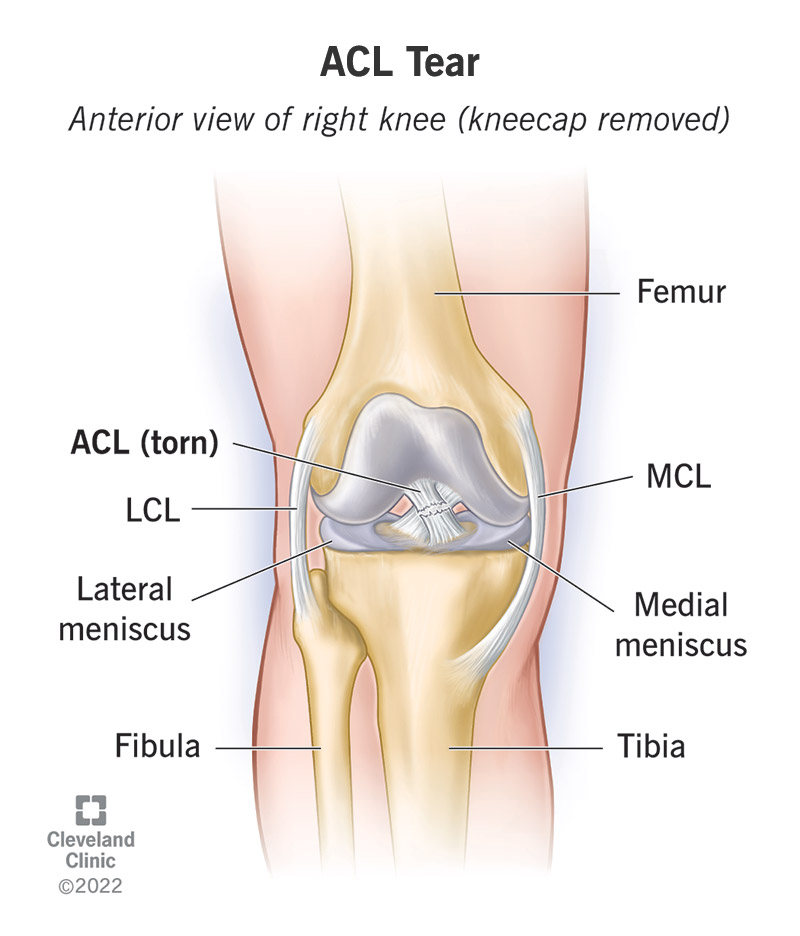
Have you recently injured your anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) and are struggling with pain and swelling? In this article, we will explore effective methods for managing pain and swelling in ACL injuries. From simple at-home remedies to professional medical interventions, we will provide you with the information and resources you need to alleviate discomfort and support your recovery. So, whether you’re an athlete looking to get back in the game or simply seeking relief from your injury, read on to discover the best strategies for managing pain and swelling in ACL injuries.
Understanding Anterior Cruciate Ligament (ACL) Injuries
The anterior cruciate ligament (ACL) is one of the major ligaments that provides stability to the knee joint. It connects the thigh bone (femur) to the shin bone (tibia). ACL injuries are typically caused by sudden movements or direct trauma to the knee, such as twisting, pivoting, or jumping. These injuries are common in sports that involve rapid changes in direction or high-impact activities. Understanding the causes, signs, and symptoms of ACL injuries is crucial for effective management and recovery.
What is the ACL?
The ACL, or anterior cruciate ligament, is a band of tissue located in the center of the knee. It plays a crucial role in stabilizing the knee joint, particularly in preventing excessive forward movement of the shin bone. Made up of strong, fibrous tissue, the ACL is essential for maintaining knee stability during various movements. Unfortunately, it is also prone to injury, especially in sports and activities that involve sudden changes in direction or high-impact movements.
Causes of ACL Injuries
ACL injuries commonly occur in sports activities that require quick changes in direction, sudden stops, or high-impact movements. These include sports like soccer, basketball, football, skiing, and gymnastics. ACL injuries can also occur due to direct trauma or accidents, such as falls or collisions. The most common mechanism of injury is when the knee is forcefully twisted or bent sideways, putting excessive stress on the ligament and causing it to tear or rupture.
Signs and Symptoms of ACL Injuries
When an ACL injury occurs, there are several signs and symptoms that may indicate its presence. The most common symptom is a sudden, intense pain in the knee. You may also experience a “popping” sound or sensation at the time of injury. Swelling and stiffness usually develop within a few hours, making it difficult to move the knee joint. Instability or a feeling of the knee giving way is also common, particularly when bearing weight or attempting to change direction. If you suspect an ACL injury, it is important to seek medical attention promptly for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management.
