Living with Celiac Disease can be challenging, but with the right knowledge and strategies, you can manage its symptoms effectively. Celiac Disease is an autoimmune disorder that affects the digestive system and is triggered by the consumption of gluten. In this article, you will discover useful tips and techniques to alleviate discomfort, maintain a gluten-free diet, and live a healthy and fulfilling life despite the challenges of managing Celiac Disease. So, let’s explore how you can take control of your symptoms and thrive with this condition.

What is Celiac Disease?
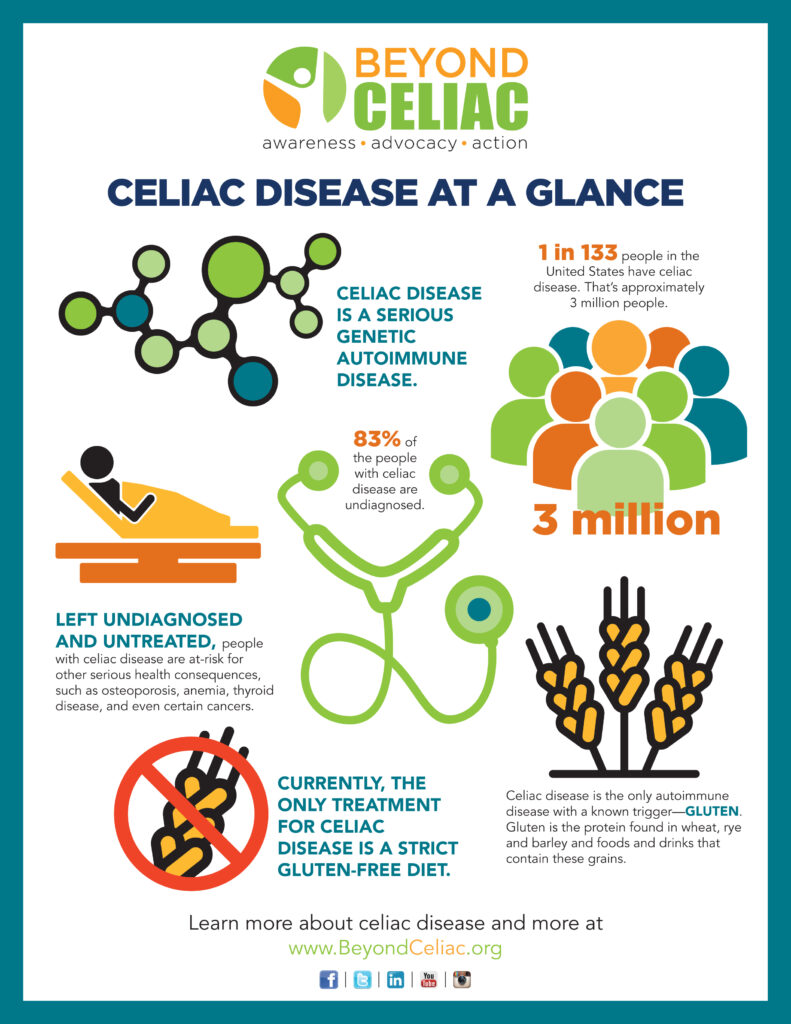
Celiac Disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that affects the small intestine. When someone with Celiac Disease consumes gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye, their immune system reacts by damaging the lining of the small intestine. This damage prevents the absorption of essential nutrients, leading to various health complications. Celiac Disease affects approximately 1% of the global population, and the only effective treatment is a strict gluten-free diet.
Diagnosing Celiac Disease
If you suspect you may have Celiac Disease, it is crucial to seek a proper diagnosis from a medical professional. The diagnosis process typically involves several steps, including reviewing your symptoms and medical history, conducting Celiac Disease antibody tests, and performing an intestinal biopsy.
Symptoms and signs
Common symptoms of Celiac Disease can vary from person to person. Some individuals may experience digestive issues such as bloating, gas, diarrhea, and constipation. Others might face more general symptoms like fatigue, weight loss, or malnutrition. It’s important to remember that some people with Celiac Disease may not have any noticeable symptoms, making diagnosis even more crucial.
Celiac disease antibody tests
Celiac Disease antibody tests are blood tests that can help determine if you have the condition. These tests measure the levels of specific antibodies that are commonly found in individuals with Celiac Disease. It’s important to note that if you have already started a gluten-free diet, the tests may not accurately reflect the presence of Celiac Disease. Therefore, it is recommended to continue consuming gluten until after the tests are completed.
Intestinal biopsy
In some cases, an intestinal biopsy may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of Celiac Disease. During this procedure, a small tissue sample is taken from the lining of the small intestine and examined for damage characteristic of Celiac Disease. This test is considered the gold standard for diagnosing the condition.
