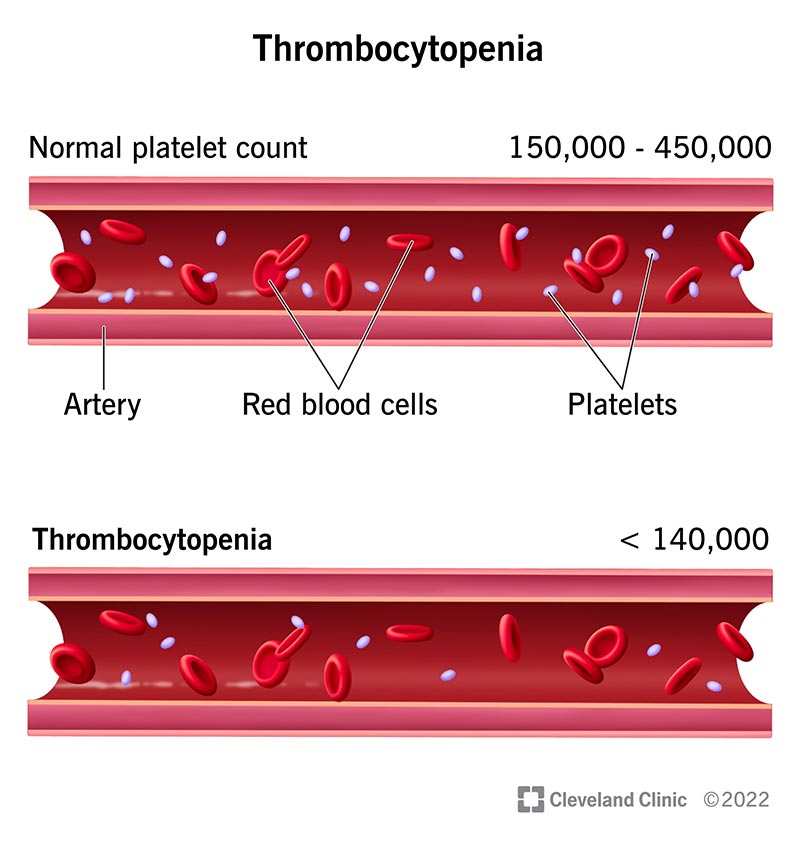
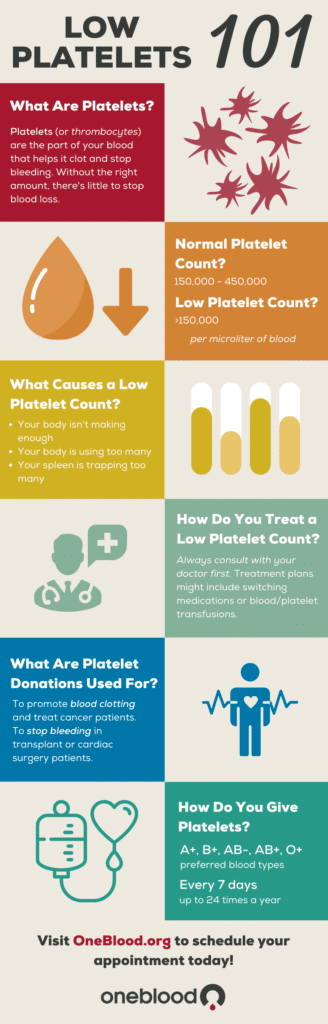
You have probably heard about the importance of blood platelets in your body, but did you know that low levels of these small cells can lead to complications? In this article, we will explore the potential problems that can arise from low blood platelets and discuss some preventative measures that you can take to keep them within a healthy range. So, grab your cup of tea and let’s dive into the world of blood platelets!
Managing Lifestyle Factors
Exercise regularly
Regular exercise is an essential lifestyle factor that can contribute to the management of low blood platelets. Engaging in physical activity on a consistent basis helps improve blood circulation, which can enhance platelet production and function. Activities such as brisk walking, jogging, swimming, and cycling are excellent options to consider. Aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week, or 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise.
Maintain a Healthy Weight
Maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for individuals with low blood platelets. Excess weight can strain the body, leading to various health complications, including platelet disorders. By adopting a balanced diet and engaging in regular exercise, you can achieve and maintain a healthy weight. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to develop a personalized weight management plan that suits your specific needs.
