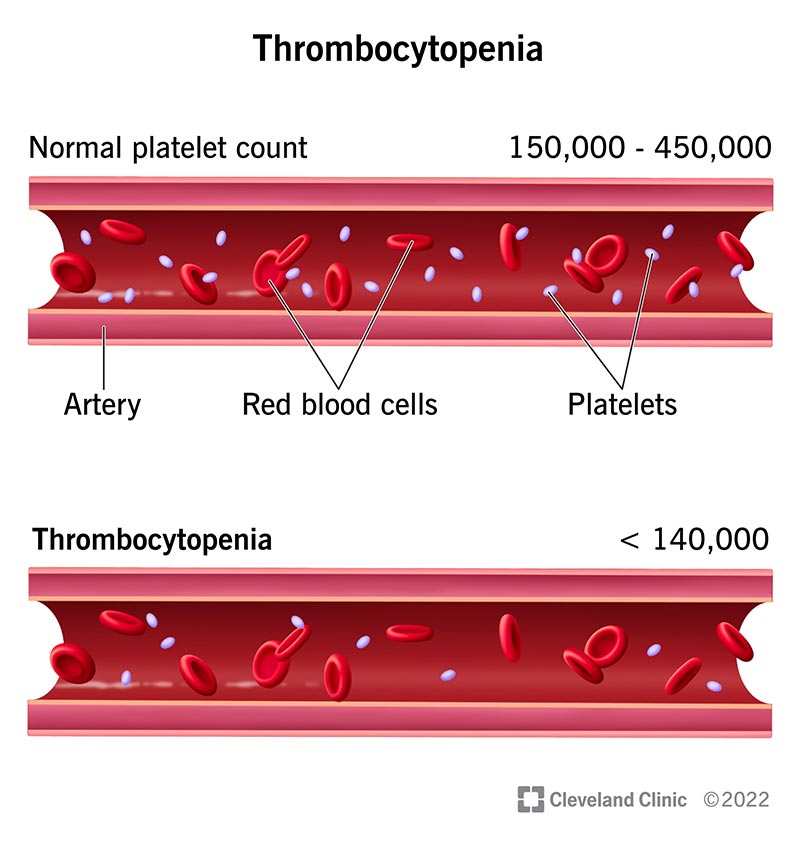
Having low blood platelets can cause various health concerns that you should be aware of. In this article, we will explore the essential information you need to know about low blood platelets. From the potential causes and symptoms to the available treatment options, we aim to provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this condition. So, whether you or someone you know is dealing with low blood platelets, stay tuned to gain valuable insights that can help you navigate through this aspect of your health.

Causes of Low Blood Platelets
Low blood platelets, also known as thrombocytopenia, can be caused by a variety of factors. Understanding these causes can help you better understand and manage your condition.
Idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
ITP is a condition where the immune system mistakenly attacks and destroys platelets in the body. This can result in low platelet levels and an increased risk of bleeding. The exact cause of ITP is unknown, but it is thought to be related to abnormal immune function.
Viral infections
Certain viral infections, such as hepatitis C, HIV, and Epstein-Barr virus, can cause low blood platelet counts. These viruses can affect the production and function of platelets, leading to decreased levels.
Bacterial infections
Similar to viral infections, bacterial infections can also contribute to low platelet counts. Infections such as sepsis and certain types of bacterial endocarditis can disrupt the normal production and survival of platelets in the body.
Medications
Some medications, including certain antibiotics, anticonvulsants, and diuretics, can cause a decrease in platelet production or function. It’s important to discuss any medications you are taking with your healthcare provider to determine if they may be contributing to your low platelet count.
Toxin exposure
Exposure to certain toxins, such as pesticides or certain chemicals, can damage the bone marrow where platelets are produced. This can result in decreased platelet counts and an increased risk of bleeding.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause changes in blood composition, including a decrease in platelet counts. This is often considered a normal physiological response to pregnancy, but it can still present risks, especially during delivery.
Alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can have detrimental effects on the body, including disrupting the normal production and function of platelets. Chronic alcohol abuse can lead to a decrease in platelet counts and increased bleeding risk.
Autoimmune disorders
Some autoimmune disorders, such as lupus and rheumatoid arthritis, can cause the immune system to mistakenly attack platelets, resulting in low platelet counts.
Blood disorders
Certain blood disorders, such as leukemia and aplastic anemia, can affect the production and survival of platelets. These conditions can lead to a decrease in platelet counts and an increased risk of bleeding.
Chemotherapy
The use of chemotherapy drugs to treat cancer can have a negative impact on the bone marrow, where platelets are produced. This can result in a decrease in platelet counts and an increased risk of bleeding.
Symptoms of Low Blood Platelets
Detecting the symptoms of low blood platelets early on is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Be aware of the following signs and symptoms:
Easy bruising
One of the most common signs of low platelet count is easy bruising. Even minor bumps or injuries can result in significant bruising due to the decreased ability of the blood to clot properly.