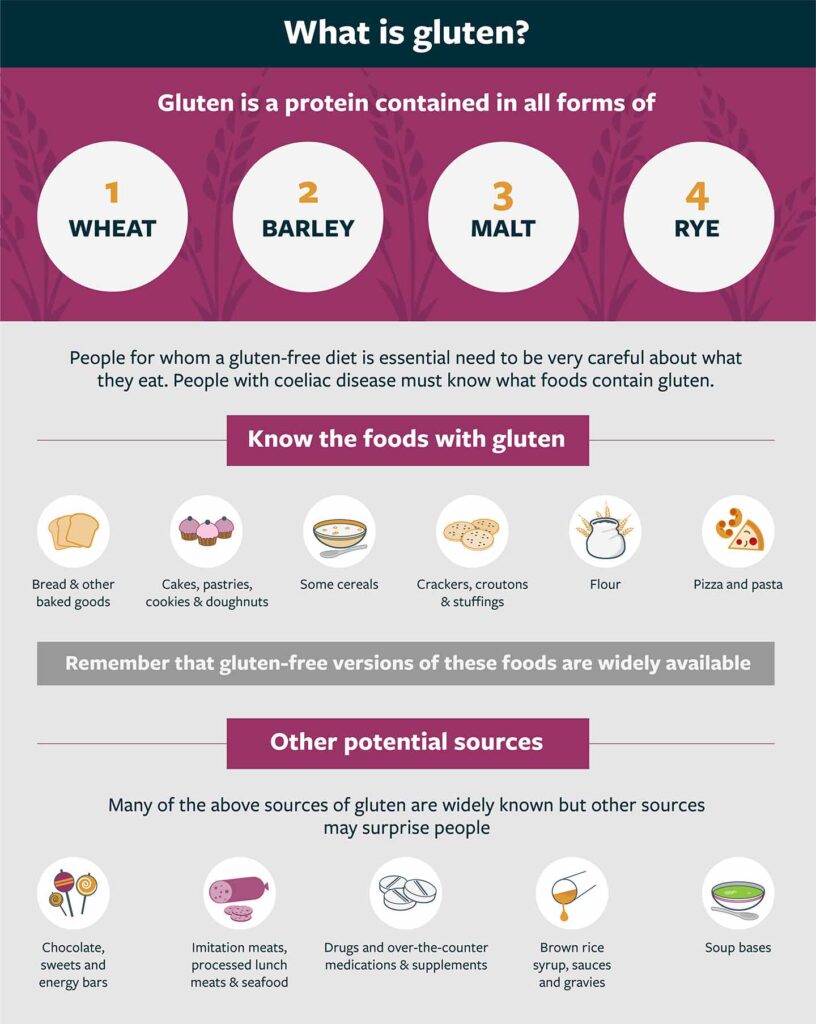
Gluten-Free Diet
Following a strict gluten-free diet is essential for individuals with Celiac Disease to manage their symptoms and prevent further complications. It involves eliminating gluten from your diet entirely and being mindful of cross-contamination.
Eliminating gluten from your diet
Eliminating gluten from your diet means avoiding any foods that contain wheat, barley, and rye. This includes products made with these grains such as bread, pasta, cereals, and pastries. It’s important to read food labels carefully as gluten can often hide in unexpected places, such as sauces, soups, and processed foods.
Reading food labels
When living with Celiac Disease, reading food labels becomes a necessary habit. Look for labels that clearly state “gluten-free” or check for ingredients that are known to contain gluten. It’s also essential to be aware of potential cross-contamination risks, as products that are manufactured in facilities that also process gluten-containing foods may not be safe to consume.
Gluten-free alternatives
Fortunately, there are numerous gluten-free alternatives available to replace traditional gluten-containing products. For example, there are gluten-free bread, pasta, and flour options that can be used in cooking and baking. It may require some trial and error to find your preferred gluten-free alternatives, but with time, you can discover delicious and satisfying substitutes for your favorite gluten-containing foods.
Managing Digestive Symptoms
Digestive symptoms are a common aspect of Celiac Disease and can greatly impact your quality of life. Here are some tips for managing these symptoms.
Bloating and gas
To alleviate bloating and gas, it is essential to identify and avoid foods that trigger these symptoms. Keep a food diary to track your symptoms and identify any patterns. Additionally, incorporating digestive enzymes or probiotics into your routine may help improve digestion and reduce bloating.
Diarrhea and constipation
If you experience diarrhea, it may be helpful to increase your fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and gluten-free grains like quinoa or brown rice. On the other hand, if you have constipation, staying hydrated and consuming fiber-rich foods alongside probiotics can help regulate your bowel movements.
Abdominal pain
Abdominal pain can be managed through a combination of dietary changes and medication if necessary. Following a gluten-free diet diligently can alleviate abdominal pain in most cases. However, if the pain persists, consult your healthcare provider for appropriate pain management strategies.

Nutritional Deficiencies and Supplementation
Celiac Disease can lead to deficiencies in essential vitamins and minerals due to malabsorption in the small intestine. Supplementation may be necessary to address these deficiencies and maintain overall health.
Vitamin and mineral deficiencies
Common deficiencies in individuals with Celiac Disease include iron, calcium, vitamin D, vitamin B12, and folic acid. These nutrients are crucial for various bodily functions, including bone health, red blood cell production, and immune system support. Regular blood tests can help identify any deficiencies, and your healthcare provider can recommend appropriate supplementation.
