Did you know that there are preventive measures you can take to reduce your risk of vulval cancer? This article will provide you with important information about this type of cancer and highlight effective strategies for prevention. By understanding the factors that contribute to the development of vulval cancer and adopting healthy habits, you can significantly minimize your chances of being affected by this disease. Read on to discover how to protect yourself and stay informed about your well-being.
Understanding Vulval Cancer
Vulval cancer refers to the abnormal growth of cancerous cells in the vulva, the outer surface area of a woman’s genitals. This type of cancer is relatively rare, accounting for approximately 5% of all gynecological cancers. While it predominantly affects older women, it can occur at any age. Understanding the basics of vulval cancer, its various types, risk factors, and symptoms is crucial for early detection and effective treatment.
What is Vulval Cancer?
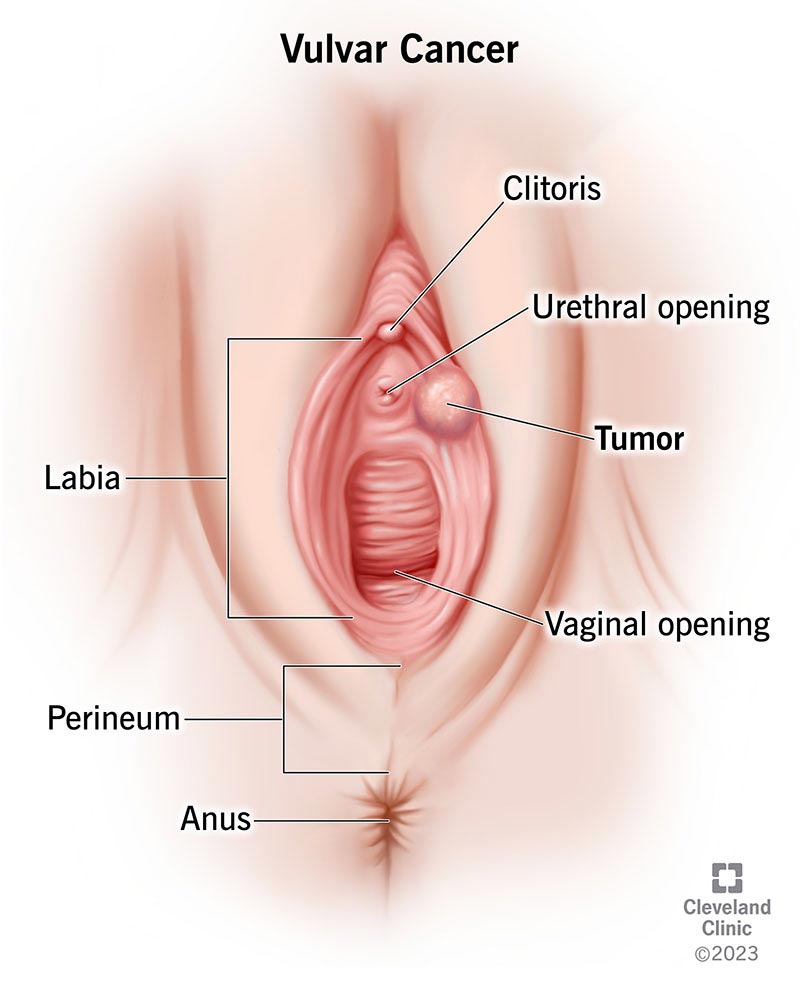
Vulval cancer occurs when malignant cells develop in the tissues of the vulva. The vulva consists of the outer lips (labia majora), inner lips (labia minora), clitoris, vaginal opening, and perineum (the area between the vulva and anus). The most common type of vulval cancer is squamous cell carcinoma, which affects the thin, flat cells lining the vulva. Other rare types include basal cell carcinoma, adenocarcinoma, and melanoma.
Types of Vulval Cancer
-
Squamous Cell Carcinoma: This is the most prevalent type of vulval cancer, accounting for about 90% of all cases. It usually affects the labia minora and labia majora and is linked to human papillomavirus (HPV) infection.
-
Basal Cell Carcinoma: This type of vulval cancer is less common and starts in the basal cells of the skin. It tends to grow slowly and rarely spreads to other parts of the body.
-
Adenocarcinoma: Adenocarcinoma of the vulva originates from the glandular cells and is relatively rare. It typically develops in older women and has a higher chance of spreading to nearby lymph nodes.
