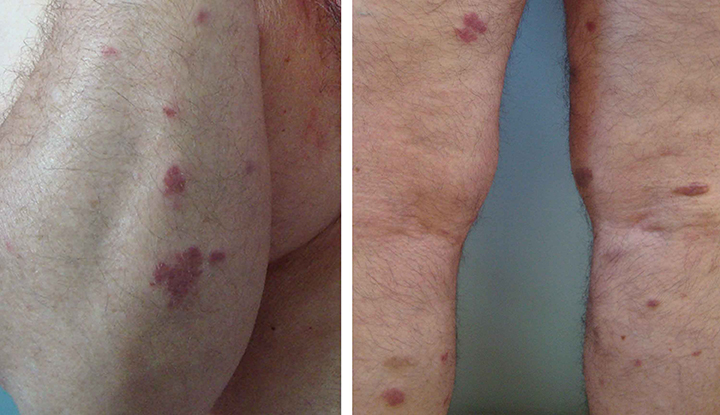
Imagine sitting down with a cup of tea, ready to learn something new and fascinating. Today, we’ll be exploring the ins and outs of a rare form of cancer called Kaposi’s Sarcoma. This eye-opening article will take you on a journey to better understand the causes, symptoms, and treatment options for this condition. So, grab a comfy seat and get ready to expand your knowledge on Kaposi’s Sarcoma!
Understanding Kaposi’s Sarcoma: Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
Overview of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
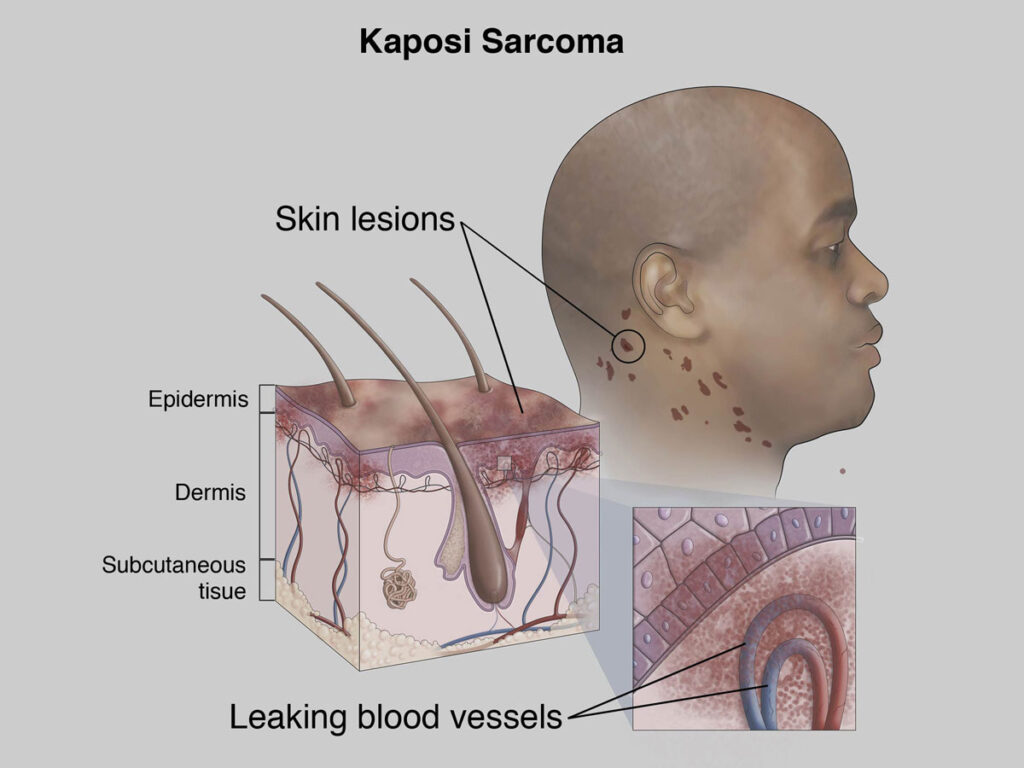
Kaposi’s Sarcoma is a rare form of cancer that primarily affects the skin but can also involve other organs, such as the mouth, lungs, and gastrointestinal tract. It is caused by a virus known as the human herpesvirus 8 (HHV-8), also called Kaposi’s sarcoma-associated herpesvirus (KSHV). This virus is usually transmitted through sexual contact, blood transfusions, or organ transplants. Kaposi’s Sarcoma is more commonly seen in individuals with weakened immune systems, particularly those living with HIV/AIDS. The cancer manifests as lesions or tumors on the skin or mucous membranes, which can range in color from brown to reddish-purple.
