Hey there! Have you ever wondered what hyperthyroidism is all about? Well, wonder no more! In this informative article, we’re going to uncover the causes, symptoms, and treatments of hyperthyroidism. So, whether you’ve recently been diagnosed with this condition or just want to know more about it, we’ve got you covered. Let’s get started!
What is Hyperthyroidism?
Hyperthyroidism is a condition in which the thyroid gland becomes overactive and produces an excessive amount of thyroid hormones. The thyroid gland, located in the front of your neck, plays a vital role in regulating various bodily functions. It produces hormones that control metabolism, heart rate, and body temperature, among other things. When the thyroid gland becomes hyperactive, it can lead to a range of symptoms and health complications.
Definition of hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism is a medical condition characterized by the excessive production of thyroid hormones. The condition causes the body’s metabolism to speed up, leading to symptoms such as weight loss, rapid heartbeat, and anxiety.
Function of the thyroid gland
The thyroid gland secretes hormones that play a crucial role in regulating various bodily functions. These hormones, known as thyroxine (T4) and triiodothyronine (T3), control metabolism, growth, and development. They also affect heart rate, body temperature, and energy levels. The thyroid gland is regulated by the pituitary gland, which produces thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) to maintain the balance of thyroid hormones in the body.
Causes of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can be caused by several factors, including underlying medical conditions and lifestyle choices. Understanding the causes can help determine the most appropriate treatment plan.
Graves’ disease
Graves’ disease is the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. It is an autoimmune disorder in which the body’s immune system mistakenly attacks the thyroid gland, leading to the overproduction of thyroid hormones. Graves’ disease is more common in women and often runs in families.
Thyroiditis
Thyroiditis is inflammation of the thyroid gland, which can lead to temporary hyperthyroidism. This condition can occur after a viral infection or during the postpartum period. In some cases, thyroiditis may cause hypothyroidism initially, followed by a phase of hyperthyroidism.
Toxic nodular goiter
Toxic nodular goiter refers to the presence of one or more nodules in the thyroid gland that produce excess thyroid hormones. These nodules can be noncancerous (benign) or cancerous (malignant). The exact cause of toxic nodular goiter is not well understood, but it is more common in older individuals.
Excessive iodine intake
Iodine is an essential nutrient for thyroid function. However, excessive intake of iodine through diet, supplements, or medications can lead to hyperthyroidism. This is particularly true in individuals with underlying thyroid conditions.
Certain medications
Some medications, such as amiodarone (used to treat heart rhythm disorders) and interferon-alpha (used to treat certain types of cancer and viral infections), can interfere with thyroid function and cause hyperthyroidism.

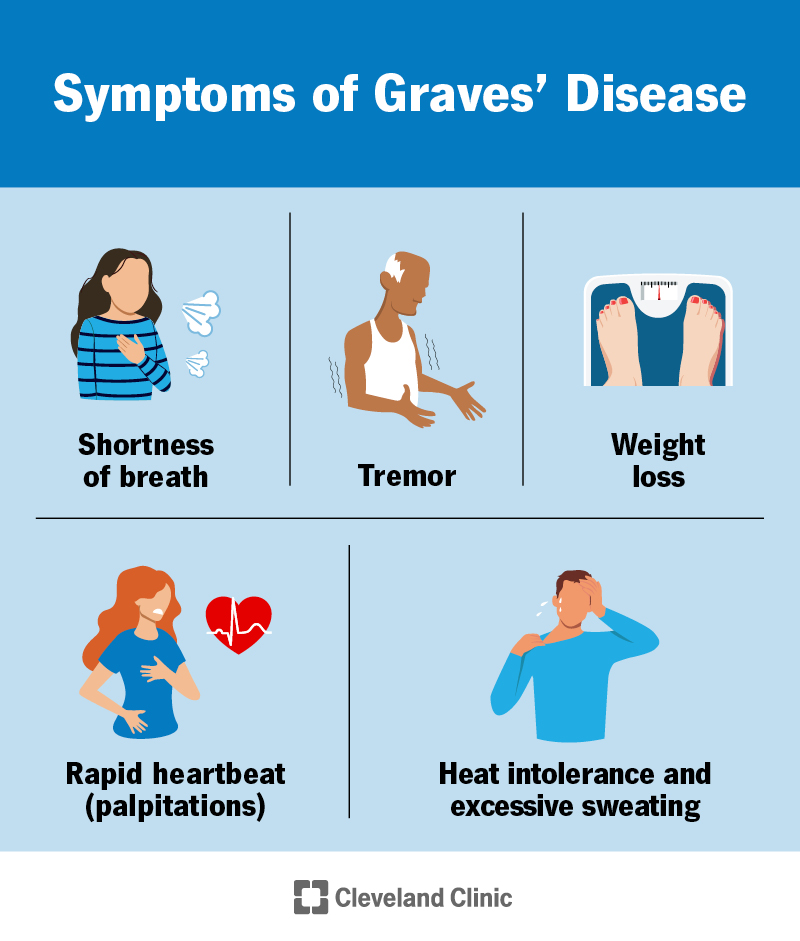
Symptoms of Hyperthyroidism
Hyperthyroidism can cause a wide range of symptoms, as the excessive thyroid hormones affect various systems in the body. Recognizing these symptoms is important for early diagnosis and treatment.