Avoid Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption
Smoking and excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on platelet function and overall health. These habits can impair platelet production, promote platelet destruction, and increase the risk of bleeding episodes. Quitting smoking and moderating your alcohol intake will greatly benefit your platelet count and reduce the risk of complications. Seek support from healthcare professionals, cessation programs, or counseling services to help you overcome these habits.
Eat a Balanced Diet
Consuming a well-balanced diet plays a vital role in managing low blood platelet levels. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats provides the body with the essential nutrients it needs for optimal platelet production and function. Include foods that are naturally high in vitamin K, such as leafy greens, broccoli, and asparagus, as this vitamin plays a role in blood clotting. Additionally, stay hydrated by drinking an adequate amount of water throughout the day.
Stay Hydrated
Staying hydrated is crucial for maintaining overall health and plays a role in managing low blood platelets. Proper hydration helps support blood circulation and ensures that platelets can efficiently fulfill their functions. Aim to drink at least eight glasses of water per day, and increase your fluid intake if you engage in strenuous activities or live in a hot climate. Avoid excessive consumption of sugary drinks and opt for water or other hydrating beverages instead.
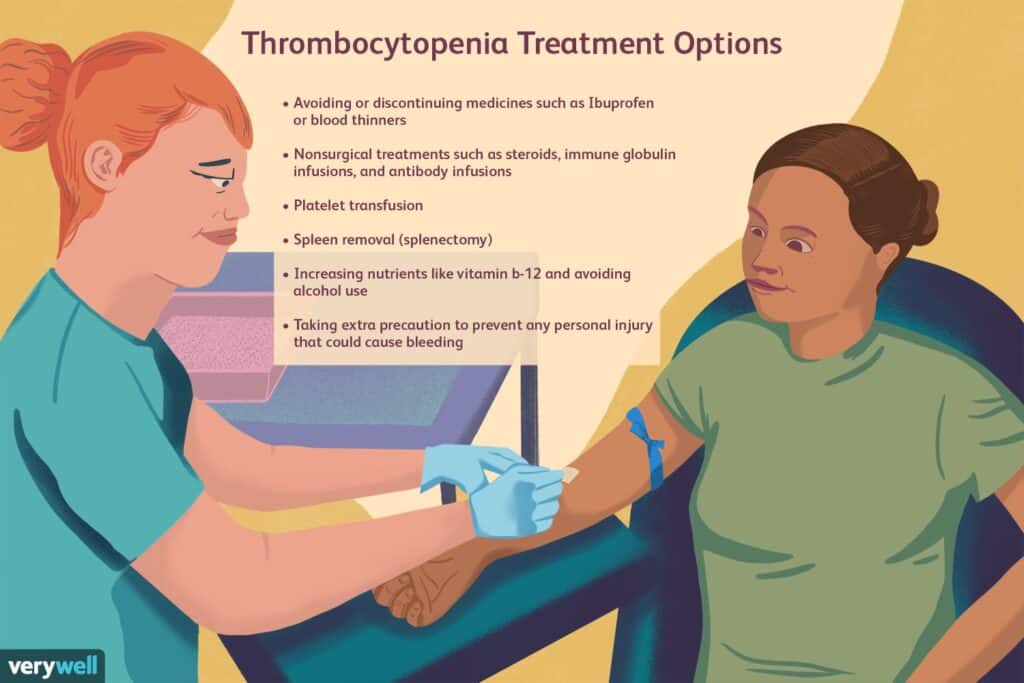
Medications and Treatments
Corticosteroids
Corticosteroids are commonly prescribed medications used to manage low blood platelet levels. These medications work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system, which can help prevent the destruction of platelets. The dosage and duration of corticosteroid therapy will be determined by your healthcare professional based on your specific condition and response to treatment. Regular monitoring is essential to ensure their effectiveness and detect any potential side effects.
Immune Globulin
For individuals with low blood platelets caused by an autoimmune disorder, immune globulin therapy may be recommended. Immune globulin consists of antibodies that can help regulate the immune system and prevent the destruction of platelets. This treatment can increase platelet counts and reduce the risk of bleeding. It is typically administered intravenously under the supervision of a healthcare professional.
Rituximab
Rituximab is a biologic medication that targets specific cells in the immune system, which may contribute to platelet destruction. It is often prescribed for individuals with chronic immune thrombocytopenia (ITP) that has not responded to other treatments. Rituximab therapy helps to modulate the immune response and increase platelet levels. It is administered intravenously over a course of several weeks and requires regular monitoring.
