Celiac disease is a condition that affects the small intestine and can lead to various complications if left untreated. Not only does it cause the body to become intolerant to gluten, but it can also have long-term effects on your health. In this article, we will explore the potential complications of celiac disease and the importance of addressing this condition promptly. From nutrient deficiencies to an increased risk of developing other autoimmune diseases, understanding these complications is essential for managing this chronic condition effectively. So, let’s delve into the world of celiac disease and uncover the potential challenges it can bring.
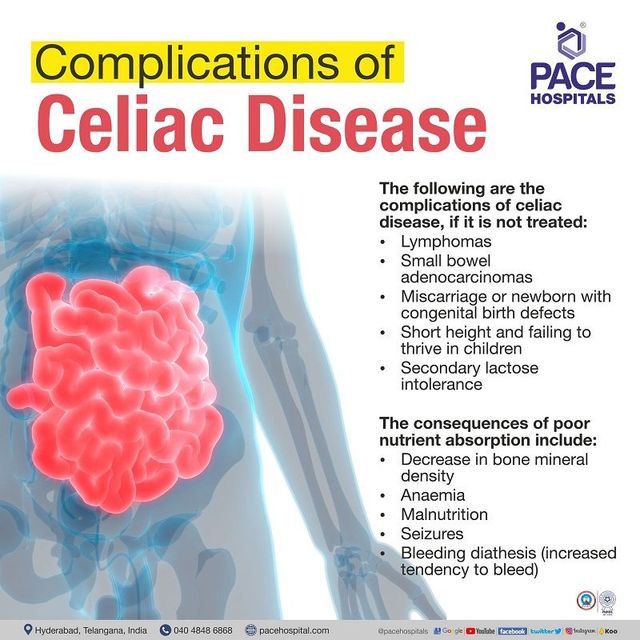
Complications of Celiac Disease
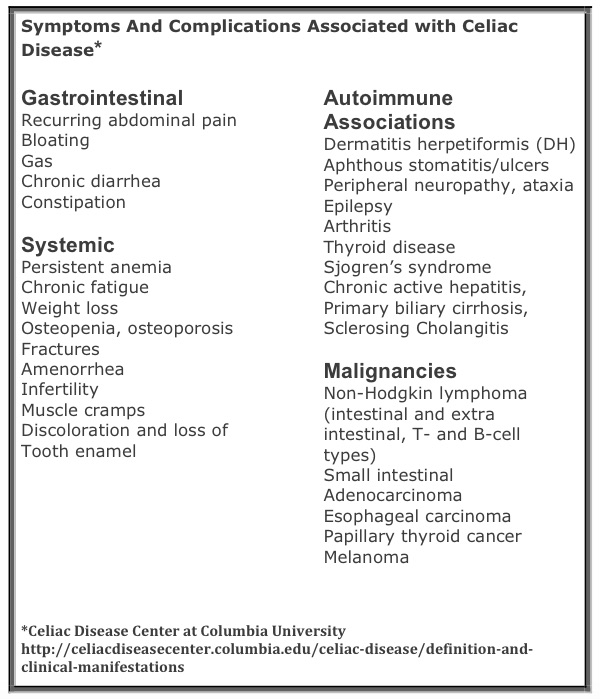
Living with Celiac Disease can be incredibly challenging, as the condition affects not only your digestive system but also various other parts of your body. While adherence to a strict gluten-free diet is essential, it is important to be aware of the potential complications that may arise from Celiac Disease. By understanding these complications, you can take proactive measures to manage your health effectively and live a fulfilling life. Let’s explore some of the most common complications associated with Celiac Disease.
1. Malnutrition
One of the main complications of Celiac Disease is malnutrition, which occurs when your body does not receive the necessary nutrients due to the damage caused to your small intestine. When gluten is consumed by someone with Celiac Disease, the immune response triggers an attack on the lining of the small intestine, preventing proper absorption of nutrients. This can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals, resulting in fatigue, weight loss, poor growth in children, and a weakened immune system.
To combat malnutrition, it is crucial for individuals with Celiac Disease to strictly adhere to a gluten-free diet. Additionally, your healthcare provider may recommend vitamin and mineral supplements, such as iron, calcium, and vitamin D, to ensure your body receives the necessary nutrients it needs.
2. Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH) is a skin condition that is strongly associated with Celiac Disease. Characterized by itchy and blistering skin rashes, DH is caused by the immune system’s reaction to gluten within the body. These rashes typically appear on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and scalp.
To effectively manage DH, maintaining a strict gluten-free diet is essential. In some cases, medication may also be prescribed to alleviate the symptoms. It is important to consult with a dermatologist or healthcare provider to determine the best course of treatment for your specific situation.

