Living with Vulval Cancer can be a challenging and overwhelming experience, but with the right support and knowledge, you can navigate through it with courage and resilience. This article sheds light on the realities of living with vulval cancer, providing insights into the emotional and physical aspects of the disease, while offering practical tips on managing symptoms and finding a strong support system. Whether you are a patient, a caregiver, or simply seeking to understand this condition better, this article aims to empower you with information and compassion as you embark on this journey.
Understanding Vulval Cancer
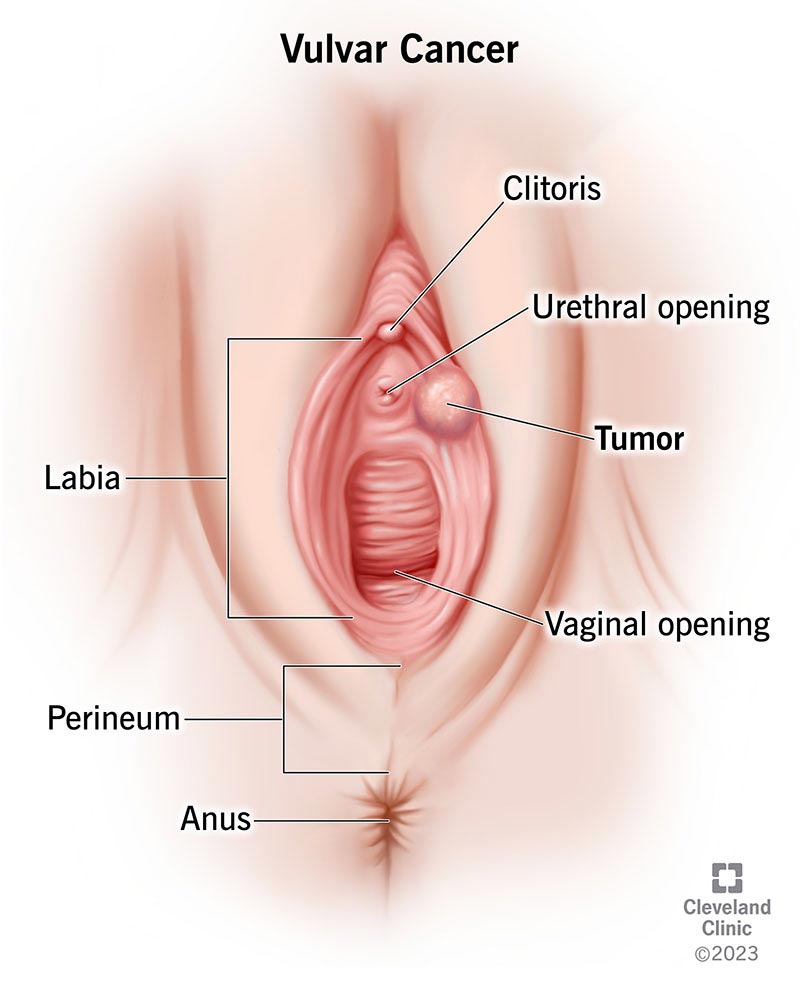
Vulval cancer is a type of cancer that affects the external female genitalia, specifically the vulva. The vulva consists of the labia majora, labia minora, clitoris, vaginal opening, and the area between the vagina and anus. This type of cancer is relatively rare, but it is essential to understand its causes, symptoms, and treatment options to ensure timely diagnosis and appropriate management.
What is vulval cancer?
Vulval cancer refers to the abnormal growth of cells in the vulva. It can affect women of all ages but is more common in older women. The most common type of vulval cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, which accounts for approximately 90% of cases. Other less common types include basal cell carcinoma, melanoma, adenocarcinoma, and verrucous carcinoma.
Types of vulval cancer
As mentioned earlier, the most common type of vulval cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, which arises from the flat cells that cover the surface of the vulva. Basal cell carcinoma originates from the lower layers of the epidermis and is less aggressive. Melanoma, a type of skin cancer, can also develop on the vulva, as well as adenocarcinoma, which begins in the glandular tissue. Verrucous carcinoma is a rare type of vulval cancer that grows slowly and is less likely to spread.
Causes of vulval cancer
The exact cause of vulval cancer is unknown, but several factors are believed to contribute to its development. One of the primary risk factors is infection with certain types of human papillomavirus (HPV), particularly HPV types 16 and 18. Other risk factors include smoking, chronic vulval skin conditions, a weakened immune system, and a history of precancerous vulval lesions. It is important to note that having these risk factors does not guarantee the development of vulval cancer, but they may increase the chances.
