Hey there! Have you ever wondered what causes bronchitis and how to treat it? Well, look no further because we’ve got you covered! In this article, we’ll be exploring the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for bronchitis. So, if you’ve been experiencing a persistent cough or difficulty breathing, keep reading to gain a better understanding of this common respiratory condition and how to find relief.

Overview
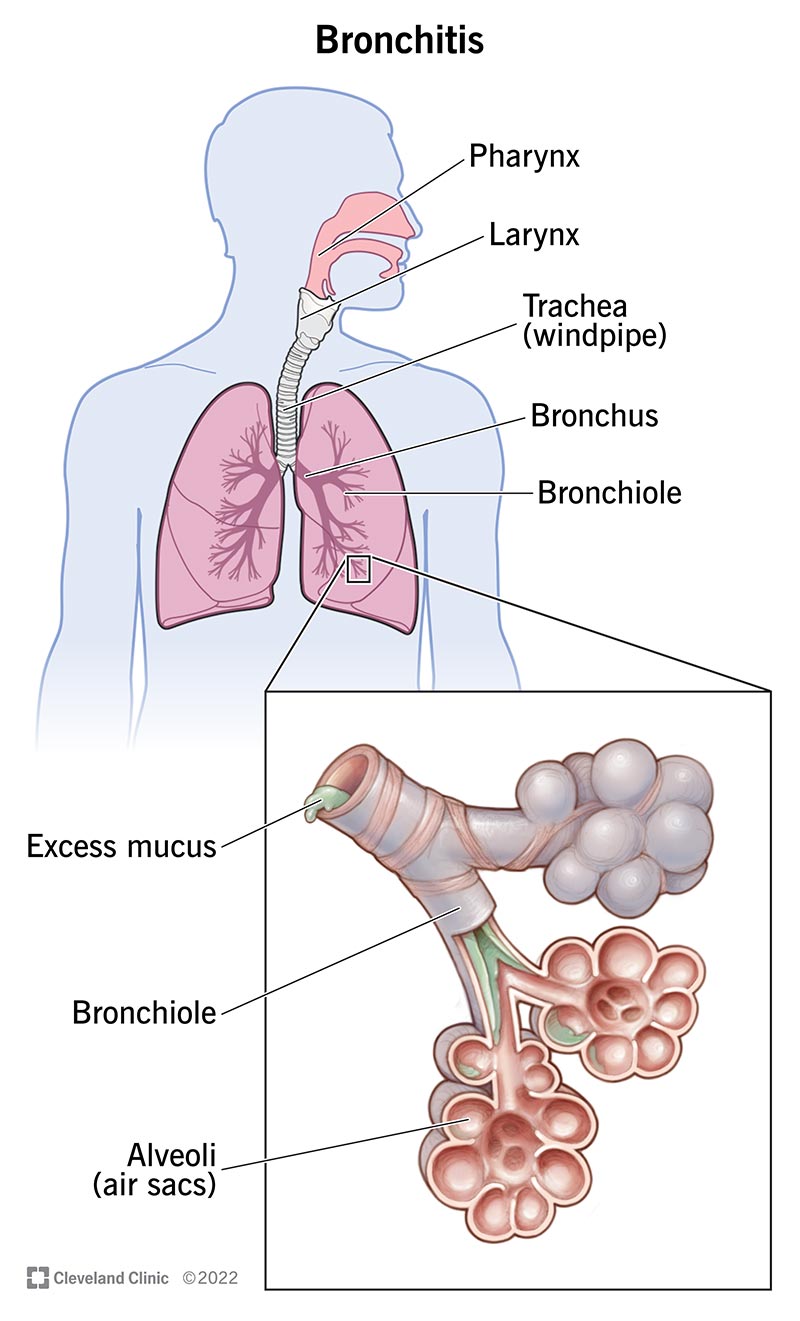
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that is characterized by inflammation of the bronchial tubes, which are the airways in the lungs. It can be caused by various factors, including viral or bacterial infections, environmental factors, smoking, and repeated exposure to irritants. There are two main types of bronchitis: acute bronchitis, which is a short-term condition, and chronic bronchitis, which is a long-term condition.
