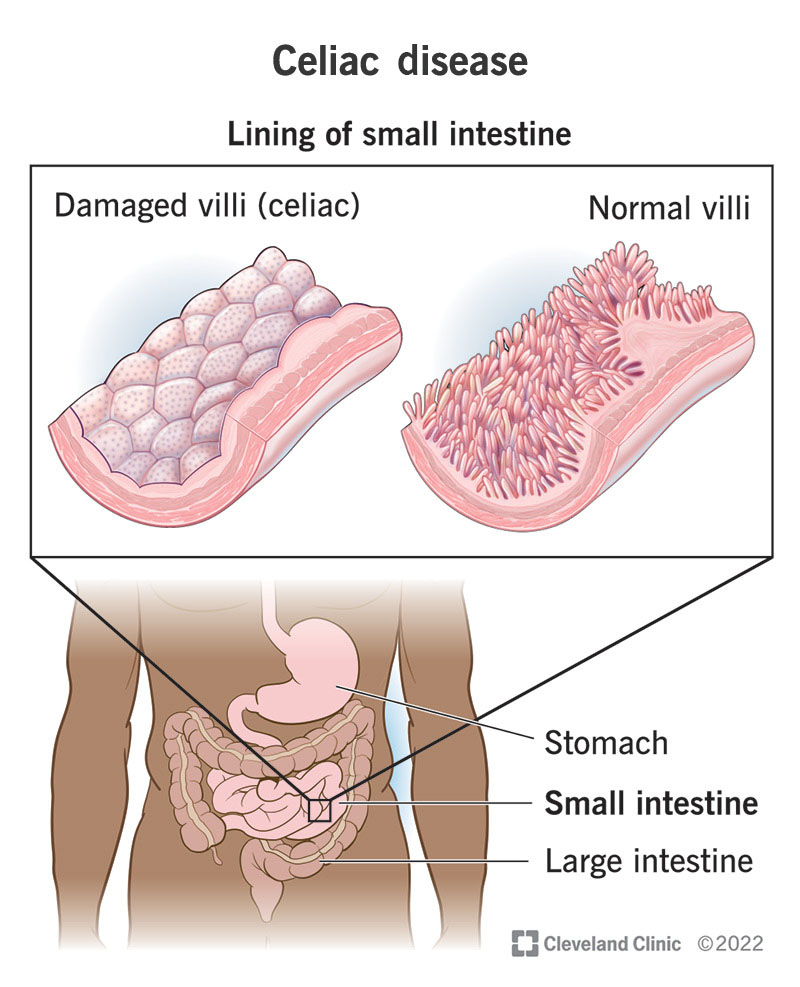
You might be surprised to learn that there is a common autoimmune disorder that affects nearly 1 in 100 people worldwide – Celiac Disease. This chronic condition is triggered by consuming gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye. The fascinating aspect of this disease lies in its wide array of symptoms, which can vary from mild gastrointestinal disturbances to severe nutrient deficiencies. Understanding the symptoms of Celiac Disease is crucial in identifying and managing this condition effectively. So, let’s explore some of the key signs that may indicate you or someone you know could be experiencing this often misunderstood disorder.
Symptoms of Celiac Disease
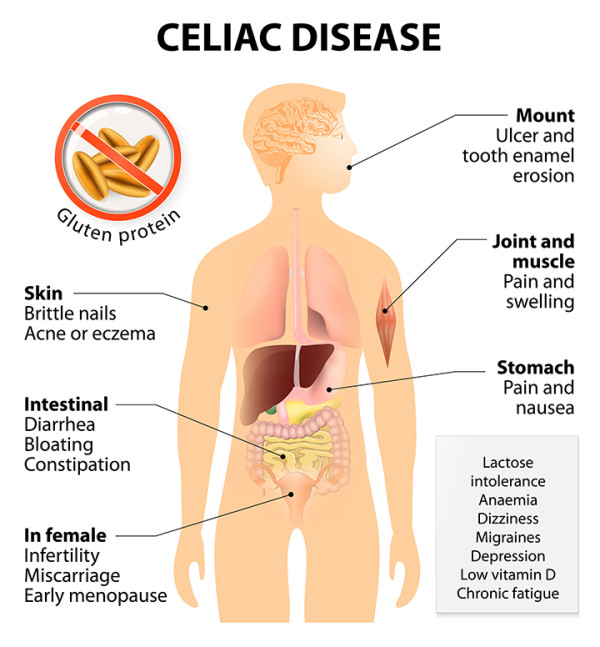
Digestive Symptoms
When it comes to the symptoms of celiac disease, there can be a wide range of digestive issues that individuals may experience. These symptoms can vary in severity and may include abdominal pain, bloating, diarrhea or constipation, gas, and even vomiting. These digestive symptoms are often the most common and can be the first signs that something may be wrong. Paying attention to these symptoms and seeking medical advice can be crucial in identifying celiac disease early on.