-
Melanoma: Vulval melanoma is a rare but aggressive form of cancer that arises from the pigment-producing cells (melanocytes) in the skin. It often presents as an irregularly shaped, dark-colored lesion.
Risk Factors for Vulval Cancer
Several factors may increase a woman’s risk of developing vulval cancer. It’s important to note that having one or more risk factors does not necessarily mean a person will develop cancer. The following risk factors may contribute to the development of vulval cancer:
-
Age: The risk of vulval cancer increases with age, particularly in women over 60.
-
HPV Infection: Certain strains of HPV, particularly HPV 16 and 18, increase the risk of vulval cancer. Practicing safe sex and getting vaccinated against HPV can help reduce this risk.
-
Smoking: Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of developing various cancers, including vulval cancer.
-
Chronic Vulval Inflammation: Conditions such as human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), lichen sclerosus, or lichen planus can contribute to chronic inflammation of the vulva, increasing the risk of vulval cancer.
-
Precancerous Changes: Having precancerous changes in the vulva, known as vulvar intraepithelial neoplasia (VIN), can increase the risk of developing vulval cancer.
-
Family History: A family history of vulval cancer or other types of cancer may elevate the risk.
Symptoms
Early detection of vulval cancer is crucial for successful treatment. Recognizing the common symptoms and knowing when to seek medical attention can aid in early diagnosis. It’s important to note that these symptoms may also be caused by other benign conditions, but it is still essential to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation.
Common Symptoms of Vulval Cancer
- Persistent itching or tenderness in the vulval area
- A lump, sore, or wart-like growth on the vulva
- Bleeding not related to menstruation
- Skin discoloration, such as redness or white patches
- Pain or discomfort during sex
- Persistent pain in the vulval area
- Change in the appearance or size of the vulva
When to See a Doctor
If you experience any of the symptoms mentioned above, it is important to see a doctor for a proper evaluation. They will be able to assess your condition and determine if further tests or examinations are necessary. While these symptoms can be caused by other conditions, early detection is key in managing vulval cancer effectively.

Prevention
While it may not be possible to completely prevent vulval cancer, you can take certain steps to reduce the risk and promote overall vaginal health. Incorporating regular self-examinations, opting for HPV vaccination, and maintaining good hygiene practices are essential preventive measures.
Regular Self-Examinations
Performing regular self-examinations of the vulva can help in early detection of any changes or abnormalities. Examine the vulva visually and tactually to check for any lumps, sores, or abnormal growths. If you notice any concerning changes, promptly consult a healthcare professional for further evaluation.
HPV Vaccination
Human papillomavirus (HPV) infection is a significant risk factor for vulval cancer. Getting vaccinated against HPV can help prevent infection with the high-risk strains of the virus. Vaccination is most effective when administered before an individual becomes sexually active, but it can still provide benefits for those who have already been sexually active.
Maintaining Good Hygiene
Good vulval hygiene is an important aspect of overall vaginal health. Here are some hygiene practices to consider:
- Avoid using harsh soaps or douches in the vulval area.
- Always wipe from front to back after using the toilet to prevent the spread of bacteria.
- Wear breathable cotton underwear and avoid tight-fitting clothing that can trap moisture.
- During menstruation, change tampons or pads frequently to maintain cleanliness.
By practicing these hygiene measures, you can keep the vulval area clean and reduce the risk of infection or inflammation.
Reducing Risk Factors
Certain lifestyle choices and practices can play a role in reducing the risk of developing vulval cancer. By making positive changes, such as smoking cessation, safe sex practices, and adopting a healthy diet and exercise regimen, you can help decrease your chances of developing this form of cancer.
Smoking Cessation
Smoking has been linked to an increased risk of vulval cancer, as well as other cancers. The harmful chemicals present in cigarette smoke can damage the DNA and other genetic material in the cells, increasing the likelihood of cancerous growth. Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of vulval cancer, as well as improve overall health and well-being.
Safe Sex Practices
Engaging in safe sex practices can reduce the risk of contracting HPV, a major risk factor for vulval cancer. Consistently using condoms, limiting sexual partners, and discussing vaccination status with potential partners can help reduce the transmission of HPV and protect against sexually transmitted infections.
Healthy Diet and Exercise
Maintaining a healthy lifestyle that includes a balanced diet and regular physical activity can contribute to overall well-being, including reducing the risk of vulval cancer. Incorporate a variety of fruits and vegetables into your diet while limiting processed foods and sugary beverages. Regular exercise can also help maintain a healthy body weight, which is associated with a lower risk of developing cancer.