Signs and symptoms of vulval cancer
Early detection of vulval cancer is crucial for successful treatment. It is essential to be aware of the signs and symptoms so that prompt medical attention can be sought. Common symptoms include persistent itching, pain, tenderness, a lump or swelling in the vulva, bleeding that is not related to menstruation, open sores or ulcers, and changes in the color or thickness of the skin of the vulva. If you notice any of these symptoms, it is important to consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
Diagnosis and Staging
Screening for vulval cancer
Currently, there is no specific screening test available for the early detection of vulval cancer. However, routine gynecological examinations can help identify any abnormalities in the vulva and prompt further investigation if necessary. Regular check-ups with a healthcare professional are essential for the prevention and early detection of various health conditions, including vulval cancer.
Diagnostic tests
If vulval cancer is suspected, a healthcare professional may recommend various diagnostic tests to confirm the diagnosis. These tests may include a biopsy, where a small sample of tissue from the vulva is taken for examination under a microscope. Imaging tests such as ultrasound, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), or computed tomography (CT) scan may also be performed to determine the extent of the cancer.
Determining the stage of vulval cancer
Staging is an important aspect of the diagnostic process as it helps determine the treatment options and prognosis. The stage of vulval cancer is determined by the size and location of the tumor, as well as whether it has spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. There are four main stages (I, II, III, and IV) that indicate the extent of the cancer and guide treatment decisions.
Treatment Options
Surgery
Surgery is the primary treatment for vulval cancer and aims to remove the cancerous tissue while preserving as much healthy tissue as possible. The specific surgical procedure will depend on the stage and location of the cancer. In early-stage vulval cancer, a wide local excision may be performed to remove the tumor and a small margin of healthy tissue. In more advanced cases, a radical vulvectomy may be necessary, which involves removing more extensive areas of the vulva and nearby tissues.
Radiation therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy beams to kill cancer cells and shrink tumors. It may be used before surgery to reduce the size of the tumor or after surgery to destroy any remaining cancer cells. External beam radiation therapy is the most common type used for vulval cancer, where radiation is delivered from outside the body. In some cases, internal radiation therapy, also known as brachytherapy, may be used, where a radioactive implant is placed near the tumor.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body. It is often used in combination with surgery or radiation therapy to treat vulval cancer that has spread to nearby lymph nodes or distant organs. Systemic chemotherapy is administered through the veins or taken orally and can have systemic side effects due to its impact on healthy cells as well.
Immunotherapy
Immunotherapy is a newer treatment option for vulval cancer that aims to stimulate the body’s immune system to recognize and destroy cancer cells. Monoclonal antibodies are specific proteins that can target certain cancer cells, and they may be used in combination with other treatments. Immunotherapy can have different side effects compared to traditional chemotherapy, and it is important to discuss potential benefits and risks with a healthcare professional.
Palliative care
Palliative care focuses on providing relief from pain and symptoms, improving the quality of life, and offering support to patients and their families. It is an essential component of vulval cancer treatment, especially for advanced or recurrent cases. Palliative care can be provided alongside curative treatments and can help manage treatment side effects, provide emotional support, and assist with decision-making.
Managing Side Effects
Surgical side effects
Like any surgical procedure, surgery for vulval cancer can have side effects. These can include pain, swelling, bruising, and temporary difficulty in urination or bowel movements. In some cases, lymphedema, a condition characterized by swelling in the legs or genital area, may also occur. It is important to closely follow the post-operative care instructions provided by the healthcare professionals and report any unusual symptoms or concerns.
Radiation side effects
Radiation therapy for vulval cancer can cause skin changes in the treated area, such as redness, dryness, and itching. Fatigue, vaginal dryness or narrowing, and changes in bowel or bladder function may also occur. These side effects are usually temporary and can be managed with the help of a healthcare team. It is crucial to communicate any discomfort or distress experienced during radiation therapy to ensure appropriate support and management.
Chemotherapy side effects
Chemotherapy drugs can have various side effects, which may vary depending on the specific drugs used and individual factors. Common side effects may include fatigue, nausea and vomiting, hair loss, decreased appetite, and increased risk of infection. It is important to discuss potential side effects with the healthcare team and seek appropriate support and management strategies.
Emotional effects
A diagnosis of vulval cancer can have emotional impacts, and it is perfectly normal to feel a range of emotions such as fear, anxiety, sadness, or anger. It is essential to address these emotions and seek emotional support from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals. Open communication, maintaining a positive outlook, and implementing stress-reducing techniques like meditation or counseling can help cope with the emotional effects of vulval cancer.

Living with Vulval Cancer
Coping with emotions
A diagnosis of vulval cancer can be overwhelming, and it is crucial to find healthy and effective ways to cope with the emotional challenges that arise. Engaging in activities that bring joy and relaxation, such as hobbies, exercise, or spending time with loved ones, can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being. It is also beneficial to seek support from mental health professionals or support groups to share experiences, concerns, and emotions with individuals who understand the journey.
Support from loved ones
Having a strong support system can make a significant difference in coping with vulval cancer. Family, friends, and loved ones can offer emotional support, accompany you to medical appointments, and provide practical assistance during treatment and recovery. Open communication is vital to express needs and concerns, and loved ones can also benefit from educational resources to better understand the challenges faced and provide informed support.