3. Osteoporosis
Celiac Disease can have long-term effects on bone health, ultimately leading to the development of osteoporosis. The damage to the small intestine caused by gluten triggers an inflammatory response that impairs the body’s ability to absorb calcium and vitamin D, both of which are crucial for maintaining strong and healthy bones.
To prevent or manage osteoporosis, individuals with Celiac Disease should work closely with their healthcare provider. Alongside a gluten-free diet, regular exercise, particularly weight-bearing exercises, can help improve bone density. In some cases, supplementation with calcium and vitamin D may be necessary.
4. Lactose Intolerance
Lactose intolerance is a common complication in individuals with untreated Celiac Disease. The damage to the small intestine can affect the production of lactase, the enzyme responsible for digesting lactose, the sugar found in milk and dairy products. As a result, consuming lactose can lead to uncomfortable gastrointestinal symptoms, including bloating, gas, and diarrhea.
If you experience lactose intolerance symptoms, it is recommended to avoid lactose-containing products or consider lactase supplements or dairy alternatives. Your healthcare provider can guide you on the best approach for managing lactose intolerance alongside Celiac Disease.
5. Anemia
Anemia is a condition characterized by a deficiency of red blood cells or hemoglobin in the blood. For individuals with Celiac Disease, anemia can occur due to malabsorption of iron, folic acid, and vitamin B12, all of which are essential for the production of healthy red blood cells. Common symptoms of anemia include fatigue, weakness, pale skin, and shortness of breath.
Treating anemia in individuals with Celiac Disease involves addressing the nutrient deficiencies through a gluten-free diet and potential supplementation. Regular monitoring of blood levels and ongoing communication with your healthcare provider are crucial for managing anemia effectively.
6. Infertility
Infertility can be a challenge for individuals with Celiac Disease, particularly in women. The underlying inflammation caused by gluten consumption can impact hormonal balance and disrupt the menstrual cycle, leading to difficulties in conceiving. In some cases, men may also experience fertility issues due to the impact on sperm quality and motility.
If you are trying to conceive and have Celiac Disease, it is advisable to seek guidance from a reproductive specialist. Working together with your healthcare provider, they can help you navigate the challenges and explore potential treatment options to increase your chances of successful conception.
7. Neurological Disorders
Celiac Disease has been linked to various neurological disorders, including migraines, peripheral neuropathy, epilepsy, and depression. The exact mechanisms behind these associations are still being researched, but it is believed that inflammation and nutrient deficiencies play a role.
If you experience any neurological symptoms, it is important to discuss them with your healthcare provider. They can help determine the appropriate course of action, which may involve a combination of a gluten-free diet, medication, and lifestyle changes.
8. Cancer Risk
Untreated Celiac Disease can increase the risk of developing certain types of cancer, particularly intestinal lymphomas and gastrointestinal cancers. The prolonged exposure to inflammation and the damage caused to the small intestine can contribute to the development of malignancies.
To reduce the risk of cancer, it is crucial to maintain a strict gluten-free diet and attend regular check-ups with your healthcare provider. They may recommend additional screenings and surveillance to monitor your health and detect any potential issues early on.

9. Dental Problems
Celiac Disease can affect dental health, leading to problems such as tooth enamel defects, canker sores, and a higher risk of cavities. The enamel defects may result in discoloration, pitting, or weak spots on the teeth. Canker sores, which are small and painful ulcers, can occur inside the mouth.
To protect your dental health, regular dental check-ups and practicing good oral hygiene are essential. Additionally, ensuring a well-balanced diet that includes gluten-free sources of calcium and vitamin D can support dental health.
10. Gluten Ataxia
Gluten ataxia is a rare neurological condition that affects individuals with Celiac Disease. It is characterized by problems with muscle coordination and balance, leading to difficulties with movement and voluntary muscle control. Gluten ataxia is believed to be caused by an immune response to gluten that damages the cerebellum, the part of the brain responsible for coordination.
If you experience symptoms of gluten ataxia, it is crucial to consult with a neurologist or healthcare provider who specializes in movement disorders. A strict gluten-free diet is the primary treatment for gluten ataxia, although it may take time to see improvements in symptoms.
In conclusion, while Celiac Disease may present challenges, being proactive in managing your health can help minimize the potential complications. Adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, working closely with your healthcare provider, and staying well-informed can empower you to lead a fulfilling and healthy life with Celiac Disease. Remember, you are not alone in this journey, and support is available to help you navigate the complexities of the condition.