Non-Digestive Symptoms
While digestive symptoms are often associated with celiac disease, it is important to note that there are also non-digestive symptoms that can occur. These symptoms can vary from individual to individual and may include fatigue, joint pain, iron-deficiency anemia, headaches, and even depression or anxiety. These non-digestive symptoms can sometimes be overlooked or attributed to other causes, so it is important to consider celiac disease as a potential underlying condition.

Children Symptoms
Celiac disease can affect individuals of all ages, including children. In children, the symptoms may present differently than in adults. Some common symptoms in children include abdominal pain, diarrhea, poor growth or weight loss, delayed puberty, and even behavioral changes such as irritability or difficulty concentrating. If you notice these symptoms in your child, it is essential to consult with a healthcare professional for appropriate evaluation and diagnosis.
Adult Symptoms
In adults, the symptoms of celiac disease can also vary. Some adults may experience the classic digestive symptoms mentioned earlier, while others may have less obvious symptoms. Fatigue, joint pain, and unexplained weight loss can be common symptoms in adults with celiac disease. Additionally, some individuals may develop skin conditions, such as a rash called dermatitis herpetiformis, which is associated with celiac disease. Being aware of these symptoms can help you recognize and discuss them with your doctor, leading to a proper diagnosis.
Dermatitis Herpetiformis
Dermatitis herpetiformis is a skin condition linked to celiac disease. It is characterized by a chronic itchy rash that is often present on the elbows, knees, buttocks, and hairline. This rash may come and go and can be accompanied by small blisters or bumps. Dermatitis herpetiformis is caused by the same immune reaction to gluten that occurs in celiac disease. If you notice any skin changes or persistent itching, it is essential to speak with a dermatologist or healthcare professional to determine the cause and appropriate treatment options.
Asymptomatic Celiac Disease
It is important to recognize that not everyone with celiac disease experiences obvious symptoms. Some individuals may have asymptomatic celiac disease, meaning they do not show any noticeable symptoms. However, even without symptoms, the damage to the small intestine caused by gluten ingestion can still occur. This makes it crucial for individuals with a family history of celiac disease or other risk factors to undergo screening tests to identify the condition early and prevent potential complications.
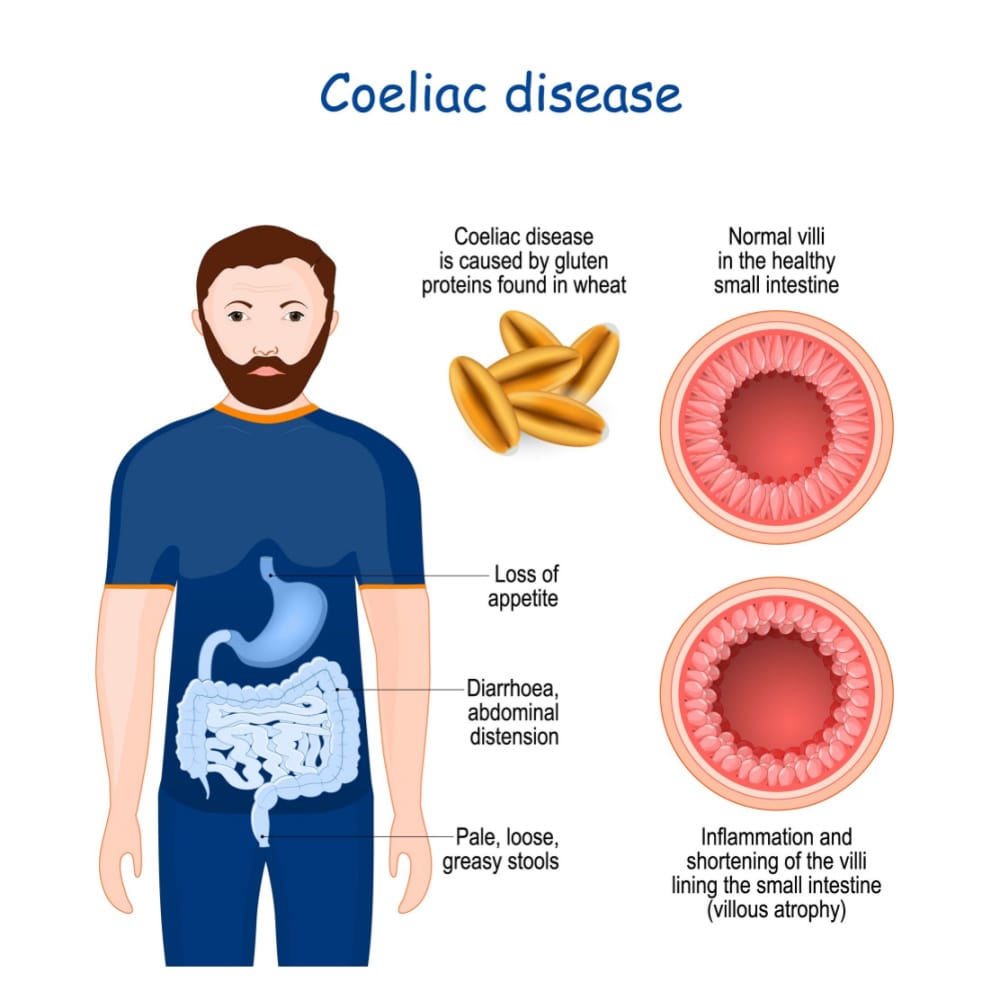
Potential Complications