Frequent nosebleeds
Low platelet levels can cause frequent or recurring nosebleeds. These nosebleeds may be spontaneous or triggered by minor trauma, and they can be difficult to stop.
Petechiae
Petechiae are pinpoint-sized, reddish-purple spots that appear on the skin. They occur when small blood vessels leak, and they can be a sign of low platelet count.
Excessive bleeding
Bleeding that takes longer than usual to stop is another symptom of low platelet count. This can include prolonged bleeding from cuts, as well as heavy or prolonged menstrual periods in women.
Fatigue
Low blood platelet count can contribute to fatigue and weakness. Platelets play a crucial role in blood clotting, and their deficiency can lead to internal bleeding and anemia, resulting in tiredness.
Heavy menstrual periods
Women with low platelet count may experience heavy menstrual periods. This can be a result of abnormal blood clotting and increased bleeding during menstruation.
Blood in urine or stool
A low platelet count can lead to blood in the urine or stool. This can be a sign of internal bleeding, which should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Prolonged bleeding from cuts
If you notice that cuts or wounds take longer than usual to stop bleeding, it may be an indication of low platelet count. It’s important to seek medical attention if you experience this symptom.

Diagnosis of Low Blood Platelets
To determine if you have low blood platelets, your healthcare provider will perform a series of diagnostic tests. These tests will help them assess your platelet count and identify any underlying causes.
Medical history and physical examination
Your healthcare provider will begin by taking a detailed medical history and performing a physical examination. They will ask about your symptoms, any medications you are taking, and any previous medical conditions that may be relevant.
Complete blood count (CBC) test
A complete blood count (CBC) is a common blood test used to measure the number of platelets, red blood cells, and white blood cells in your body. A low platelet count may indicate thrombocytopenia.
Blood smear
A blood smear is a test in which a small sample of your blood is examined under a microscope. This allows your healthcare provider to assess the size, shape, and number of platelets present.
Bone marrow biopsy
In some cases, a bone marrow biopsy may be necessary to evaluate the production and function of platelets. This involves taking a small sample of bone marrow from the hipbone or sternum and examining it under a microscope.
Additional tests
Depending on the results of the initial tests, additional tests may be performed to identify underlying causes of low platelet count. These may include tests for autoimmune disorders, viral or bacterial infections, or clotting disorders.
Treatment for Low Blood Platelets
The treatment for low blood platelets will depend on the underlying cause and the severity of your condition. Here are some common treatment options:
Treating the underlying cause
If a specific underlying cause is identified, such as an infection or medication, treating or removing that cause may help improve your platelet count.
Medications
Your healthcare provider may prescribe medications to help increase platelet production or decrease platelet destruction. These may include corticosteroids, immunoglobulins, or immune-suppressing medications.
Platelet transfusion
In severe cases of low platelet count, a platelet transfusion may be necessary. This involves receiving donated platelets to increase your platelet count quickly.
Splenectomy
In some cases, the spleen may be removing platelets from the bloodstream, leading to low platelet counts. If this is the case, your healthcare provider may recommend a splenectomy, which involves removing the spleen.
Immune globulin therapy
Immune globulin therapy involves receiving intravenous infusions of immunoglobulins, which can help boost platelet levels and decrease platelet destruction.
Lifestyle changes
Making certain lifestyle changes, such as avoiding excessive alcohol consumption and maintaining a healthy diet and exercise routine, can help improve your overall health and potentially increase platelet levels.
Prevention of Low Blood Platelets
While it may not always be possible to prevent low blood platelets, there are some steps you can take to reduce your risk. Here are some preventative measures to consider:
Avoiding excessive alcohol consumption
Excessive alcohol consumption can contribute to low platelet counts. By avoiding or limiting alcohol intake, you can help maintain healthy platelet levels.
Avoiding certain medications
If you are at risk for low platelet counts, it’s important to discuss any medications you are taking with your healthcare provider. They can help identify any medications that may be contributing to your condition and recommend alternatives if necessary.
Protecting against infections
Practicing good hygiene, avoiding close contact with individuals who are sick, and staying up to date on vaccinations can help protect against viral or bacterial infections that may lead to low platelet counts.
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle
Eating a balanced diet, exercising regularly, and managing stress can help support overall health and potentially prevent or manage conditions that may cause low platelet count.
Seeking regular medical check-ups
Regular medical check-ups with your healthcare provider can help detect any changes in your platelet count early on. This allows for timely intervention and management of any underlying causes.
Complications of Low Blood Platelets
Low blood platelets can lead to several complications. Understanding these potential complications can help you recognize the importance of early diagnosis and treatment.