Initial Management of ACL Injuries
When dealing with ACL injuries, initial management is crucial to reduce pain, swelling, and further damage. The following steps should be taken to ensure proper care:
Rest and Immobilization
Immediately after an ACL injury, it is essential to rest the affected leg and avoid putting any weight on it. Using crutches or a brace can help immobilize the knee and prevent further injury. Rest is vital during the early stages of healing to allow the damaged tissues to repair and recover.
Ice and Compression Therapy
The application of ice and compression is an effective way to reduce pain and swelling associated with ACL injuries. Ice should be applied to the injured knee for 15-20 minutes every 2-3 hours during the first 72 hours. Compression can be achieved by using a compression bandage or wrap, which helps reduce swelling and provides support to the injured knee.
Elevation of the Injured Leg
Elevating the injured leg above the heart level helps reduce swelling by promoting fluid drainage. It is recommended to elevate the leg whenever possible, especially during periods of rest or sleep. This simple technique can significantly alleviate swelling and discomfort.
Pain Management
Managing pain is an important part of ACL injury management. Over-the-counter pain medications, such as acetaminophen or non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) like ibuprofen, can be used to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional before taking any medication to ensure proper dosage and to avoid potential contraindications.
Pharmacological Management of Pain
Pharmacological management of pain involves the use of medications to alleviate pain and reduce inflammation associated with ACL injuries. Here are some commonly used medications:
Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs)
Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, or NSAIDs, are commonly used to manage pain and reduce inflammation in ACL injuries. Medications such as ibuprofen and naproxen sodium work by blocking the production of prostaglandins, chemicals responsible for pain and inflammation. NSAIDs should be used as directed and under the guidance of a healthcare professional to avoid potential side effects.
Acetaminophen
Acetaminophen is another widely used pain medication that can be effective in managing pain associated with ACL injuries. Unlike NSAIDs, acetaminophen does not have anti-inflammatory properties but can help reduce pain. It is a safe option for individuals who cannot tolerate NSAIDs or have contraindications for their use. As always, it is important to follow the recommended dosage and consult a healthcare professional when using any medication.
Opioids
In some cases, opioids may be prescribed for the management of severe pain following ACL injuries. These medications are powerful pain relievers and should only be used under close medical supervision due to the risk of dependence and potential side effects. Opioids should be taken as prescribed and for the shortest duration possible.
Muscle Relaxants
Muscle relaxants may be prescribed in cases where spasms or muscle stiffness accompany an ACL injury. These medications work by reducing muscle contractions and promoting relaxation. They are typically used for short-term relief and under medical supervision due to potential side effects such as drowsiness and dizziness.
Non-Pharmacological Approaches to Pain Management
In addition to medication, non-pharmacological approaches can be beneficial in managing pain associated with ACL injuries. These methods focus on alternative therapies and techniques that do not involve the use of medications. Here are some common non-pharmacological approaches:
Physical Therapy
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in ACL injury rehabilitation and pain management. A trained physical therapist can develop a personalized program that includes exercises to improve range of motion, strengthen the knee, and enhance overall knee function. Physical therapy can also help reduce pain by addressing any imbalances or weaknesses that may be contributing to the pain.
Bracing and Support
The use of braces, supports, or orthotic devices can provide added stability and support to the injured knee, reducing pain and preventing further injury. These devices can help protect the knee during activities and provide an additional level of security during the healing process.
Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS)
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation, or TENS, is a technique that uses low-voltage electrical currents to relieve pain. TENS units are portable devices that deliver electrical impulses through electrodes placed on the skin near the site of pain. These impulses can help block or disrupt pain signals, providing temporary relief. TENS should be used under the guidance of a healthcare professional or a qualified therapist.
Heat and Cold Therapy
Heat and cold therapy are commonly used to manage pain and reduce inflammation associated with ACL injuries. Heat can be applied using heating pads or warm packs to increase blood flow and promote relaxation. Cold therapy, on the other hand, involves the use of ice packs or cold packs to reduce swelling and numb the area, providing pain relief. Both heat and cold therapy should be used with caution and for a limited duration to avoid skin damage.

Managing Swelling in ACL Injuries
Swelling is a common and often uncomfortable symptom of ACL injuries. Managing swelling effectively can help reduce pain and promote healing. Here are some strategies to manage swelling:
RICE Method (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation)
The RICE method is a widely recognized approach for managing swelling and promoting healing in ACL injuries. It stands for Rest, Ice, Compression, and Elevation. Resting the injured leg, applying ice, using compression bandages or wraps, and elevating the leg above heart level can help minimize swelling and provide relief.
