth-degree burns are the most severe type of burn. These burns extend through all layers of the skin, underlying tissues, and reach the muscles and bones. The burned area may appear charred and can lead to permanent damage or loss of limbs.
Causes of Fourth-Degree Burns
Fourth-degree burns are usually caused by long-term exposure to electricity, severe chemical burns, or intense flames.
Symptoms of Fourth-Degree Burns
Symptoms of fourth-degree burns include charred or blackened skin, the involvement of deep tissues, muscle or bone exposure, and a lack of sensation due to extensive nerve damage.
Treatment for Fourth-Degree Burns
Fourth-degree burns are extremely serious and require immediate medical attention. The initial priority is to remove the victim from the source of the burn and call for emergency help. Do not attempt to treat the burn yourself. In the hospital, pain management, intravenous fluids, and surgical interventions may be necessary. Extensive rehabilitation and specialized medical care are often required for long-term recovery.
Conclusion
Understanding the different types of burns is essential for timely and appropriate treatment. Remember, first-degree burns can often be managed at home, while second, third, and fourth-degree burns require professional medical attention. Always prioritize seeking medical help in severe burn cases. Stay aware of potential burn hazards and take necessary precautions to prevent burns. Stay safe and protect yourself from burns!