Severe bleeding
Low platelet count significantly increases the risk of severe bleeding. This can include internal bleeding, gastrointestinal bleeding, and hemorrhages that may require immediate medical attention.
Organ damage
When blood clotting is impaired due to low platelet count, it can result in damage to vital organs. Internal bleeding can damage organs such as the brain, liver, or kidneys, leading to long-term complications.
Infection
Low platelet count can weaken the immune system, making you more susceptible to infections. It’s important to take extra precautions to protect yourself from infections and seek medical attention if you develop any signs of infection.
Impaired clotting ability
Platelets play a crucial role in the clotting process. A low platelet count can impair the body’s ability to form clots, leading to prolonged and excessive bleeding.
Emotional impact
Dealing with a chronic condition like low blood platelets can have a significant emotional impact. It’s important to seek support from loved ones, healthcare professionals, or support groups to help cope with the emotional challenges that may arise.

When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the following symptoms, it’s important to seek medical attention:
Unexplained bruising or bleeding
If you notice unexplained bruises or bleeding without obvious cause, it may indicate a low platelet count. This should be evaluated by a healthcare professional.
Recurrent nosebleeds
Frequent nosebleeds that occur without trauma or recurrent nosebleeds that are difficult to stop should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
Prolonged or excessive bleeding
If bleeding from cuts or wounds takes longer than usual to stop or is excessive, it’s important to seek medical attention. This may be a sign of a low platelet count.
Blood in urine or stool
The presence of blood in the urine or stool can be a sign of internal bleeding, which requires immediate medical attention.
Unexplained fatigue or weakness
If you experience persistent fatigue or weakness without an identifiable cause, it’s important to consult with a healthcare provider. Low platelet count can contribute to these symptoms.
Risk Factors for Low Blood Platelets
Several factors can increase the risk of developing low blood platelets. Being aware of these risk factors can aid in early detection and management of the condition.
Age
As individuals age, the risk of developing certain medical conditions that can cause low platelet count increases. Older adults may also be more susceptible to medication side effects that can affect platelet levels.
Gender
Women are more likely to develop low blood platelets during pregnancy due to the physiological changes that occur in the body. Hormonal fluctuations during menstruation can also contribute to low platelet counts in women.
Certain medical conditions
Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as autoimmune disorders, liver disease, or cancer, may have a higher risk of developing low platelet counts.
Medication usage
Certain medications, such as anticoagulants, can affect platelet counts and increase the risk of low blood platelets. It’s important to discuss medication usage with your healthcare provider.
Family history
Having a family history of low blood platelets or a history of inherited bleeding disorders may increase the risk of developing low platelet counts.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy can cause physiological changes in the body that can lead to low platelet counts. It’s important for pregnant individuals to receive regular prenatal care to monitor platelet levels.

Living with Low Blood Platelets
While living with low blood platelets may present challenges, there are several measures you can take to manage your condition effectively.
Self-care measures
Adopting self-care measures can help improve overall health and effectively manage low blood platelets. This includes eating a nutritious diet, exercising regularly, and getting enough rest.
Monitoring for symptoms
Regularly monitoring for symptoms of low platelet count, such as bruising, bleeding, or fatigue, can help you detect any changes early on. This allows for timely medical intervention.
Managing medications
If you are taking any medications that may contribute to low platelet count, it’s important to work closely with your healthcare provider to manage and monitor their effects on your platelet levels.
Seeking support
Living with a chronic condition like low blood platelets can be challenging. Seeking support from loved ones, friends, or support groups can provide emotional support and guidance throughout your journey.
Educating oneself
Taking the time to educate yourself about low blood platelets, its causes, and treatment options can empower you to actively participate in your care and make informed decisions.
Future Outlook for Low Blood Platelets
Advancements in medical research and ongoing studies offer hope for the future outlook of low blood platelets.
Advancements in treatment options
Researchers are constantly exploring new treatment options for low platelet counts. Advances in medication, immunotherapies, and targeted therapies show promise for improving platelet levels and reducing complications.
Ongoing research and studies
Ongoing research studies are dedicated to gaining a better understanding of the causes and mechanisms of low blood platelets. This research can lead to improved diagnostic techniques and more effective treatment strategies.
Improved diagnostic techniques
Advancements in diagnostic techniques, such as genetic testing and molecular testing, can help identify underlying causes of low platelet count more accurately and efficiently.
Education and awareness
Increased education and awareness about low blood platelets can help improve early detection and management of the condition. Public awareness campaigns and healthcare provider education can contribute to better outcomes for individuals with low platelet counts.
In conclusion, low blood platelets can be caused by various factors, and understanding these causes can aid in early detection and management. Recognizing the symptoms, seeking timely medical attention, and implementing preventative measures can help minimize complications and improve overall quality of life. With ongoing advancements in research and improved diagnostic techniques, the future outlook for individuals with low blood platelets holds promise for better understanding and more effective treatment options.