If left untreated, celiac disease can lead to various complications. Malabsorption of nutrients can result in deficiencies in important vitamins and minerals, leading to conditions such as anemia and osteoporosis. The inflammation caused by the immune response to gluten can also increase the risk of developing other autoimmune disorders, such as type 1 diabetes or thyroid disease. Additionally, long-term untreated celiac disease may increase the risk of certain types of cancer, including lymphoma and small intestinal adenocarcinoma. It is crucial to promptly diagnose and manage celiac disease to minimize the risk of these potential complications.
Celiac Crisis
In rare cases, individuals with untreated or undiagnosed celiac disease may experience a severe reaction known as celiac crisis. This is a life-threatening condition characterized by severe diarrhea, dehydration, and electrolyte imbalances. Celiac crisis requires immediate medical attention, as it can be fatal if not promptly treated. It is critical to understand the importance of early diagnosis and adherence to a strict gluten-free diet to prevent such emergencies.
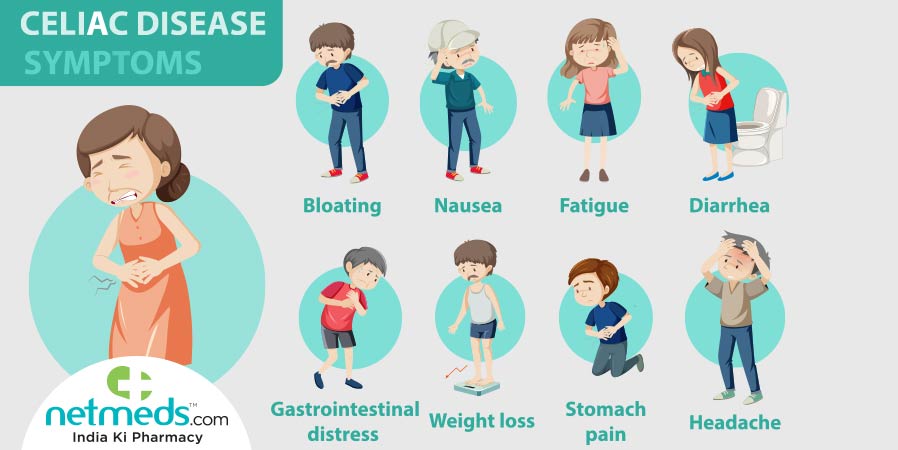
Differential Diagnosis
When considering the possibility of celiac disease, it is essential to rule out other conditions that may present with similar symptoms. Conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), inflammatory bowel disease (IBD), lactose intolerance, and even certain food allergies can mimic the symptoms of celiac disease. Through a detailed medical history, physical examination, and appropriate diagnostic tests, healthcare professionals can differentiate between these conditions and determine the most accurate diagnosis.
Diagnosing Celiac Disease
Diagnosing celiac disease involves multiple steps. It often begins with a thorough review of symptoms, medical history, and possible risk factors. Blood tests that measure specific antibodies related to celiac disease, such as tissue transglutaminase (tTG) antibodies, are commonly used as initial screening tests. If blood tests indicate a possibility of celiac disease, further evaluation may involve an endoscopy with biopsy to assess the damage to the small intestine. A gluten-free diet may also be recommended as a diagnostic tool to see if symptoms improve. It is important to consult with a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and appropriate management of celiac disease.
In conclusion, recognizing the symptoms of celiac disease is crucial for early diagnosis and management. Digestive and non-digestive symptoms can vary among individuals, with children often showing different signs than adults. Dermatitis herpetiformis, an itchy skin rash, can also be associated with celiac disease. Being aware of these symptoms, potential complications, and the importance of diagnosis can help individuals seek appropriate medical attention and adopt a gluten-free lifestyle if necessary. Remember, if you suspect celiac disease, consult with a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and guidance.