Increased metabolism
An increased metabolic rate is a hallmark symptom of hyperthyroidism. This means that your body burns calories at a faster rate than usual, resulting in unintended weight loss. You may find it difficult to maintain or gain weight, despite an increased appetite.
Weight loss
Unexplained weight loss is a common symptom of hyperthyroidism. The increased metabolism caused by excess thyroid hormones leads to the breakdown of body fat and muscle tissue. Additionally, hyperthyroidism can affect the digestive system, leading to increased bowel movements and diarrhea, further contributing to weight loss.
Rapid heartbeat
Hyperthyroidism can cause a rapid heart rate, even at rest. This symptom, known as tachycardia, occurs due to the increased production of thyroid hormones, which stimulate the heart to beat faster. You may also experience palpitations, a sensation of fluttering or pounding in the chest.
Anxiety and irritability
Hyperthyroidism can have a profound impact on your mood and mental wellbeing. Excess thyroid hormones can cause heightened anxiety, irritability, and restlessness. You may experience difficulty concentrating or feel easily overwhelmed by stressors.
Heat intolerance
Individuals with hyperthyroidism often have an increased sensitivity to heat. This can manifest as excessive sweating, feeling hot or flushed, and an intolerance to warm environments. You may notice that you feel uncomfortable in situations where others feel perfectly fine.
Tremors or trembling hands
Hand tremors are a common symptom of hyperthyroidism. The excess thyroid hormones can affect the central nervous system, leading to involuntary muscle movements. This can be particularly noticeable in the hands, causing trembling or shaking that can interfere with fine motor skills.
Diagnosis of Hyperthyroidism
Diagnosing hyperthyroidism involves a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, physical examination, and laboratory tests. An accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining the underlying cause and developing an appropriate treatment plan.
Physical examination
During a physical examination, your doctor will assess your overall health and look for physical signs of hyperthyroidism. This may include examining your neck for an enlarged thyroid gland (goiter) and assessing your heart rate and blood pressure.
Blood tests
Blood tests are an essential component of the diagnostic process for hyperthyroidism. These tests measure the levels of thyroid hormones (T3 and T4) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) in your blood. High levels of thyroid hormones and low levels of TSH indicate hyperthyroidism.
Radioactive iodine uptake test
In some cases, a radioactive iodine uptake test may be necessary to determine the cause of hyperthyroidism. This test involves the ingestion or injection of a small dose of radioactive iodine, followed by measurements of its uptake by the thyroid gland. Different patterns of iodine uptake can provide valuable information about the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism.
Thyroid scan
A thyroid scan is often performed alongside the radioactive iodine uptake test. This imaging test uses a special camera to visualize the structure and function of the thyroid gland. It can help identify abnormalities such as nodules or areas of increased or decreased activity.

Complications of Hyperthyroidism
If left untreated or poorly managed, hyperthyroidism can lead to various complications that affect different organs and systems in the body. Recognizing and addressing these potential complications is crucial for maintaining overall health.