Use of Compression Bandages or Wraps
Compression bandages or wraps are commonly used to manage swelling in ACL injuries. These snugly fit wraps help reduce fluid build-up and support the injured knee, promoting healing and reducing discomfort. It is important to apply compression bandages correctly and avoid excessive tightness to prevent circulation problems.
Lymphatic Drainage Massage
Lymphatic drainage massage is a gentle massage technique that helps promote the flow of lymph fluid, reducing swelling and addressing cellular waste buildup. This technique is typically performed by a trained therapist and can be beneficial in managing swelling associated with ACL injuries. However, it is important to consult a healthcare professional or a qualified therapist before undergoing lymphatic drainage massage.
Swelling Reduction Exercises
Certain exercises and movements can help reduce swelling in ACL injuries. These exercises typically involve gentle movements and stretches that promote circulation and improve lymphatic flow. Ankle pumps, quad sets, and calf pumps are examples of exercises that can be beneficial in reducing swelling. It is important to consult a physical therapist or healthcare professional before attempting any exercises to ensure safety and effectiveness.
Surgical Management of ACL Injuries
In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to repair or reconstruct the damaged ACL. Surgical management is typically considered when there is significant instability or if the individual wishes to return to high-level sports or activities that require a stable knee joint. Here are some key aspects of surgical management for ACL injuries:
Indications for Surgical Intervention
Not all ACL injuries require surgery. The decision for surgical intervention is usually based on various factors, including the individual’s age, activity level, presence of associated injuries, and the degree of instability. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional or orthopedic surgeon is essential to determine if surgery is necessary.
ACL Reconstruction Surgery
ACL reconstruction surgery is the most common surgical procedure for ACL injuries. During this procedure, the damaged ACL is replaced with a graft, typically taken from a tendon (autograft) or a cadaver (allograft). The graft serves as a scaffold for new tissue growth, eventually restoring stability to the knee joint. The surgery is typically performed arthroscopically, allowing for smaller incisions and faster recovery.
Post-Surgical Rehabilitation
Following ACL reconstruction surgery, a comprehensive rehabilitation program is crucial for optimal recovery and return to normal function. This program typically includes physical therapy, range of motion exercises, strengthening exercises, and functional training. The rehabilitation process can take several months, and close adherence to the prescribed program is important to ensure a successful outcome.
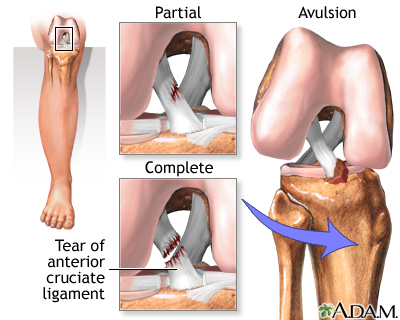
Rehabilitation and Physical Therapy
Rehabilitation and physical therapy play a key role in the recovery of ACL injuries. A structured program aimed at restoring strength, range of motion, and overall function is vital for a successful recovery. Here are some aspects of rehabilitation and physical therapy:
Range of Motion Exercises
Range of motion exercises help restore the normal movement of the knee joint following an ACL injury. These exercises typically involve gentle, controlled movements that gradually increase the range of motion. It is important to perform these exercises under the guidance of a physical therapist to ensure safety and proper progression.
Strengthening Exercises
Strengthening exercises are crucial to regain stability and muscle strength in the knee joint. These exercises target the muscles surrounding the knee, such as the quadriceps, hamstrings, and calf muscles. A physical therapist can design a personalized strengthening program that gradually increases the intensity and complexity of exercises to facilitate optimal recovery.
Balance and Proprioception Training
Balance and proprioception training aim to improve the body’s ability to maintain balance and coordination. These exercises often involve challenging the stability of the injured knee by performing various movements on an unstable surface. Proprioception training can help reduce the risk of reinjury by improving neuromuscular control and joint stability.
Functional Training
Functional training focuses on restoring the ability to perform specific movements and activities required for daily life, work, or sports participation. This phase of rehabilitation involves exercises and activities that mimic real-life movements and gradually progress in intensity and complexity. Functional training helps bridge the gap between rehabilitation and a safe return to normal activities.