Causes of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
As mentioned earlier, the primary cause of Kaposi’s Sarcoma is the human herpesvirus 8. This virus is commonly found in the general population but usually remains dormant without causing any symptoms. In individuals with weakened immune systems, such as those living with HIV/AIDS, the virus can reactivate and lead to the development of Kaposi’s Sarcoma. Other factors that can contribute to the development of the disease include certain genetic factors and environmental triggers, although more research is needed to fully understand these connections.
Risk Factors for Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing Kaposi’s Sarcoma. The most significant risk factor is having a weakened immune system, which can result from conditions such as HIV/AIDS, organ transplantation, or long-term use of immunosuppressive medications. Additionally, being of Mediterranean, Eastern European, or African descent may also increase the risk. It is important to note that Kaposi’s Sarcoma is relatively rare and the majority of individuals with the above risk factors will not develop the disease.
Symptoms of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
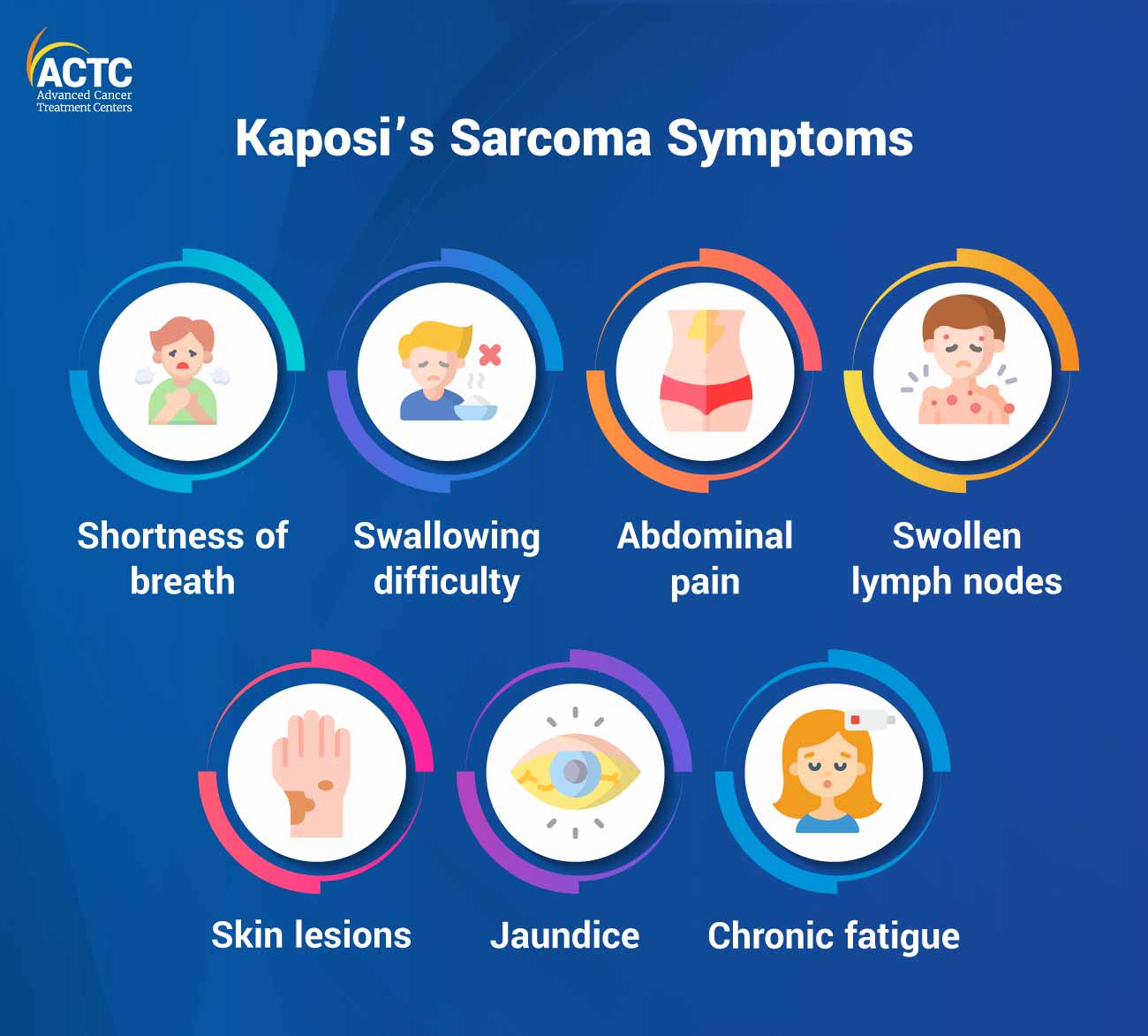
The symptoms of Kaposi’s Sarcoma can vary depending on the location and extent of the lesions or tumors. In the early stages, the most common symptom is the development of skin lesions, which typically appear as red, purple, or brown patches or nodules. These lesions can be flat or raised, and they may be painless or accompanied by discomfort or itching. In advanced cases, when the disease has spread to other organs, symptoms may include shortness of breath, coughing, and gastrointestinal problems.