Cardiovascular problems
Hyperthyroidism can put strain on the cardiovascular system, increasing the risk of developing heart-related complications. These may include high blood pressure, rapid or irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), and an increased risk of developing cardiovascular diseases such as heart failure or atrial fibrillation.
Osteoporosis
Excess thyroid hormones can lead to accelerated bone loss, increasing the risk of osteoporosis. Osteoporosis is a condition characterized by weakened bones that are more prone to fractures. It is especially concerning for postmenopausal women, who already have an increased risk of developing osteoporosis.
Eye problems
In some cases of hyperthyroidism, the immune system can mistakenly attack the tissues around the eyes, leading to a condition called Graves’ ophthalmopathy or thyroid eye disease. This can cause symptoms such as bulging eyes (exophthalmos), dryness, redness, and swelling around the eyes, double vision, and decreased eye movement.
Thyroid storm
Thyroid storm is a rare but life-threatening complication of hyperthyroidism. It occurs when there is a sudden and severe exacerbation of hyperthyroid symptoms, leading to extreme physiological distress. Symptoms may include high fever, severe rapid heartbeat, confusion, agitation, and even organ failure. Immediate medical attention is necessary if thyroid storm is suspected.
Treatment Options for Hyperthyroidism
The treatment of hyperthyroidism depends on the underlying cause, the severity of symptoms, and individual factors. Several treatment options are available, each with its own benefits and considerations. A healthcare professional will help determine the most appropriate treatment plan for you.
Anti-thyroid medications
Anti-thyroid medications work by reducing the production and release of thyroid hormones from the thyroid gland. These medications, such as methimazole and propylthiouracil, are often prescribed for individuals with mild to moderate hyperthyroidism or as a temporary treatment before other interventions.
Radioactive iodine therapy
Radioactive iodine therapy involves the oral ingestion of radioactive iodine, which is selectively taken up by the overactive thyroid gland. The radiation destroys the thyroid tissue, reducing hormone production. This treatment is commonly recommended for individuals with Graves’ disease or toxic nodular goiter.
Beta blockers
Beta blockers are medications that block the effects of adrenaline, reducing the symptoms of hyperthyroidism such as rapid heartbeat, tremors, and anxiety. While beta blockers do not address the underlying cause of hyperthyroidism, they can provide symptomatic relief and improve quality of life.
Surgery
In some cases, surgery may be necessary to remove a portion or the entire thyroid gland. This is often recommended when other treatment options are not suitable or have failed to control hyperthyroidism. Surgery may also be considered if there is a concern of cancerous nodules or when the thyroid gland is significantly enlarged.

Managing Hyperthyroidism
In addition to medical treatments, there are several strategies and lifestyle modifications that can help manage hyperthyroidism and improve overall well-being.
Lifestyle modifications
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle is important for managing hyperthyroidism. This includes getting regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, and managing stress levels. Regular physical activity can help reduce anxiety and promote overall cardiovascular health. A well-balanced diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins, provides essential nutrients needed for optimal thyroid function. Managing stress through techniques such as meditation, deep breathing exercises, or engaging in hobbies can help maintain hormonal balance.
Regular medical follow-ups
Regular follow-up appointments with your healthcare provider are important for monitoring your progress, adjusting treatment as needed, and assessing for any potential complications. They can also provide guidance on lifestyle modifications and answer any questions or concerns you may have. Staying proactive and engaged in your healthcare ensures optimal management of hyperthyroidism.
Stress management
Managing stress is crucial for individuals with hyperthyroidism, as stress can exacerbate symptoms and impact overall well-being. Finding healthy stress management techniques that work for you, such as practicing mindfulness or engaging in hobbies, can help reduce anxiety and promote a sense of calm.
Dietary considerations
While there is no specific diet for hyperthyroidism, certain dietary considerations can support overall health and thyroid function. This includes avoiding excessive consumption of iodine-rich foods, such as seaweed, iodized salt, and seafood, as they can aggravate hyperthyroidism. Consuming a variety of nutrient-rich foods and maintaining a balanced diet is essential for supporting thyroid health and overall well-being.