Early Detection
Early detection plays a crucial role in the successful treatment of vulval cancer. Regular check-ups and screenings can help identify any potential issues early on, allowing for timely intervention and better treatment outcomes.
Importance of Regular Check-ups
Scheduling regular visits to your healthcare provider is essential for maintaining good health. During these appointments, your doctor will perform a thorough examination, including a pelvic exam, to check for any abnormalities or signs of vulval cancer. They may also ask about any symptoms you may have and discuss any concerns or questions you may have.
Screening for Vulval Cancer
Screening for vulval cancer involves various methods, such as a colposcopy or a biopsy, to assess any abnormalities found during a pelvic exam or if a person is experiencing symptoms. Your doctor will tailor the screening approach based on your specific situation, considering factors such as age, medical history, and risk factors.
Treatment Options
The treatment options available for vulval cancer depend on various factors, including the stage of the cancer, its location, and the individual’s overall health. The primary treatment modalities for vulval cancer include surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and targeted therapy.
Surgery
Surgery is often the primary treatment for vulval cancer. The extent of surgery may vary depending on the stage and location of the cancer. It may involve removing a portion or the entire vulva, nearby lymph nodes, or other affected tissues. Reconstructive surgery may also be performed to restore the appearance and function of the vulva.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy uses high-energy X-rays or other particles to kill cancer cells or shrink tumors. It may be administered externally or internally, depending on the specific situation. Radiation therapy is often used in combination with surgery or chemotherapy to increase treatment efficacy.
Chemotherapy
Chemotherapy involves the use of drugs to kill cancer cells or inhibit their growth. It can be used before surgery to shrink tumors, after surgery to kill any remaining cancer cells, or as a palliative treatment to relieve symptoms in advanced cases. Chemotherapy can be given orally or intravenously, depending on the drugs prescribed.
Targeted Therapy
Targeted therapy is a relatively new treatment option for vulval cancer. It involves using drugs that specifically target certain molecules or genetic abnormalities found in cancer cells. These targeted drugs can interfere with the cancer cells’ growth and division, improving treatment outcomes.

Supportive Care
Receiving a diagnosis of vulval cancer can be emotionally challenging. Alongside medical treatment, it is crucial to prioritize emotional well-being and seek support during this time. Coping with a vulval cancer diagnosis and accessing appropriate resources and support can greatly assist in managing the physical, emotional, and psychological aspects of the disease.
Coping with Vulval Cancer Diagnosis
A vulval cancer diagnosis can evoke a range of emotions, including fear, anxiety, and sadness. It is important to acknowledge and express these emotions, as well as seek support from loved ones, support groups, or mental health professionals. Open communication with your healthcare team can also provide reassurance and guidance during your treatment journey.
Resources for Emotional Support
Various resources are available to provide emotional support and guidance for those affected by vulval cancer. Online forums, support groups, and counseling services can offer a safe space for individuals to share experiences, gather information, and connect with others facing similar challenges. Additionally, healthcare facilities and nonprofit organizations often provide educational materials and support programs tailored to vulval cancer patients and their families.
Future Research
Advancements in vulval cancer research and treatment options continue to progress. Ongoing studies and clinical trials seek to improve outcomes, develop targeted therapies, and refine screening and diagnostic techniques.
Advancements in Vulval Cancer Treatment
Research in vulval cancer treatment has seen significant progress in recent years. Advances such as minimally invasive surgical techniques, personalized medicine, and immunotherapy have shown promise in improving treatment outcomes and minimizing side effects. These developments highlight the importance of ongoing research and investment in the field of vulval cancer.
Promising Clinical Trials
Clinical trials play a crucial role in expanding treatment options, refining existing therapies, and improving the overall management of vulval cancer. These trials investigate new drugs, combinations of treatments, and novel approaches to diagnosis and prevention. Participating in clinical trials can provide access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the advancement of vulval cancer care.
Conclusion
Awareness and prevention are paramount in the fight against vulval cancer. Understanding the basics of vulval cancer, recognizing the symptoms, and minimizing risk factors through lifestyle modifications can greatly reduce the chances of its development. Early detection through regular check-ups and screenings is essential for timely intervention and successful treatment. By taking control of your health through self-examinations, vaccination, and maintenance of good hygiene practices, you can empower yourself in the face of vulval cancer. Remember, your well-being matters, and early actions can make a significant difference in your health journey.