Diagnosis of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
To diagnose Kaposi’s Sarcoma, a healthcare professional will typically conduct a thorough physical examination, review the patient’s medical history, and perform a biopsy of the affected tissue. The biopsy involves taking a small sample of the lesion or tumor for microscopic examination. In some cases, additional imaging tests may be recommended, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI scans, to determine the extent of the disease and assess whether it has spread to other areas of the body.
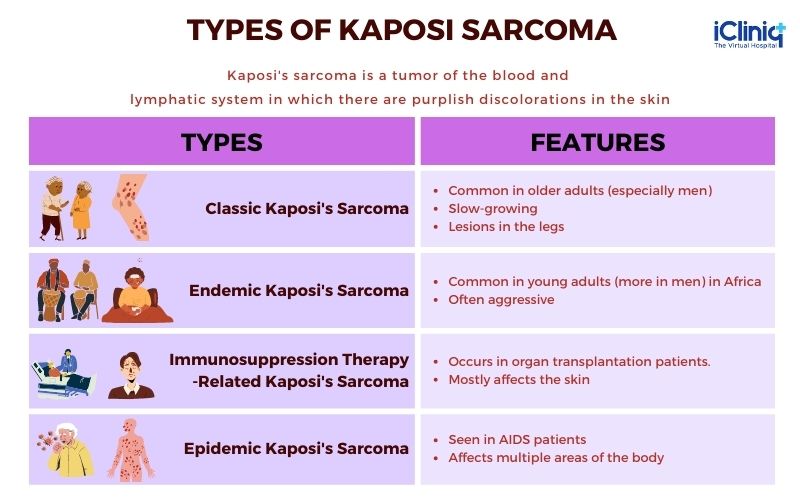
Types of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
There are four main types of Kaposi’s Sarcoma: classic, endemic, immunosuppressive therapy-related, and epidemic. The classic type primarily affects older men of Mediterranean or Eastern European descent and typically presents as lesions on the lower extremities. Endemic Kaposi’s Sarcoma is seen in Africa and usually affects children and young adults. Immunosuppressive therapy-related Kaposi’s Sarcoma occurs in individuals who have received organ transplants or long-term immunosuppressive medications. Finally, epidemic Kaposi’s Sarcoma is the most common type and is associated with HIV/AIDS.
Treatment Options for Kaposi’s Sarcoma
The treatment of Kaposi’s Sarcoma depends on several factors, including the extent of the disease, the symptoms experienced by the patient, and the individual’s overall health. Some common treatment options include radiation therapy, chemotherapy, and immunotherapy. Radiation therapy involves targeting the affected areas with high-energy beams to kill cancer cells. Chemotherapy uses drugs to kill cancer cells throughout the body, while immunotherapy boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer. In some cases, surgery may be necessary, especially if the lesions or tumors are causing significant symptoms or obstructing vital organs.
Prevention of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
Since Kaposi’s Sarcoma is primarily associated with a weakened immune system, HIV prevention is critical in reducing the risk of developing the disease. Practicing safe sex, using barrier methods (such as condoms), and avoiding sharing needles for drug use are crucial preventive measures. Regular screening for HIV and other sexually transmitted infections is also recommended. Additionally, individuals who have undergone organ transplantation or are taking immunosuppressive medications should be closely monitored by their healthcare providers and take necessary precautions to reduce the risk of Kaposi’s Sarcoma.

Prognosis and Complications of Kaposi’s Sarcoma
The prognosis for Kaposi’s Sarcoma varies depending on several factors, including the type and stage of the disease and the individual’s overall health. For individuals with HIV/AIDS-related Kaposi’s Sarcoma, the prognosis has significantly improved with the advancement of antiretroviral therapy (ART) for HIV. However, for individuals with advanced or widespread disease, the prognosis may be less favorable. Complications of Kaposi’s Sarcoma can include infection, internal bleeding, lymphedema, and psychological distress due to cosmetic changes.
Support and Resources for Kaposi’s Sarcoma Patients
Receiving a diagnosis of Kaposi’s Sarcoma can be overwhelming, but it is essential to remember that you are not alone. Numerous support groups, organizations, and resources are available to help individuals and their loved ones navigate the challenges of living with Kaposi’s Sarcoma. These resources provide emotional support, access to information, and assistance in finding healthcare providers and treatment options. Some notable organizations include the American Cancer Society, Sarcoma Foundation of America, and the AIDS Healthcare Foundation, among others.
In conclusion, understanding Kaposi’s Sarcoma involves recognizing its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. It is crucial to be aware of the risk factors, preventive measures, and available support for individuals living with this rare form of cancer. By promoting awareness, advocating for early detection and diagnosis, and supporting ongoing research, we can make a difference in the lives of those affected by Kaposi’s Sarcoma. Remember, you are not alone, and there is hope and support available on your journey.