Sexuality and intimacy
Vulval cancer and its treatment can have a significant impact on a person’s sexuality and intimate relationships. Physical changes, such as scarring or loss of genital sensation, as well as emotional and body image concerns, can affect sexual function and desire. It is essential to have open and honest communication with your partner and healthcare team to address these concerns and explore ways to maintain intimacy and sexual satisfaction, such as counseling, education, or alternative techniques.
Making lifestyle adjustments
Living with vulval cancer may require making adjustments to daily routines and lifestyle choices. It is essential to prioritize self-care, including maintaining a nutritious diet, engaging in regular physical activity as advised by healthcare professionals, and getting proper rest. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can also help in coping with the challenges of vulval cancer.
Addressing financial concerns
Vulval cancer treatment and ongoing care can be accompanied by significant financial costs. It is important to discuss financial concerns with the healthcare team to explore potential resources or financial assistance programs available. Additionally, reaching out to financial advisors or organizations specializing in cancer-related financial support can help alleviate financial stress and allow for a more focused approach on treatment and recovery.
Fertility and Pregnancy
Fertility preservation options
Vulval cancer and its treatments can have implications for fertility and may impact the ability to conceive naturally. It is crucial to have open discussions with healthcare professionals regarding fertility preservation options before starting treatment. Techniques such as egg or embryo freezing can be explored to preserve fertility for future family planning. Each case is unique, and personalized guidance from healthcare professionals specializing in fertility preservation is essential.
Pregnancy considerations
For women who have been treated for vulval cancer and wish to become pregnant, careful consideration is required. It is advisable to consult with healthcare professionals to assess the impact of previous treatments and determine the best approach for pregnancy planning and monitoring. Close monitoring during pregnancy is essential to ensure the well-being of both mother and baby.

Follow-Up Care and Survivorship
Regular check-ups
After completing treatment for vulval cancer, regular follow-up appointments with healthcare professionals are vital. These appointments may include physical exams, imaging tests, and screenings to monitor for any signs of recurrence or new cancer development. The frequency and duration of follow-up appointments may vary depending on individual factors, treatment modalities, and healthcare professional recommendations.
Managing long-term effects
Vulval cancer and its treatments can have long-term effects that require ongoing management and support. Possible long-term effects may include lymphedema, sexual or urinary function changes, or emotional adjustments. Working closely with healthcare professionals, including specialists such as physical therapists, sexual health counselors, or mental health professionals, can help in managing these long-term effects and improving overall quality of life.
Support for survivors
Survivorship support is crucial in helping individuals navigate life after vulval cancer. Support can be found through community organizations, support groups, or online platforms dedicated to cancer survivorship. These resources provide opportunities to connect with others who have experienced similar journeys, share experiences, and find comfort in knowing that you are not alone. Healthcare professionals can also provide guidance and information on survivorship resources.
Alternative Therapies and Complementary Medicine
Exploring alternative therapies
Some individuals may choose to explore alternative therapies alongside conventional treatments for vulval cancer. These therapies can include acupuncture, massage, herbal supplements, or dietary changes. While some alternative therapies may offer benefits in symptom management or overall well-being, it is important to discuss these options with healthcare professionals to ensure they are safe and do not interfere with conventional treatments.
Complementary approaches
Complementary medicine refers to practices that are used alongside conventional medical treatments. These can include techniques such as relaxation exercises, meditation, or yoga, which can help manage stress, alleviate side effects, and support overall well-being. It is crucial to inform healthcare professionals about any complementary approaches you are considering to ensure they are integrated safely and effectively into your care plan.

Research and Clinical Trials
Advancements in vulval cancer research
Advancements in medical research continue to enhance our understanding of vulval cancer and its management. Ongoing studies aim to identify new treatment options, improve diagnostic techniques, and enhance the overall outcomes for individuals diagnosed with vulval cancer. Staying informed about current research developments through reputable sources or discussions with healthcare professionals may provide insights into emerging treatment options or clinical trials.
Participating in clinical trials
Clinical trials are an essential aspect of medical research and provide opportunities to access innovative treatments or interventions. Participating in a clinical trial can contribute to medical knowledge and potentially offer individuals with vulval cancer access to cutting-edge treatments. It is important to discuss clinical trial options with healthcare professionals to determine whether participation is suitable, considering individual factors such as stage of cancer, overall health, and treatment goals.
Conclusion
Understanding vulval cancer, its types, causes, and treatment options is vital for individuals diagnosed with this rare form of cancer. Early detection, accurate diagnosis, and appropriate treatment are essential for favorable outcomes. Managing side effects, coping with emotions, and seeking support from loved ones and healthcare professionals can help individuals navigate the challenges of living with and beyond vulval cancer. Research advancements and participation in clinical trials continue to contribute to improved treatment options and outcomes, offering hope for the future.