Living with celiac disease can present numerous challenges, with even the smallest trace of gluten causing painful symptoms. However, there is hope for those with this autoimmune condition, as researchers and medical professionals continue to explore and develop new treatment options. In this article, you will discover the latest advancements in the field, from medications to dietary modifications, that can help individuals effectively manage their celiac disease and lead a healthy, gluten-free life. Whether you have recently been diagnosed or are seeking alternative treatments, this comprehensive guide will provide you with valuable insights and information.
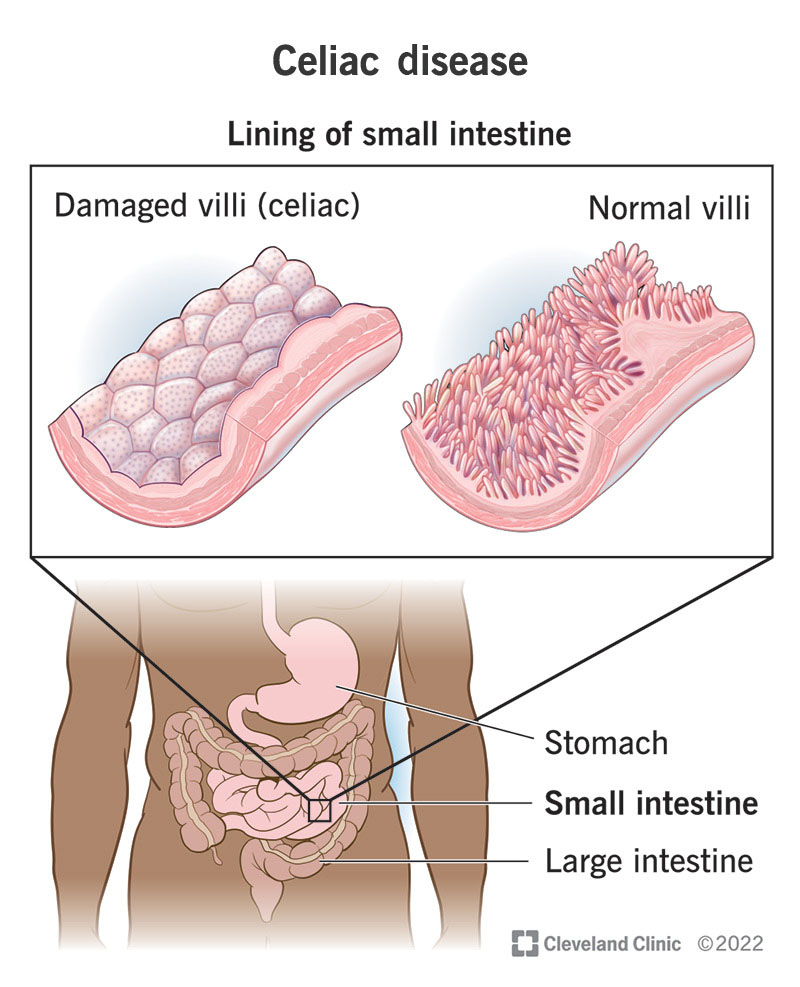
Overview of Celiac Disease
Celiac Disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine and is triggered by the ingestion of gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. When individuals with celiac disease consume gluten, their immune system responds by attacking the lining of the small intestine, which leads to damage and inflammation. This can result in a wide range of symptoms and complications, including abdominal pain, diarrhea, bloating, weight loss, anemia, and fatigue.
Diagnosis of Celiac Disease
Signs and symptoms
The signs and symptoms of celiac disease can vary greatly from person to person. Some individuals may experience digestive issues such as abdominal pain, bloating, and diarrhea, while others may have non-specific symptoms like fatigue, anemia, and joint pain. Skin rashes, mouth ulcers, and even neurological symptoms like headaches and numbness can also occur. It is important to note that symptoms can develop at any age, and even individuals with no apparent symptoms can still have celiac disease.
Screening and testing
If you suspect you may have celiac disease, it is important to undergo proper screening and testing. The first step is a blood test that checks for the presence of specific antibodies associated with celiac disease. If the blood test results are positive, the next step is a biopsy confirmation, which involves removing a small piece of tissue from the small intestine during an endoscopy and examining it under a microscope. A biopsy is necessary to confirm the diagnosis of celiac disease definitively.