Causes
Viral Infections
Viral infections are the most common cause of acute bronchitis. The viruses that commonly cause bronchitis include the flu virus, respiratory syncytial virus (RSV), and the common cold virus. These viruses can be spread through droplets in the air when an infected person coughs or sneezes.
Bacterial Infections
Bacterial infections can also cause bronchitis, although they are less common than viral infections. Bacterial bronchitis is usually caused by bacteria such as Streptococcus pneumoniae or Haemophilus influenzae. These bacteria can enter the airways and cause inflammation and infection.
Environmental Factors
Exposure to certain environmental factors can increase the risk of developing bronchitis. This includes exposure to air pollution, dust, and chemicals. People who work in industries such as coal mining, construction, or manufacturing are at a higher risk of developing bronchitis due to their exposure to these irritants.
Smoking
Smoking is one of the biggest risk factors for developing both acute and chronic bronchitis. The harmful chemicals in cigarette smoke can irritate the bronchial tubes and lead to inflammation. Long-term smoking can also damage the cilia in the airways, which are responsible for clearing mucus and debris from the lungs.
Repeated Exposure to Irritants
Repeated exposure to irritants such as secondhand smoke, air pollution, or chemical fumes can also contribute to the development of bronchitis. This is especially true for individuals who have a weakened immune system or pre-existing respiratory conditions.
Symptoms
Acute Bronchitis Symptoms
Acute bronchitis is usually a self-limiting condition that lasts for a few weeks. The symptoms of acute bronchitis include a persistent cough that may produce mucus, chest discomfort or tightness, wheezing, and shortness of breath. Some individuals may also experience low-grade fever, fatigue, and sore throat.
Chronic Bronchitis Symptoms
Chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition that is characterized by a persistent cough that lasts for at least three months in a year, for two consecutive years. In addition to the symptoms of acute bronchitis, individuals with chronic bronchitis may experience frequent respiratory infections, worsening of cough and shortness of breath, and production of excessive mucus.
Diagnosis
To diagnose bronchitis, your doctor will perform a thorough evaluation. This may include:
Medical History
Your doctor will ask about your symptoms, medical history, and any factors that may have contributed to the development of bronchitis. This can help determine the underlying cause and guide appropriate treatment.
Physical Examination
During a physical examination, your doctor will listen to your lungs with a stethoscope to check for abnormal sounds such as wheezing or crackles. They may also examine your throat, nose, and ears to evaluate for signs of infection.
Chest X-ray
A chest X-ray may be ordered to rule out other conditions and to check for signs of pneumonia or other lung diseases that may be causing your symptoms.
Pulmonary Function Tests
Pulmonary function tests measure how well your lungs are functioning. These tests can help determine if there is any obstruction in the airways and assess the severity of bronchitis. Spirometry is a common pulmonary function test that measures the amount of air you can inhale and exhale forcefully.
Sputum Culture
A sputum culture may be done to identify the presence of bacteria or other infectious agents in the mucus produced by coughing.
Blood Tests
Blood tests may be ordered to rule out other potential causes of your symptoms. These tests can help assess your overall health and check for signs of infection or inflammation.

Treatment Options
Home Remedies
For mild cases of bronchitis, home remedies can help alleviate symptoms and promote healing. These may include getting plenty of rest, staying hydrated, using a humidifier or steam inhalation to soothe the airways, and avoiding irritants such as smoke or strong odors.
Medications
In some cases, medications may be prescribed to help manage the symptoms of bronchitis. This may include over-the-counter cough suppressants to relieve coughing, bronchodilators to open up the airways and improve breathing, or antibiotics if a bacterial infection is suspected or confirmed.
Airway Clearance Techniques
Airway clearance techniques, such as chest physiotherapy or postural drainage, may be recommended to help loosen and clear mucus from the airways. These techniques involve specific movements and positions to facilitate the removal of mucus.