Thrombopoietin Receptor Agonists
Thrombopoietin receptor agonists are a newer class of medications used in the management of low blood platelets. These medications mimic the action of thrombopoietin, a hormone that stimulates platelet production in the bone marrow. By stimulating platelet production, thrombopoietin receptor agonists can help increase platelet counts and reduce the risk of bleeding. These medications are typically taken orally and require regular monitoring.

Managing Underlying Conditions
Treating Infections Promptly
Prompt treatment of infections is crucial for individuals with low blood platelet levels. Infections can further suppress platelet production and function, leading to an increased risk of bleeding. If you develop any signs or symptoms of an infection, such as fever, cough, or unusual discharge, seek medical attention promptly. Follow your healthcare professional’s recommendations for appropriate treatment, which may include antibiotics or antiviral medications.
Controlling Autoimmune Diseases
Autoimmune diseases can contribute to low blood platelet levels by causing the immune system to mistakenly attack and destroy platelets. Effectively managing autoimmune diseases is essential for maintaining platelet counts within a healthy range. Work closely with your healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan that includes medications, lifestyle modifications, and regular monitoring to keep your autoimmune condition under control.
Addressing Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies, particularly deficiencies in vitamins and minerals, can have an impact on platelet production and function. It is essential to identify and address any nutritional deficiencies you may have through dietary changes or supplementation. For example, iron deficiency can lead to decreased platelet counts, so consuming iron-rich foods or taking iron supplements may be necessary. Consult with a healthcare professional or a registered dietitian to determine any necessary dietary modifications or supplements.
Managing Liver or Kidney Problems
Liver or kidney problems can affect platelet production and function, leading to low platelet levels. It is crucial to manage these underlying conditions to support healthy platelet counts. Work closely with your healthcare professional to develop a treatment plan tailored to your specific condition. This may include medications, lifestyle changes, and regular monitoring to ensure the health of these vital organs and promote optimal platelet function.
Avoiding Triggers and Risks
Minimize Exposure to Toxins and Chemicals
Toxins and chemicals present in the environment can have adverse effects on platelet production and function. Minimizing your exposure to such substances is important in managing low blood platelet levels. Avoid smoking, limit your contact with household and industrial chemicals, and make an effort to choose natural and organic products whenever possible. Taking these precautions can help reduce the risk of complications and promote overall health.
Protect Against Injuries and Trauma
Individuals with low blood platelet levels are at an increased risk of bleeding and bruising. Taking measures to protect yourself against injuries and trauma is crucial. Use caution when engaging in physical activities and avoid contact sports or activities that may pose a higher risk of injury. Wear protective gear, such as helmets and knee pads, when necessary. By prioritizing your safety and minimizing the risk of physical trauma, you can reduce the likelihood of bleeding complications.
Avoid Certain Medications
Certain medications can interfere with platelet function or contribute to a decrease in platelet counts. It is important to consult with your healthcare professional about the potential impact of any medications you are currently taking on your platelet levels. They can provide guidance on whether alternative medications or dosage adjustments are necessary to manage your condition effectively. Never stop or modify any medication without first consulting with a healthcare professional.
Prevent Infections
Infections can have detrimental effects on low blood platelet levels and overall health. Taking steps to prevent infections is essential. Practice good hygiene, such as frequently washing your hands with soap and water, using hand sanitizers when necessary, and avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick. Stay up-to-date with vaccinations, as they can help protect you against certain infectious diseases. By adopting these preventive measures, you can reduce the risk of infections and their impact on your platelet levels.
Regular Medical Monitoring
Routine Blood Tests
Regular blood tests are necessary to monitor your platelet counts and overall health. Your healthcare professional will determine the frequency of these blood tests based on your specific condition and treatment plan. Monitoring your platelet counts allows healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of any treatments and detect any potential complications or changes in your condition promptly. Stay consistent with your scheduled appointments and follow any recommended blood testing protocols.
Monitoring Symptoms
Being aware of and monitoring any symptoms related to your low blood platelet levels is essential. Symptoms such as easy bruising, prolonged bleeding from minor cuts, nosebleeds, or petechiae (small red or purple spots on the skin) should be promptly reported to your healthcare professional. Regularly assessing and communicating any changes or new symptoms will allow your healthcare team to evaluate and address your condition effectively.