Biopsy confirmation
Biopsy confirmation is considered the gold standard for diagnosing celiac disease. During the endoscopy procedure, the doctor will visually assess the small intestine for any signs of inflammation or damage. If the small intestine lining appears flattened or damaged, it is a strong indication of celiac disease. The biopsy results will not only confirm the diagnosis but also reveal the extent of intestinal damage, which can guide treatment decisions and provide important information for monitoring the disease.
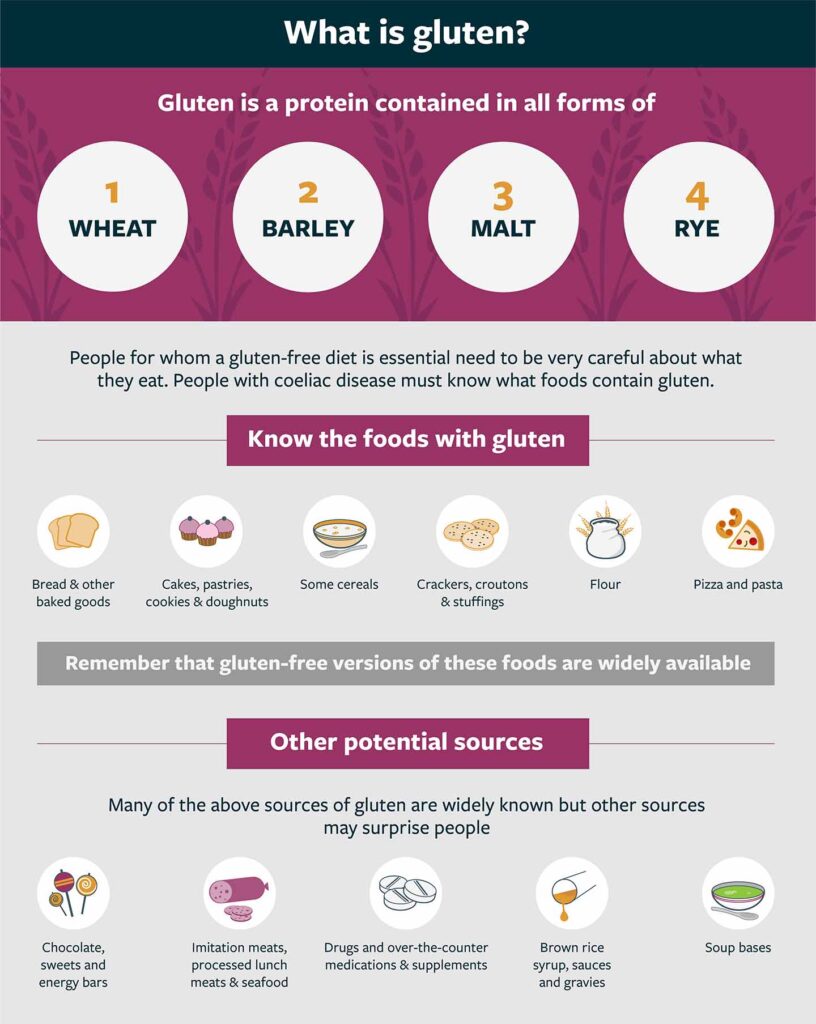
Gluten-Free Diet
Importance of a gluten-free diet
Following a strict gluten-free diet is currently the only treatment for celiac disease. By eliminating gluten from your diet, you can prevent further damage to the small intestine and alleviate the associated symptoms. Adhering to a gluten-free diet can also reduce the risk of developing complications such as osteoporosis, infertility, and certain types of cancer. It is important to note that even small amounts of gluten, as little as a crumb, can trigger an immune response in individuals with celiac disease.
Foods to avoid
When following a gluten-free diet, it is essential to avoid all sources of gluten. This includes obvious sources like wheat, barley, and rye, but also hidden sources that can be found in processed foods, medications, and even personal care products. It is important to carefully read ingredient labels and look for gluten-free certifications on products to ensure they are safe to consume. Common gluten-containing foods and ingredients to avoid include bread, pasta, cereals, beer, sauces, and certain types of soups.