Natural Remedies for Hyperthyroidism
While natural remedies cannot cure hyperthyroidism, some individuals find them helpful as complementary approaches to conventional treatments. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any natural remedies, as they may interact with medications or exacerbate underlying medical conditions.
Herbs and supplements
Certain herbs and supplements may have potential benefits for individuals with hyperthyroidism. These include bugleweed, lemon balm, motherwort, and ashwagandha. However, the effectiveness and safety of these remedies may vary, and some may have adverse effects or interact with medications. It is important to discuss the use of herbs and supplements with a healthcare provider.
Mind-body practices
Mind-body practices such as yoga, meditation, and deep breathing exercises can help manage stress and promote overall well-being. These practices can have a calming effect on the nervous system, reducing anxiety and promoting a sense of balance. Incorporating mind-body practices into your routine can complement conventional treatments for hyperthyroidism.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is an ancient Chinese practice that involves the insertion of thin needles into specific points on the body. Some individuals find acupuncture helpful for managing symptoms of hyperthyroidism, such as anxiety and palpitations. However, more research is needed to understand its effectiveness and mechanisms of action in the context of hyperthyroidism.
Limiting exposure to environmental toxins
Exposure to environmental toxins, such as heavy metals or chemicals, can potentially affect thyroid function. Minimizing exposure to toxins by using natural cleaning products, choosing organic foods when possible, and ensuring good air quality in your home can support thyroid health. Additionally, avoiding cigarette smoke and other sources of secondhand smoke is essential, as smoking can worsen thyroid function.

Hyperthyroidism during Pregnancy
Hyperthyroidism can present unique challenges during pregnancy and requires careful management to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and baby.
Adverse effects on pregnancy
Uncontrolled hyperthyroidism during pregnancy can increase the risk of complications, such as preterm birth, low birth weight, preeclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), and fetal thyroid dysfunction. It is essential for pregnant individuals with hyperthyroidism to receive appropriate medical care and closely monitor their thyroid hormone levels.
Management strategies
Treatment options for pregnant individuals with hyperthyroidism may differ from those for non-pregnant individuals due to the potential risks to the developing fetus. Antithyroid medications, such as propylthiouracil, are often the primary treatment choice during pregnancy. Close monitoring of thyroid hormone levels and regular prenatal care are essential for optimal management.
Monitoring and care
Pregnant individuals with hyperthyroidism require close monitoring throughout their pregnancy. This may involve regular blood tests to assess thyroid hormone levels, monitoring fetal growth, and evaluating any potential complications. Working closely with a healthcare team that includes an obstetrician and endocrinologist specialized in managing thyroid disorders is imperative for ensuring the health of both mother and baby.
Prevention of Hyperthyroidism
While it may not be possible to prevent all cases of hyperthyroidism, there are certain steps one can take to reduce the risk or minimize the impact of the condition.
Avoiding excessive iodine intake
Excessive iodine intake is a risk factor for hyperthyroidism, particularly in individuals with underlying thyroid conditions. It is important to be mindful of iodine intake from dietary sources and to avoid overconsumption of iodine-rich supplements or medications, unless specifically recommended by a healthcare provider.
Quitting smoking
Smoking has been associated with an increased risk of developing Graves’ disease, the most common cause of hyperthyroidism. Quitting smoking is not only beneficial for thyroid health but also for overall health and well-being.
Managing stress
Stress has been linked to the development and exacerbation of various health conditions, including hyperthyroidism. Finding effective stress management techniques, such as mindfulness, exercise, or seeking support from a therapist, can help reduce the impact of stress on your health.
Regular thyroid check-ups
Regularly monitoring thyroid function through routine check-ups with a healthcare provider can help detect any abnormalities or changes in thyroid hormone levels. This is particularly important for individuals with a family history of thyroid disorders or those at an increased risk of developing hyperthyroidism.
In conclusion, hyperthyroidism is a condition that requires attention and appropriate management to minimize its impact on overall health and well-being. By understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and seeking timely medical care, individuals with hyperthyroidism can take steps towards a healthier and more balanced life. Working closely with a healthcare professional and adopting lifestyle modifications can help individuals effectively manage hyperthyroidism and maintain optimal thyroid health.