Tracking Platelet Count
In addition to routine blood tests, tracking your own platelet count can provide valuable information about the effectiveness of your treatment and alert you to any changes. Your healthcare professional will guide you on how to monitor your platelet count at home, such as with a portable device or logbook. Being proactive in tracking your platelet count and sharing this information with your healthcare team can help optimize your treatment plan and ensure your platelet levels remain within a safe range.
Scheduling Regular Check-ups
Regular check-ups with your healthcare professional are vital for managing low blood platelets. During these appointments, your platelet counts and overall health will be evaluated, and any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan can be made. Additionally, regular check-ups provide an opportunity to discuss any concerns or questions you may have about your condition or treatment. Be proactive in scheduling and attending these appointments to stay on top of your platelet health.
Emergency Preparedness
Educate Yourself and Others
Educating yourself and those around you about your low blood platelet condition is crucial for emergency preparedness. Make sure you understand the signs of bleeding or other complications and know how to respond in an emergency. Educate your family members, friends, and close contacts about your condition and teach them how to administer first aid or seek medical assistance if needed. By spreading awareness and knowledge, you can create a supportive network that can help in times of emergency.
Wear a Medical Alert Bracelet
Wearing a medical alert bracelet is a simple yet effective way to communicate your low blood platelet condition to healthcare professionals in case of an emergency. These bracelets typically include important medical information, such as your diagnosis, medications, and emergency contacts. In an emergency situation where you may not be able to communicate, the medical alert bracelet provides critical information that can help guide appropriate medical treatment.
Keep Emergency Contact Information Handy
In the event of an emergency, having immediate access to your emergency contact information is essential. Ensure that your emergency contacts are readily available, both in your phone’s contact list and written down in a visible location, such as on your fridge or in your wallet. This information will enable healthcare professionals or individuals assisting you to quickly reach out to your designated emergency contacts and update them on your condition.
Carrying a Personal Medical File
Creating and carrying a personal medical file can be immensely helpful in emergency situations. This file should include relevant medical documents, such as your diagnosis, treatment plan, current medications, and any allergies you may have. Additionally, include a list of your healthcare team’s contact information and any other important medical information. Having this file readily accessible can ensure that healthcare professionals have the necessary information to provide you with the appropriate care.
Natural Remedies and Supplements
Vitamin C and Antioxidants
Vitamin C and antioxidants play a crucial role in maintaining overall health and supporting platelet function. Foods rich in vitamin C include citrus fruits, berries, kiwi, and leafy greens. Additionally, antioxidant-rich foods such as dark chocolate, berries, and green tea can provide additional support. However, it is important to consult with your healthcare professional or a registered dietitian before starting any new supplements or drastically changing your diet to ensure they are appropriate for your specific health needs.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Omega-3 fatty acids have anti-inflammatory properties and are known to support heart health and overall well-being. These essential fatty acids can be found in fatty fish (such as salmon and sardines), flaxseeds, chia seeds, and walnuts. If you are considering omega-3 supplements, consult with your healthcare professional for personalized guidance on dosage and potential interactions with any medications you may be taking.
Probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support gut health and immune function. Maintaining a healthy gut microbiome is important for overall well-being, including optimal platelet function. Probiotics can be found in fermented foods such as yogurt, kefir, sauerkraut, and kimchi. If you are considering probiotic supplements, consult with your healthcare professional to determine the appropriate strain and dosage for your specific needs.
Herbal Supplements
Certain herbal supplements have been traditionally used to support platelet health and overall immune function. Examples include ginseng, astragalus, and herbs rich in flavonoids, such as bilberry and grape seed extract. However, it is essential to approach herbal supplements with caution and consult with a healthcare professional before starting any herbal regimen, as they may interact with medications or have side effects. Herbal supplements should be used under the guidance of a knowledgeable healthcare professional.
Essential Oils
Some essential oils, such as frankincense, helichrysum, and lavender, are believed to possess anti-inflammatory and immune-boosting properties that may support platelet health. However, it is important to note that essential oils should be used with caution and under the guidance of a qualified aromatherapist or healthcare professional. Essential oils are highly concentrated substances and may have interactions or sensitivities that vary from person to person.
Preventing Bleeding Complications
Avoiding Injuries and Falls
Individuals with low blood platelets are at an increased risk of bleeding and bruising. Therefore, taking preventive measures to avoid injuries and falls is crucial. Be mindful of your surroundings, remove tripping hazards in your living spaces, and use caution when engaging in physical activities or walking on slippery surfaces. By being proactive and minimizing the risk of physical trauma, you can greatly reduce the likelihood of bleeding complications.