Alternative ingredients and substitutes
Fortunately, there are many gluten-free alternatives and substitutes available to help make the transition to a gluten-free diet easier. A variety of grains, flours, and starches are naturally gluten-free, including rice, corn, quinoa, millet, and amaranth. These can be used as substitutes for wheat flour in baking and cooking. Additionally, there are numerous gluten-free products on the market, such as bread, pasta, and cookies, that are specially formulated to be safe for individuals with celiac disease.
Medication Options
Gluten enzyme supplements
Gluten enzyme supplements, also known as gluten digestives, are a type of over-the-counter medication that can help individuals with celiac disease manage accidental gluten exposure. These supplements contain enzymes that assist in the breakdown of gluten, making it easier for the body to process and reducing the risk of symptoms and intestinal damage. However, it is important to note that gluten enzyme supplements are not a substitute for a strict gluten-free diet and should only be used in specific situations.
Immunosuppressants
In some cases, individuals with celiac disease may require immunosuppressant medications to help manage the autoimmune response and reduce inflammation in the small intestine. These medications work by suppressing the immune system’s overactivity, thus preventing it from attacking the intestinal lining. However, immunosuppressants are typically reserved for individuals who do not respond well to a gluten-free diet or have severe symptoms and complications associated with celiac disease.
Intestinal healing agents
Research is ongoing to develop medications specifically designed to promote intestinal healing in individuals with celiac disease. These agents aim to repair the damage caused by gluten ingestion and restore the normal functioning of the small intestine. While these medications are not yet widely available, they hold great promise for the future management of celiac disease and may provide additional options for individuals who struggle with the strict adherence to a gluten-free diet.

Managing Nutritional Deficiencies
Iron deficiency
Iron deficiency is a common nutritional deficiency in individuals with celiac disease, primarily due to the damage to the small intestine that impairs iron absorption. To manage iron deficiency, it is important to consume iron-rich foods such as lean red meat, dark leafy greens, legumes, and fortified cereals. Iron supplements may also be prescribed by a healthcare professional, especially in cases of severe deficiency. It is important to note that improving iron absorption may take time, and regular monitoring of iron levels is essential.
Vitamin D deficiency
Vitamin D deficiency is another common issue in individuals with celiac disease, as the damaged small intestine may have a reduced ability to absorb this essential vitamin. To address this deficiency, it may be necessary to increase sun exposure, consume vitamin D-rich foods like fatty fish, fortified dairy products, and eggs, and consider vitamin D supplements under the guidance of a healthcare professional. Regular monitoring of vitamin D levels is crucial to ensure optimal supplementation.
B12 deficiency
B12 deficiency can occur in individuals with celiac disease due to the damage to the small intestine that impairs its absorption. To manage B12 deficiency, it is important to consume foods high in B12, such as meat, fish, eggs, and dairy products. In some cases, B12 supplements or injections may be necessary to correct the deficiency effectively. Regular monitoring of B12 levels is essential to ensure adequate supplementation and prevent complications associated with deficiency.
Probiotics and Gut Health
Benefits of probiotics
Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that can help improve gut health and support the overall well-being of individuals with celiac disease. These live microorganisms can restore the balance of the gut microbiome, enhance digestion, reduce inflammation, and strengthen the immune system. Probiotics have been shown to alleviate digestive symptoms commonly associated with celiac disease, such as bloating and diarrhea, and may also help improve nutrient absorption and reduce the risk of complications.
Choosing the right probiotic
When selecting a probiotic supplement, it is essential to choose a product specifically formulated for individuals with celiac disease and one that does not contain any gluten or other allergens. Look for a reputable brand that provides clear information about the strains of bacteria included, the number of colony-forming units (CFUs), and any additional ingredients. Working with a healthcare professional or dietitian can help in selecting the most appropriate probiotic for your specific needs.
Improving gut microbiome
In addition to incorporating probiotics into your routine, there are other measures you can take to improve the health of your gut microbiome. Consuming a diverse range of fiber-rich foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and legumes, can promote the growth of beneficial bacteria. Avoiding unnecessary use of antibiotics, managing stress levels, and staying physically active are also important factors in supporting a healthy gut. It is crucial to maintain good gut health as it can positively impact the management of celiac disease and overall well-being.