Prevention of Further Injuries
Preventing further injuries to the ACL is essential to maintain knee stability and overall joint health. Here are some strategies to prevent future ACL injuries:
ACL Injury Prevention Programs
ACL injury prevention programs are specially designed training programs that focus on enhancing neuromuscular control, strength, and biomechanics to reduce the risk of ACL injuries. These programs typically involve exercises and drills that target proper landing, cutting, and body mechanics. Participating in an ACL injury prevention program can significantly reduce the risk of re-injury and future ACL tears.
Proper Warm-up and Stretching
Proper warm-up and stretching before engaging in physical activities or sports can help prepare the body for movement, reduce muscle stiffness, and enhance flexibility. Dynamic warm-up exercises that involve active movements and stretching exercises specific to the muscles and joints involved in the activity help prevent strains and tears, including ACL injuries.
Wearing Protective Gear
Wearing appropriate protective gear, such as knee braces, can provide added support and stability to the knee joint during physical activities or sports. Depending on the individual’s specific needs and the nature of the activity, a healthcare professional may recommend the use of protective gear to reduce the risk of ACL injuries.
Avoiding High-Risk Activities
Avoiding high-risk activities or modifying movement techniques can significantly reduce the risk of ACL injuries. Activities that involve sudden changes in direction, jumping, or pivoting put excessive stress on the knees and increase the risk of injury. Engaging in alternative activities or modifying movement patterns can help lower the risk and protect the knees from potential damage.
Psychological Factors in ACL Injury Recovery
ACL injuries can have significant psychological impacts on individuals, affecting their mental well-being and overall recovery. Understanding and addressing these psychological factors are crucial for a holistic approach to ACL injury management. Here are some key considerations:
Psychological Impact of ACL Injuries
ACL injuries can lead to feelings of frustration, anger, sadness, and disappointment. The sudden loss of mobility, the inability to participate in desired activities, and the fear of reinjury can significantly impact an individual’s mental well-being. It is not uncommon for individuals to experience anxiety or depression during the recovery process. Recognizing and addressing these psychological impacts is an important part of the recovery journey.
Coping Strategies and Support
Developing effective coping strategies and seeking appropriate support are essential for individuals recovering from ACL injuries. Engaging in relaxation techniques, mindfulness, or stress management practices can help alleviate anxiety and improve overall mood. It is also beneficial to seek support from healthcare professionals, therapists, or support groups that specialize in sports injury rehabilitation.
Sports Psychology in Rehabilitation
Sports psychology can play a significant role in the rehabilitation process for ACL injuries. Working with a sports psychologist can help individuals develop mental resilience, positive self-talk, and coping mechanisms to overcome the challenges associated with ACL injuries. Sports psychologists can also assist in setting realistic goals, managing expectations, and developing strategies to enhance motivation and mental focus during the recovery process.
Returning to Sports and Physical Activity
Returning to sports and physical activity after an ACL injury requires careful consideration and a gradual progression. Rushing the process can increase the risk of reinjury and compromise long-term knee health. Here are some key aspects to consider when returning to sports:
Criteria for Return to Play
The decision to return to sports is typically made based on specific criteria assessed by a healthcare professional or sports medicine specialist. These criteria often include factors such as restoration of normal range of motion, strength, balance, proprioception, and the ability to perform sport-specific movements without pain or instability. It is important to meet these criteria before resuming sports participation.
Guidelines for Gradual Return to Sports
Returning to sports should be a gradual process that allows the body to adapt and regain the necessary strength and stability. Following a structured return-to-sport program developed by a physical therapist or sports medicine specialist is essential. This program involves progressive exercises, drills, and sport-specific training that gradually increase in intensity and complexity.
Sport-Specific Training
Sport-specific training involves exercises and drills that mimic the movements and demands of the particular sport an individual is returning to. This type of training helps improve sport-specific skills, agility, and overall performance while minimizing the risk of reinjury. Working with a qualified sports trainer or coach can be beneficial in designing a tailored program that meets the individual’s sport-related goals.
Injury Prevention Strategies
Once an individual has returned to sports or physical activity, implementing injury prevention strategies is essential to maintain knee health and reduce the risk of future ACL injuries. These strategies may include regular strength and conditioning exercises, proper warm-up and cool-down routines, maintaining flexibility, and using protective gear. Consistency in maintaining these strategies can help prevent further injuries and ensure long-term knee health.
In conclusion, understanding ACL injuries and effectively managing them is crucial for recovery and long-term knee health. From initial management of pain and swelling to surgical intervention, rehabilitation, and psychological support, a comprehensive approach is necessary for optimal outcomes. By following the appropriate management strategies discussed, individuals can reduce pain, promote healing, and safely return to their desired sports and activities while minimizing the risk of future ACL injuries.