Use Soft-Bristle Toothbrushes
Using a soft-bristle toothbrush is recommended for individuals with low blood platelets. Soft-bristle toothbrushes are less likely to cause gum irritation or bleeding, which can be a concern for individuals with reduced platelet counts. Additionally, brush gently and avoid aggressive or vigorous toothbrushing. Consult with your dentist for personalized recommendations on toothbrushes, dental care techniques, and any other necessary precautions for maintaining good oral health.
Avoid Harsh Contact Sports or Activities
Participating in contact sports or engaging in activities with an increased risk of physical impact can lead to injuries and bleeding complications in individuals with low blood platelets. It is advisable to avoid contact sports or other high-risk activities that may put you at risk of trauma. Instead, opt for low-impact exercises or recreational activities that minimize the risk of injury while still promoting physical fitness and overall well-being.
Taking Precautions During Menstruation
Menstruation can pose challenges for individuals with low blood platelets, as it increases the risk of heavy bleeding. Taking precautions during menstruation is important to manage this risk. Use sanitary products that suit your specific needs, such as pads or tampons with appropriate absorbency. Consult with your healthcare professional if you experience excessive or prolonged bleeding during your menstrual cycle, as they may recommend specific interventions or treatments to manage this concern.

Maintaining Good Oral Health
Brushing and Flossing Regularly
Maintaining good oral health is essential for individuals with low blood platelets, as oral bleeding can be a common manifestation of this condition. Brush your teeth at least twice a day using a soft-bristle toothbrush and fluoride toothpaste. Floss daily to remove plaque and food debris from between the teeth and along the gumline. Maintaining good oral hygiene practices can help prevent oral infections, gum disease, and reduce the risk of oral bleeding.
Using a Mouthwash
Using a mouthwash as part of your daily oral hygiene routine can provide additional protection against oral infections and help control plaque buildup. Opt for an alcohol-free mouthwash to minimize the risk of oral irritation or bleeding. Consult with your dentist or healthcare professional for personalized recommendations on mouthwash products that are suitable for your specific needs.
Regular Dental Check-ups and Cleanings
Regular dental check-ups and professional cleanings are crucial for maintaining good oral health and managing low blood platelet levels. During these visits, your dentist will assess your oral health, detect any signs of infection or gum disease, and provide appropriate treatment. These routine appointments also provide an opportunity for your dentist to educate you on specific oral hygiene techniques and make recommendations based on your unique needs.
Psychological Support
Coping Strategies
Coping with the challenges of managing low blood platelet levels can be emotionally challenging. Developing effective coping strategies is crucial for maintaining overall well-being. This may include techniques such as deep breathing exercises, meditation, journaling, or engaging in hobbies that promote relaxation and stress reduction. Reach out to mental health professionals or support groups for additional guidance and support in developing coping strategies that work best for you.
Support Groups
Connecting with others who share similar experiences can provide valuable support and understanding. Joining support groups, whether in-person or online, allows you to connect with individuals who are managing low blood platelet levels and can offer advice, share experiences, and provide emotional support. These groups can help you navigate the challenges of your condition and provide a sense of community.
Therapy or Counseling
Individuals managing low blood platelet levels may experience emotional distress or anxiety related to their condition. Engaging in therapy or counseling can provide a safe space to explore and address these emotions. Mental health professionals with experience in chronic illness or health-related concerns can help you develop strategies to manage stress, depression, or anxiety associated with your condition.
Social Activities and Hobbies
Participating in social activities and engaging in hobbies can promote overall well-being and provide a sense of normalcy and enjoyment. Connect with friends and loved ones, participate in activities you enjoy, and make time for hobbies that bring you fulfillment. Engaging in social interactions and pursuing your passions can have a positive impact on your mental health and overall quality of life.
In conclusion, managing low blood platelets involves a multifaceted approach that encompasses lifestyle factors, medications and treatments, managing underlying conditions, avoiding triggers and risks, regular medical monitoring, emergency preparedness, natural remedies and supplements, preventing bleeding complications, maintaining good oral health, and seeking psychological support. By implementing these strategies and working closely with healthcare professionals, individuals with low blood platelets can optimize their health, minimize complications, and enhance their overall well-being.