Complementary and Alternative Medicine
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is a traditional Chinese practice that involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate energy flow and promote healing. While there is limited scientific evidence specifically related to celiac disease, some individuals may find acupuncture helpful in managing certain symptoms, such as pain and digestive discomfort. It is important to consult with a qualified acupuncturist to determine if this complementary therapy is suitable for your individual needs.
Herbal supplements
Certain herbal supplements have been traditionally used to support digestive health and alleviate some symptoms associated with celiac disease. Chamomile, peppermint, and ginger are examples of herbs that are known for their calming and soothing effects on the digestive system. However, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare professional or trained herbalist before incorporating any herbal supplements into your routine, as they may interact with medications or have potential side effects.
Chiropractic care
Chiropractic care involves the manipulation of the spine and other joints to improve overall health and alleviate certain symptoms. While there is limited scientific evidence regarding its effectiveness in managing celiac disease, some individuals may find chiropractic care beneficial in relieving musculoskeletal pain and discomfort that can be associated with the condition. It is important to seek treatment from a qualified chiropractor who has experience working with individuals with celiac disease.
Support Groups and Counseling
Finding support groups
Joining a support group can provide valuable emotional support, practical tips, and a sense of community for individuals with celiac disease. Connecting with others who share similar experiences can be comforting and motivating, especially during challenging times. To find a support group, reach out to local celiac disease organizations, hospitals, or ask your healthcare provider or dietitian for recommendations. Many support groups also have online platforms where you can connect with others virtually.
Online communities
In addition to in-person support groups, there are numerous online communities and forums dedicated to celiac disease. These virtual platforms provide an opportunity to connect with individuals from around the world, share experiences, ask questions, and gather information. Online communities can be accessed at any time, offering support whenever it is needed. However, it is important to ensure that the information obtained from these sources is reliable and accurate.
Professional counseling
Living with celiac disease can have a significant impact on a person’s emotional well-being. It is common to experience feelings of frustration, anxiety, and even depression due to the challenges associated with the condition. Seeking professional counseling can be beneficial in addressing these emotional aspects and developing coping strategies. A trained therapist or counselor can provide guidance, support, and help you navigate the emotional impact of celiac disease and the necessary lifestyle changes.

Coping with Emotional Impact
Adjusting to lifestyle changes
Diagnosed with celiac disease, you may need to make significant lifestyle changes to manage the condition effectively. These changes can include transitioning to a gluten-free diet, careful meal planning, navigating social situations, and avoiding cross-contamination. Adjusting to these changes can be challenging and can significantly impact your daily life. It is important to be patient with yourself, seek support from others, and gather resources and information to help you navigate through this transition successfully.
Anxiety and depression
Living with celiac disease can increase the risk of anxiety and depression due to the chronic nature of the condition and the lifestyle adjustments required. It is essential to recognize and address any symptoms of anxiety or depression that may arise. Seeking support from healthcare professionals, support groups, or mental health organizations can provide the necessary guidance and assistance. Additionally, practicing stress management techniques such as mindfulness, exercise, and self-care can help alleviate anxiety and promote emotional well-being.
Self-care practices
Engaging in self-care practices is crucial for individuals with celiac disease to manage the emotional impact of the condition effectively. Taking time to prioritize your physical and mental well-being can help reduce stress, improve overall mood, and enhance resilience. This can include activities such as practicing relaxation techniques, engaging in physical exercise, spending time with loved ones, pursuing hobbies and interests, and taking breaks when needed. Incorporating self-care into your routine can greatly contribute to your overall well-being and help you cope with the emotional aspects of celiac disease.