Breathing Exercises
Breathing exercises, such as diaphragmatic breathing and pursed-lip breathing, can help improve lung function and reduce shortness of breath. These exercises focus on deep, slow breathing to help strengthen the respiratory muscles and optimize oxygen exchange.
Oxygen Therapy
In severe cases of bronchitis or if there is respiratory distress, oxygen therapy may be necessary. This involves the use of supplemental oxygen to ensure adequate oxygenation of the body.
Prevention
Avoiding Respiratory Infections
To lower your risk of developing bronchitis, it is important to take steps to avoid respiratory infections. This includes practicing good hand hygiene, avoiding close contact with sick individuals, and getting vaccinated against the flu and pneumonia.
Quitting Smoking
If you are a smoker, quitting smoking is one of the most important steps you can take to prevent bronchitis and improve your respiratory health. Smoking cessation can significantly reduce the risk of developing chronic bronchitis and other serious lung conditions.
Avoiding Lung Irritants
Limiting exposure to lung irritants such as secondhand smoke, air pollution, chemical fumes, and dust can help prevent bronchitis and protect your respiratory system.
Getting Vaccinated
Vaccinations can provide protection against infections that can lead to bronchitis. It is recommended to get vaccinated against the flu annually and to receive the pneumococcal vaccine to lower the risk of developing bacterial pneumonia, which can be a complication of bronchitis.

Complications
Pneumonia
Pneumonia is a potential complication of bronchitis, particularly in individuals with weakened immune systems or those who have pre-existing lung conditions. Pneumonia is a serious infection in the lungs that can lead to severe illness and even death if not treated promptly.
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD)
Chronic bronchitis is a form of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), which is a progressive lung disease that causes airflow limitation and breathing difficulties. If left untreated or poorly managed, chronic bronchitis can lead to the development or worsening of COPD.
Respiratory Failure
In severe cases of bronchitis, respiratory failure can occur. This is a life-threatening condition where the lungs are unable to provide sufficient oxygen to the body or effectively remove carbon dioxide, leading to a dangerous imbalance in blood gases.
Lifestyle Changes
Quitting Smoking
As mentioned earlier, quitting smoking is essential in managing bronchitis and preventing further respiratory damage. It is never too late to quit smoking, and doing so can greatly improve your respiratory health and overall well-being.
Avoiding Lung Irritants
By minimizing exposure to lung irritants such as secondhand smoke, air pollution, and occupational chemicals, you can reduce your risk of developing bronchitis and other respiratory conditions.
Eating a Healthy Diet
A balanced and nutritious diet can support your immune system and overall health. Include plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins in your diet to provide essential nutrients that can help keep your respiratory system strong.
Regular Exercise
Regular physical activity can strengthen your respiratory muscles and improve lung function. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week. Consult with your healthcare provider before starting any exercise program, especially if you have underlying respiratory conditions.

When to See a Doctor
Seek Immediate Medical Attention
In some cases, bronchitis can be severe or indicate a more serious underlying condition. Seek immediate medical attention if you experience severe shortness of breath, rapid breathing, chest pain, bluish lips or fingertips, or confusion.
Consult a Doctor
If you experience persistent or worsening symptoms of bronchitis, it is important to consult a doctor for an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment. Your doctor can help determine the underlying cause of your symptoms and develop a tailored treatment plan.
Conclusion
Bronchitis is a common respiratory condition that can be caused by viral or bacterial infections, environmental factors, smoking, and repeated exposure to irritants. Acute bronchitis is a short-term condition, while chronic bronchitis is a long-term condition. It is important to seek medical attention if you experience severe symptoms or if your symptoms persist or worsen. By taking steps to prevent respiratory infections, quitting smoking, avoiding lung irritants, and making lifestyle changes, you can reduce the risk of developing bronchitis and improve your respiratory health. Remember to consult a healthcare professional for personalized advice and treatment options.