Supplements for celiac disease
Supplements are often prescribed to individuals with Celiac Disease to ensure they receive adequate amounts of vital nutrients. It is important to work with a healthcare provider to understand your specific nutrient needs and develop a supplementation plan tailored to you. It’s worth noting that supplements should not replace a healthy gluten-free diet, but rather complement it.
Importance of a Supportive Network
Living with Celiac Disease can be challenging, both physically and emotionally. Building a supportive network can greatly enhance your well-being and ability to manage the condition successfully.
Family and friends
Educating your immediate family and close friends about Celiac Disease and its dietary requirements can facilitate understanding and empathy. They can provide emotional support and be mindful of cross-contamination risks while sharing meals or preparing food together. Having their support can make social situations and daily life much easier.
Support groups
Joining a Celiac Disease support group can provide an invaluable source of knowledge, guidance, and encouragement. These groups often consist of individuals who have firsthand experience with the condition and can offer practical advice on managing symptoms, finding gluten-free products, and navigating social situations. Many support groups also organize events and meetings where you can connect with others facing similar challenges.
Medical professionals
Establishing a strong relationship with your healthcare team is crucial for managing Celiac Disease. Regular visits to your doctor, dietitian, and other specialists can help ensure your overall health and well-being. They can monitor your condition, offer guidance on gluten-free eating, and address any concerns or complications that may arise.

Emotional and Mental Well-being
Managing Celiac Disease involves not only physical changes but also emotional and mental adjustments. Here are some tips to support your emotional well-being.
Stress management
Living with a chronic condition can cause stress and anxiety. Finding healthy ways to manage stress, such as practicing mindfulness or engaging in physical activity, can be beneficial. Take time for yourself and engage in activities that bring you joy and relaxation.
Mental health support
If you find yourself struggling with anxiety, depression, or other mental health concerns, seeking professional help is important. A mental health professional can provide strategies and support tailored to your specific needs. Remember that managing your mental health is just as important as managing your physical health.
Therapy and counseling
Engaging in therapy or counseling can help navigate the emotional challenges that may arise from living with Celiac Disease. A therapist can assist in developing coping mechanisms, improving communication skills, and overcoming any negative emotions or body image issues associated with the condition. Finding a therapist who is knowledgeable about Celiac Disease can be particularly beneficial.
Living Gluten-Free Outside of Home
Maintaining a gluten-free lifestyle extends beyond your own kitchen. Here are some tips for navigating social gatherings and dining out.
Social gatherings and restaurants
Attending social gatherings or eating out at restaurants may require some extra planning and communication. Reach out to the host or restaurant in advance to discuss your dietary needs. Offer to bring a gluten-free dish to share or suggest restaurants that have gluten-free options. Being proactive can help ensure you have safe and enjoyable experiences.
Traveling with Celiac Disease
Traveling can pose additional challenges for individuals with Celiac Disease. Researching gluten-free options at your destination and packing appropriate snacks can alleviate some anxiety. Additionally, consider carrying a gluten-free restaurant card or mobile app that translates your dietary requirements into different languages, making it easier to communicate your needs while abroad.
Celiac Disease and Skin Issues
Some individuals with Celiac Disease may also experience skin issues, such as Dermatitis Herpetiformis (DH).
Dermatitis herpetiformis
Dermatitis Herpetiformis is a skin condition characterized by a painful, itchy rash that is often symmetrically distributed. It is linked to gluten sensitivity and occurs in some individuals with Celiac Disease. If you suspect you may have DH, consult a dermatologist for diagnosis and appropriate treatment options.
Skin care tips
When managing skin issues related to Celiac Disease, it is essential to keep the affected areas clean and dry. Avoid scratching the rash, as it can lead to infection. Use gentle, hypoallergenic skincare products and consider patch testing new products before applying them to large areas of your skin.
Medical Follow-up
Regular medical follow-up is crucial for individuals with Celiac Disease to monitor their health and address any concerns that may arise.
Monitoring health
Regular check-ups, blood tests, and assessments of nutrient levels are important to ensure your body is responding positively to a gluten-free diet. Your healthcare provider can monitor any changes in symptoms, nutrient deficiencies, or other complications that may develop.
Follow-up exams and tests
Your healthcare provider may recommend follow-up exams and tests, such as repeat intestinal biopsies, to assess the healing and improvement of your small intestine. These tests can help determine if your gluten-free diet is effectively managing your condition and guide any necessary adjustments to your treatment plan.
In conclusion, living with Celiac Disease requires a comprehensive approach that involves dietary changes, symptom management, nutrient supplementation, emotional well-being, and ongoing medical follow-up. By understanding the condition, seeking the appropriate medical care, and building a supportive network, individuals with Celiac Disease can lead fulfilling lives while effectively managing their symptoms and minimizing the risk of complications. Remember, you are not alone on this journey, and there are resources available to support you every step of the way.