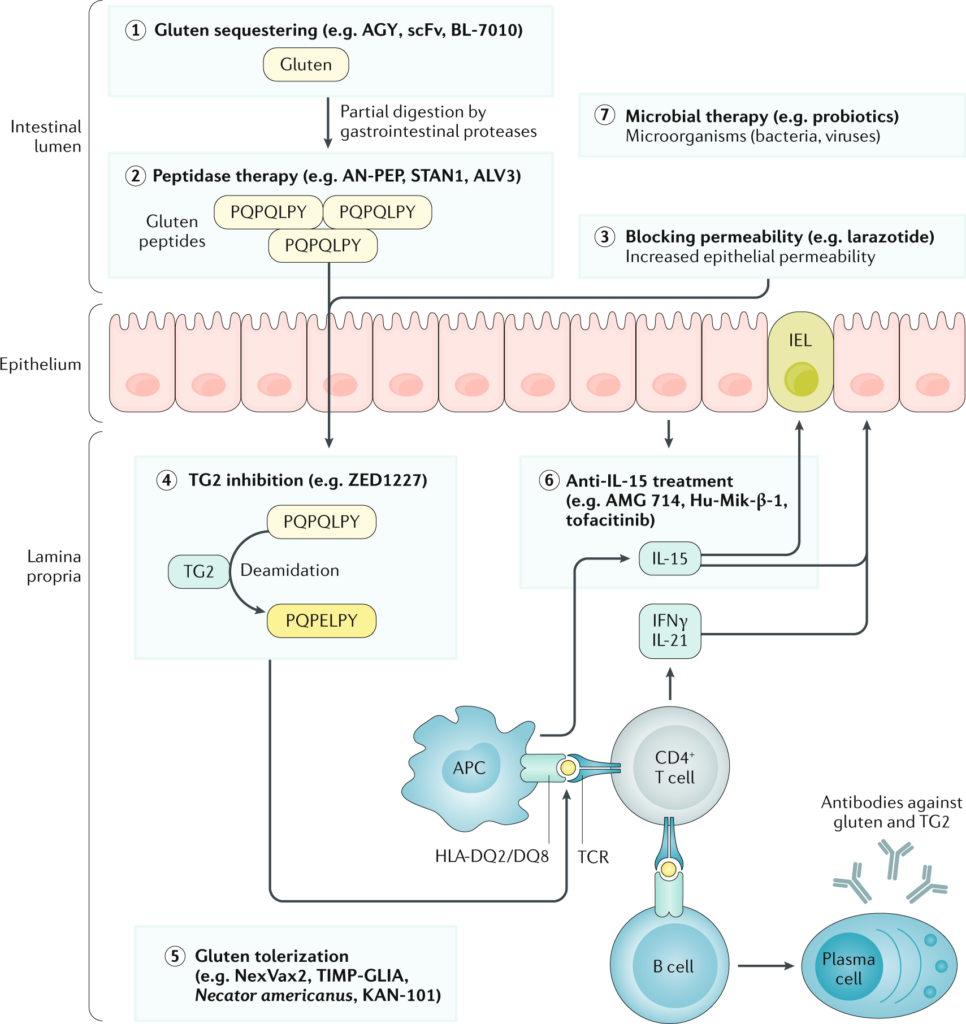
Experimental and Emerging Treatments
Novel therapies
Researchers are constantly exploring novel therapies for the treatment of celiac disease. These therapies aim to address the underlying immunological process that occurs in individuals with the condition. Some potential approaches include the development of vaccines to induce immune tolerance to gluten, the use of nanoparticles to neutralize gluten in the digestive system, and the exploration of genetic engineering techniques to modify gluten proteins. While these therapies are still in the experimental stage, they hold promise for the future management of celiac disease.
Research updates
The field of celiac disease research is continuously evolving, and new findings are emerging regularly. Researchers are working to better understand the complex mechanisms underlying the disease, identify genetic markers for improved diagnosis, develop more accurate and non-invasive diagnostic tools, and explore new treatment modalities. Staying informed about the latest research updates can help individuals with celiac disease make informed decisions, stay up to date with advancements, and potentially participate in clinical trials.
Clinical trials
Clinical trials play a crucial role in advancing the understanding and treatment of celiac disease. These trials involve testing new medications, therapies, or interventions to determine their safety, effectiveness, and potential benefits. Participating in a clinical trial can provide individuals with celiac disease access to cutting-edge treatments and contribute to the collective knowledge surrounding the disease. If you are interested in participating in a clinical trial, consult with your healthcare provider or reach out to research institutions specializing in celiac disease.
In conclusion, celiac disease is a complex condition that requires a multifaceted approach for its management. Whether it is adhering to a strict gluten-free diet, considering medication options, addressing nutritional deficiencies, focusing on gut health, exploring complementary therapies, seeking support, coping with the emotional impact, or staying informed about emerging treatments, there are various strategies and resources available to help individuals with celiac disease live a fulfilling and healthy life. It is important to work closely with healthcare professionals and seek support from others to navigate the challenges associated with the condition and optimize overall well-being.